 System Tutorial
System Tutorial LINUX
LINUX Make your Linux system start up quickly: Tips and methods to optimize startup time
Make your Linux system start up quickly: Tips and methods to optimize startup timeMake your Linux system start up quickly: Tips and methods to optimize startup time
In the modern computer world, startup time is one of the crucial factors. Sometimes, we need to quickly start the server or computer for higher efficiency and better user experience. In Linux systems, optimizing startup time is very important. This article will introduce how to use various tools to analyze and improve the boot time of your Linux system.
Quick start or quick restart plays a vital role in various situations. In order to maintain high availability and better performance of all services, fast startup of embedded devices is crucial. Consider a telecommunications device running a Linux operating system that does not have fast boot enabled. All systems, services, and users that rely on this particular embedded device may be affected. It is very important for these devices to maintain high availability of their services, and for this, fast startup and restart play a crucial role.
A glitch or shutdown of a piece of telecommunications equipment, even for just a few seconds, can cause havoc for countless users on the Internet. Therefore, for many time-critical devices and telecommunications equipment, it is very important to incorporate quick boot functions into their devices to help them get back to work quickly. Let us understand the Linux boot process from Figure 1.

Figure 1: Startup process
Monitoring tools and startup process
There are a number of factors that users should be aware of before making changes to their machine. This includes the computer's current startup speed, as well as services, processes, or applications that are hogging resources and adding to startup time.
Startup diagram
To monitor the startup speed and various services started during startup, users can use the following command to install:
sudo apt-get install pybootchartgui
Every time you start, the startup graph will save a png file in the log, allowing users to view the png file to understand the system startup process and services. To do this, use the following command:
cd /var/log/bootchart
Users may need an application to view png files. Feh is an X11 image viewer for console users. Unlike most other image viewers, it does not have a sophisticated graphical user interface, but it is only used to display images. Feh can be used to view png files. You can install it using the following command:
sudo apt-get install feh
You can use feh xxxx.png to view png files.
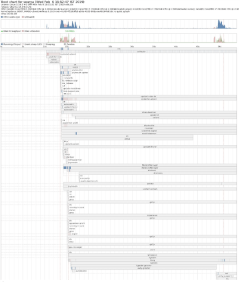
Figure 2: Startup diagram
Figure 2 shows a bootstrap image png file being viewed.
systemd-analyze
However, the boot image is no longer required for Ubuntu 15.10 and later versions. To get brief information about startup speed, use the following command:
systemd-analyze
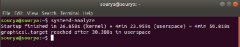
Figure 3: Systemd-analyze output
Chart 3 shows the output of the command systemd-analyze.
The command systemd-analyze blame is used to print a list of all running units based on the time taken to initialize. This information is very useful and can be used to optimize startup time. systemd-analyze blame will not show services with type=simple because systemd considers these services to be started immediately; therefore, the delay in initialization cannot be measured.
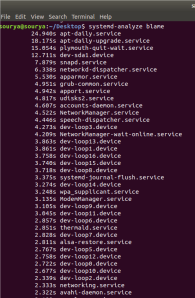
Figure 4: Output of systemd-analyze blame
Figure 4 shows the output of systemd-analyze blame.
The following command prints a tree chain of time-critical service units:
command systemd-analyze critical-chain
Figure 5 shows the output of the command systemd-analyze critical-chain. 
Figure 5: Output of systemd-analyze critical-chain
Steps to Reduce Startup Time
Shown below are some of the various steps that can be taken to reduce startup time.
BUM (Boot Manager)
BUM is a run-level configuration editor that allows initialization services to be configured at system startup or restart. It shows a list of every service that can be started at boot time. Users can turn individual services on and off. BUM has a very clear graphical user interface and is very easy to use.
In Ubuntu 14.04, BUM can be installed using the following command:
sudo apt-get install bum
To install it in 15.10 and later versions, download the package from the link http://apt.ubuntu.com/p/bum.
以基本的服务开始,禁用扫描仪和打印机相关的服务。如果你没有使用蓝牙和其它不想要的设备和服务,你也可以禁用它们中一些。我强烈建议你在禁用相关的服务前学习服务的基础知识,因为这可能会影响计算机或操作系统。图 6 显示 BUM 的图形用户界面。

图 6:BUM
编辑 rc 文件
要编辑 rc 文件,你需要转到 rc 目录。这可以使用下面的命令来做到:
cd /etc/init.d
然而,访问 init.d 需要 root 用户权限,该目录基本上包含的是开始/停止脚本,这些脚本用于在系统运行时或启动期间控制(开始、停止、重新加载、启动启动)守护进程。
在 init.d 目录中的 rc 文件被称为运行控制run control脚本。在启动期间,init 执行 rc 脚本并发挥它的作用。为改善启动速度,我们可以更改 rc 文件。使用任意的文件编辑器打开 rc 文件(当你在 init.d 目录中时)。
例如,通过输入 vim rc ,你可以更改 CONCURRENCY=none 为 CONCURRENCY=shell。后者允许某些启动脚本同时执行,而不是依序执行。
在最新版本的内核中,该值应该被更改为 CONCURRENCY=makefile。
图 7 和图 8 显示编辑 rc 文件前后的启动时间比较。可以注意到启动速度有所提高。在编辑 rc 文件前的启动时间是 50.98 秒,然而在对 rc 文件进行更改后的启动时间是 23.85 秒。
但是,上面提及的更改方法在 Ubuntu 15.10 以后的操作系统上不工作,因为使用最新内核的操作系统使用 systemd 文件,而不再是 init.d 文件。

图 7:对 rc 文件进行更改之前的启动速度

图 8:对 rc 文件进行更改之后的启动速度
E4rat
E4rat 代表 e4 减少访问时间reduced access time(仅在 ext4 文件系统的情况下)。它是由 Andreas Rid 和 Gundolf Kiefer 开发的一个项目。E4rat 是一个通过碎片整理来帮助快速启动的应用程序。它还会加速应用程序的启动。E4rat 使用物理文件的重新分配来消除寻道时间和旋转延迟,因而达到较高的磁盘传输速度。
E4rat 可以 .deb 软件包形式获得,你可以从它的官方网站 http://e4rat.sourceforge.net/下载。
Ubuntu 默认安装的 ureadahead 软件包与 e4rat 冲突。因此必须使用下面的命令安装这几个软件包:
sudo dpkg purge ureadahead ubuntu-minimal
现在使用下面的命令来安装 e4rat 的依赖关系:
sudo apt-get install libblkid1 e2fslibs
打开下载的 .deb 文件,并安装它。现在需要恰当地收集启动数据来使 e4rat 工作。
遵循下面所给的步骤来使 e4rat 正确地运行并提高启动速度。
- Access the Grub menu during startup. This can be done by holding down the shift key while the system is booting.
- Select the usual boot option (kernel version) and press e.
- Find the line starting with linux /boot/vmlinuz and add the following code at the end of the line (press the spacebar after the last letter of the sentence): init=/sbin/e4rat-collect or try – quiet splash vt.handsoff =7 init=/sbin/e4rat-collect.
- Now, press Ctrl x to continue booting. This allows e4rat to collect data after launch. Work on this machine and spend the next two minutes opening and closing applications.
- Access the log file by going to the e4rat folder and using the following command: cd /var/log/e4rat.
- If you don't find any log files, repeat the above process. Once the log file is ready, access the Grub menu again and press e for your option.
- Enter single at the end of the same line that you have edited previously. This gives you access to the command line. If other menus appear, select Resume normal boot. If you somehow can't get to the command prompt, press Ctrl Alt F1.
- After you see the login prompt, enter your login information.
- Now enter the following command: sudo e4rat-realloc /var/lib/e4rat/startup.log. This process takes a while, depending on your machine's disk speed.
- Now use the following command to restart your machine: sudo shutdown -r now.
- Now, we need to configure Grub to run e4rat on every boot.
- Access grub files using any editor. For example, gksu gedit /etc/default/grub.
- Find the line starting with GRUB CMDLINE LINUX DEFAULT= and add the following line between the quotes and before any options: init=/sbin/e4rat-preload 18.
- It should look like this: GRUB CMDLINE LINUX DEFAULT = init=/sbin/e4rat- preload quiet splash.
- Save and close the Grub menu and update Grub using sudo update-grub.
- Restart the system and you will notice a significant change in startup speed.
Figure 9 and Figure 10 show the difference between boot times before and after installing e4rat. An improvement in startup speed can be noticed. The boot time before using e4rat was 22.32 seconds, however after using e4rat the boot time was 9.065 seconds.
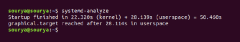
Figure 9: Startup speed before using e4rat

