 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Understand in one article: the connections and differences between AI, machine learning and deep learning
Understand in one article: the connections and differences between AI, machine learning and deep learningUnderstand in one article: the connections and differences between AI, machine learning and deep learning
In today’s wave of rapid technological changes, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) are like bright stars, leading the new wave of information technology. tide. These three words frequently appear in various cutting-edge discussions and practical applications, but for many explorers who are new to this field, their specific meanings and their internal connections may still be shrouded in mystery.
Let’s take a look at this picture first.

It can be seen that there is a close correlation and progressive relationship between deep learning, machine learning and artificial intelligence. Deep learning is a specific field of machine learning, which is an important component of artificial intelligence. The connections and mutual promotion between these fields enable the continuous development and improvement of artificial intelligence technology.
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad concept whose main goal is to develop computing systems that can simulate, extend or even surpass human intelligence. It has specific applications in many fields, such as:
- Image Recognition (Image Recognition) is an important branch of AI, which is dedicated to studying how to enable computers to obtain data through visual sensors and perform operations based on these data. Analysis to identify objects, scenes, behaviors and other information in images, simulating the recognition and understanding process of visual signals by the human eye and brain.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the ability of computers to understand and generate human natural language. It covers a variety of tasks such as text classification, semantic analysis, machine translation, etc., and strives to simulate human listening. Talk about intelligent behaviors in reading and writing.
- Computer Vision (CV) includes image recognition in a broader sense. It also involves image analysis, video analysis, three-dimensional reconstruction and other aspects. It aims to allow computers to extract information from two-dimensional or three-dimensional images. "Seeing" and understanding the world is a deep imitation of the human visual system.
- Knowledge Graph (KG) is a structured data model used to store and represent entities and their complex relationships with each other. It simulates the accumulation and development of human knowledge in the cognitive process. The ability to utilize knowledge and the process of reasoning and learning based on prior knowledge.
These high-end technologies are researched and applied around the core concept of “simulating human intelligence”. They focus on the development of different perception dimensions (such as vision, hearing, thinking logic, etc.), and jointly promote the continuous development and progress of artificial intelligence technology.
What is machine learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a crucial branch in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). It uses various algorithms to enable computer systems to automatically learn rules and patterns from data to make predictions and decisions, thereby enhancing and expanding the capabilities of human intelligence.
For example, when training a cat recognition model, the machine learning process is as follows:
- Data preprocessing: First, preprocess a large number of collected cat and non-cat pictures. Processing, including scaling, grayscale, normalization and other operations, and converting the image into a feature vector representation. These features may come from manually designed feature extraction techniques, such as Haar-like features, local binary patterns (LBP) or Feature descriptors commonly used in other computer vision fields.
- Feature selection and dimensionality reduction: Select key features according to the characteristics of the problem, remove redundant and irrelevant information, and sometimes use PCA, LDA and other dimensionality reduction methods to further reduce feature dimensions and improve algorithm efficiency.
- Model training: Then use the preprocessed labeled data set to train the selected machine learning model, and optimize the model performance by adjusting the model parameters so that the model can distinguish given features. Pictures of cats and non-cats.
- Model evaluation and verification: After training is completed, the model is evaluated using an independent test set to ensure that the model has good generalization ability and can be accurately applied to new unseen samples.
The top 10 commonly used machine learning algorithms are: decision tree, random forest, logistic regression, SVM, naive Bayes, K nearest neighbor algorithm, K-means algorithm, Adaboost algorithm, neural network, Marr Koff et al.
What is deep learning?
Deep Learning (DL) is a special form of machine learning. It simulates the way the human brain processes information through a deep neural network structure, thereby automatically extracting complex feature representations from the data.
For example, when training a cat recognition model, the deep learning process is as follows:
(1) Data preprocessing and preparation:
- Collect a large number of A dataset containing cat and non-cat images, cleaned and annotated to ensure that each image has a corresponding label (such as "cat" or "non-cat").
- Image preprocessing: Adjust all images to a uniform size, perform normalization processing, data enhancement and other operations.
(2) Model design and construction:
- Choose a deep learning architecture. For image recognition tasks, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is usually used. CNN can effectively extract local features of images and abstract them through multi-layer structures.
- Build a model hierarchy, including convolutional layers (for feature extraction), pooling layers (to reduce the amount of calculation and prevent overfitting), fully connected layers (to integrate and classify features), and possible batch reduction Unified layer, activation function (such as ReLU, sigmoid, etc.).
(3) Initialization parameters and setting hyperparameters:
- To initialize the weights and biases of each layer in the model, random initialization or a specific initialization strategy can be used.
- Set hyperparameters such as learning rate, optimizer (such as SGD, Adam, etc.), batch size, training period (epoch), etc.
(4) Forward propagation:
- Input the preprocessed image into the model, and perform operations such as convolution, pooling, and linear transformation at each layer , and finally obtain the predicted probability distribution of the output layer, that is, the probability that the model determines that the input picture is a cat.
(5) Loss function and backpropagation:
- Use the cross-entropy loss function or other suitable loss function to measure the difference between the model prediction results and the real label difference.
- After calculating the loss, execute the back propagation algorithm to calculate the gradient of the loss with respect to the model parameters in order to update the parameters.
(6) Optimization and parameter update:
- Use gradient descent or other optimization algorithms to adjust model parameters based on gradient information, with the purpose of minimizing the loss function.
- During each training iteration, the model will continue to learn and adjust parameters, gradually improving its ability to recognize cat images.
(7) Verification and evaluation:
- Regularly evaluate the model performance on the verification set, monitor changes in accuracy, precision, recall and other indicators to This guides hyperparameter tuning and early stopping strategies during model training.
(8) Training completion and testing:
- When the model’s performance on the validation set becomes stable or reaches the preset stopping conditions, stop training.
- Finally, evaluate the generalization ability of the model on an independent test set to ensure that the model can effectively identify cats on new unseen samples.
The difference between deep learning and machine learning
The difference between deep learning and machine learning is:
1. Method of solving problems
Machine Learning algorithms usually rely on human-designed feature engineering, that is, key features are extracted in advance based on background knowledge of the problem, and then models are built based on these features and optimized solutions are performed.
Deep learning adopts an end-to-end learning method, automatically generating high-level abstract features through multi-layer nonlinear transformation, and these features are continuously optimized during the entire training process, without manual selection and construction of features. Closer to the cognitive processing method of the human brain.
For example, if you want to write a software to identify a car, if you use machine learning, you need to manually extract the characteristics of the car, such as size and shape; and if you use deep learning, Then the artificial intelligence neural network will extract these features on its own, but it requires a large number of pictures labeled as cars to learn.

