Chinese entity recognition methods and commonly used data sets

Named entity recognition (NER) is an important task in natural language processing. It aims to identify entities with specific meanings from text, such as names of people, places, organizations, etc. Chinese NER faces more challenges because the Chinese language has special characteristics and requires the use of more language processing technologies and rules to deal with it.
Chinese named entity recognition methods mainly include rule-based, statistics-based and hybrid methods. Rule-based methods identify entities by manually constructing rules or rule templates. Statistics-based methods use machine learning algorithms to learn entity recognition models from large corpora. Hybrid methods combine two methods to take advantage of both rules and statistical learning.
For the specific implementation of Chinese named entity recognition, the following steps can generally be used:
1. Word segmentation: Split the Chinese text into one by one words for subsequent processing.
2. Part-of-speech tagging: Tag each segmented word with a part-of-speech tag for subsequent processing.
3. Entity recognition: Identify entities in the text based on preset rules or trained models.
In the process of entity recognition, you need to pay attention to the following points:
1. Definition of entity categories: It is necessary to determine which entities are needed Identified and classified into different categories, such as names of people, places, organizations, etc.
2. Determination of entity boundaries: It is necessary to determine the starting position and end position of the entity for subsequent labeling of the entity.
3. Solution to the problem of entity duplication: The same entity may appear multiple times in the text, and it needs to be uniformly marked as the same entity to avoid repeated counting.
Chinese named entity recognition is widely used. For example, in natural language processing tasks such as information extraction, information retrieval, text classification, and machine translation, named entity recognition needs to be performed first. At the same time, it is also widely used in social media, news media, advertising and other fields. For example, identifying users' personal information in social media can provide support for precise advertising and marketing; in news reports, identifying the names of people, places, organizations and other entities involved in the event can help users more quickly Understand the background and relevant information of the incident.
Chinese Named Entity Recognition Dataset
The Chinese Named Entity Recognition Dataset is the basis for training and evaluating named entity recognition models. Currently, there are Multiple Chinese named entity recognition datasets are widely used. The following is an introduction to some commonly used Chinese named entity recognition data sets:
1) MSRA-NER data set: MSRA-NER is Chinese named entity recognition data created by Microsoft Research Asia The set contains more than 80,000 news texts, of which more than 60,000 are used for training and more than 20,000 are used for testing. The entity categories of this data set include person names, place names, organization names and other entities.
2) PKU and MSRA’s People’s Daily dataset: This dataset was jointly created by Peking University and Microsoft Research Asia and includes news reports, editorials and comments from People’s Daily and other types of articles. This dataset is large in size and contains more than 500,000 entity annotations.
3) WeiboNER dataset: This dataset was created by Tsinghua University and contains a large amount of Chinese text from Sina Weibo, including names of people, places, organizations, and times. , dates, professional terms and other entity types. The dataset also contains challenging entities such as internet slang and new vocabulary.
4) OntoNotes dataset: This dataset was created by the National Institute of Standards and Technology and contains text data and entity annotations in multiple languages (including Chinese). The dataset is large in size and contains more than 100,000 entity annotations.
5) CCKS 2017 Task 2 Dataset: This dataset was created by the Chinese Information Society of China and is a task of the 2017 CCKS (Chinese Knowledge Graph Research Area of the Chinese Information Society of China) One, including news, encyclopedias, Weibo and other text types, including names of people, place names, organization names and other entity types. This data set is large in size and contains approximately 100,000 entity annotations.
In short, Chinese named entity recognition is an important task in natural language processing. It has a wide range of applications and has important practical significance.
The above is the detailed content of Chinese entity recognition methods and commonly used data sets. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AMSince 2008, I've championed the shared-ride van—initially dubbed the "robotjitney," later the "vansit"—as the future of urban transportation. I foresee these vehicles as the 21st century's next-generation transit solution, surpas
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
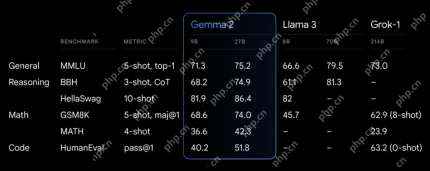 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.