Figure 10: Startup speed after using e4rat
Some Easy Adjustments
Good startup speed can also be achieved with very small adjustments, two of which are listed below.
SSD
Using a solid state device instead of a regular hard drive or other storage device will definitely improve boot speed. SSDs also help speed up file transfers and running applications.
Disable GUI
Graphical user interfaces, desktop graphics, and window animations take up a lot of resources. Disabling the GUI is another great way to get good startup speeds.
In short, through this article, we learned how to use various tools to diagnose and optimize the startup time of Linux systems. Whether it is reducing the number of services, removing unnecessary modules, or optimizing file systems or applications, these methods can effectively reduce the startup time of the Linux system and provide us with a smoother and more efficient experience.
The above is the detailed content of Make your Linux system start up quickly: Tips and methods to optimize startup time. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Compare and contrast the security models of Linux and Windows.Apr 24, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Compare and contrast the security models of Linux and Windows.Apr 24, 2025 am 12:03 AMThe security models of Linux and Windows each have their own advantages. Linux provides flexibility and customizability, enabling security through user permissions, file system permissions, and SELinux/AppArmor. Windows focuses on user-friendliness and relies on WindowsDefender, UAC, firewall and BitLocker to ensure security.
 How does hardware compatibility differ between Linux and Windows?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:15 AM
How does hardware compatibility differ between Linux and Windows?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:15 AMLinux and Windows differ in hardware compatibility: Windows has extensive driver support, and Linux depends on the community and vendors. To solve Linux compatibility problems, you can manually compile drivers, such as cloning RTL8188EU driver repository, compiling and installing; Windows users need to manage drivers to optimize performance.
 What are the differences in virtualization support between Linux and Windows?Apr 22, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
What are the differences in virtualization support between Linux and Windows?Apr 22, 2025 pm 06:09 PMThe main differences between Linux and Windows in virtualization support are: 1) Linux provides KVM and Xen, with outstanding performance and flexibility, suitable for high customization environments; 2) Windows supports virtualization through Hyper-V, with a friendly interface, and is closely integrated with the Microsoft ecosystem, suitable for enterprises that rely on Microsoft software.
 What are the main tasks of a Linux system administrator?Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AM
What are the main tasks of a Linux system administrator?Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AMThe main tasks of Linux system administrators include system monitoring and performance tuning, user management, software package management, security management and backup, troubleshooting and resolution, performance optimization and best practices. 1. Use top, htop and other tools to monitor system performance and tune it. 2. Manage user accounts and permissions through useradd commands and other commands. 3. Use apt and yum to manage software packages to ensure system updates and security. 4. Configure a firewall, monitor logs, and perform data backup to ensure system security. 5. Troubleshoot and resolve through log analysis and tool use. 6. Optimize kernel parameters and application configuration, and follow best practices to improve system performance and stability.
 Is it hard to learn Linux?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:23 AM
Is it hard to learn Linux?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:23 AMLearning Linux is not difficult. 1.Linux is an open source operating system based on Unix and is widely used in servers, embedded systems and personal computers. 2. Understanding file system and permission management is the key. The file system is hierarchical, and permissions include reading, writing and execution. 3. Package management systems such as apt and dnf make software management convenient. 4. Process management is implemented through ps and top commands. 5. Start learning from basic commands such as mkdir, cd, touch and nano, and then try advanced usage such as shell scripts and text processing. 6. Common errors such as permission problems can be solved through sudo and chmod. 7. Performance optimization suggestions include using htop to monitor resources, cleaning unnecessary files, and using sy
 What is the salary of Linux administrator?Apr 17, 2025 am 12:24 AM
What is the salary of Linux administrator?Apr 17, 2025 am 12:24 AMThe average annual salary of Linux administrators is $75,000 to $95,000 in the United States and €40,000 to €60,000 in Europe. To increase salary, you can: 1. Continuously learn new technologies, such as cloud computing and container technology; 2. Accumulate project experience and establish Portfolio; 3. Establish a professional network and expand your network.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 Does the internet run on Linux?Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Does the internet run on Linux?Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AMThe Internet does not rely on a single operating system, but Linux plays an important role in it. Linux is widely used in servers and network devices and is popular for its stability, security and scalability.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.