2. Application Scenarios
The application of machine learning in fingerprint recognition, characteristic object detection and other fields has basically met the requirements of commercialization.
Deep learning is mainly used in text recognition, face technology, semantic analysis, intelligent monitoring and other fields. At present, it is also rapidly deploying in intelligent hardware, education, medical and other industries.
3. Required amount of data
Machine learning algorithms can also show good performance in small sample cases. For some simple tasks or problems where features are easy to extract, less data Satisfactory results can be achieved.
Deep learning usually requires a large amount of annotated data to train deep neural networks. Its advantage is that it can directly learn complex patterns and representations from the original data. Especially when the data size increases, the performance of the deep learning model improves. more significant.
4. Execution time
In the training phase, because the deep learning model has more layers and a large number of parameters, the training process is often time-consuming and requires the support of high-performance computing resources, such as GPU cluster.
In comparison, machine learning algorithms (especially those lightweight models) usually have smaller training time and computing resource requirements, and are more suitable for rapid iteration and experimental verification.
The above is the detailed content of Understand in one article: the connections and differences between AI, machine learning and deep learning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AM
Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis article explores the growing concern of "AI agency decay"—the gradual decline in our ability to think and decide independently. This is especially crucial for business leaders navigating the increasingly automated world while retainin
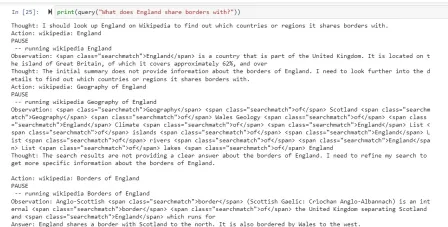 How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AM
How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AMEver wondered how AI agents like Siri and Alexa work? These intelligent systems are becoming more important in our daily lives. This article introduces the ReAct pattern, a method that enhances AI agents by combining reasoning an
 Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM"I think AI tools are changing the learning opportunities for college students. We believe in developing students in core courses, but more and more people also want to get a perspective of computational and statistical thinking," said University of Chicago President Paul Alivisatos in an interview with Deloitte Nitin Mittal at the Davos Forum in January. He believes that people will have to become creators and co-creators of AI, which means that learning and other aspects need to adapt to some major changes. Digital intelligence and critical thinking Professor Alexa Joubin of George Washington University described artificial intelligence as a “heuristic tool” in the humanities and explores how it changes
 Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AM
Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AMLangChain is a powerful toolkit for building sophisticated AI applications. Its agent architecture is particularly noteworthy, allowing developers to create intelligent systems capable of independent reasoning, decision-making, and action. This expl
 What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AM
What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AMRadial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs): A Comprehensive Guide Radial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs) are a powerful type of neural network architecture that leverages radial basis functions for activation. Their unique structure make
 The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AMBrain-computer interfaces (BCIs) directly link the brain to external devices, translating brain impulses into actions without physical movement. This technology utilizes implanted sensors to capture brain signals, converting them into digital comman
 Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis "Leading with Data" episode features Ines Montani, co-founder and CEO of Explosion AI, and co-developer of spaCy and Prodigy. Ines offers expert insights into the evolution of these tools, Explosion's unique business model, and the tr
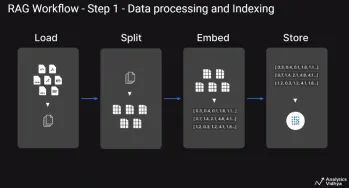 A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AMThis article explores Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems and how AI agents can enhance their capabilities. Traditional RAG systems, while useful for leveraging custom enterprise data, suffer from limitations such as a lack of real-time dat


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools





