 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI NetEase Fuxi won the CVPR 2023 UG2+ and VizWiz competitions, and his paper was selected as TIP
NetEase Fuxi won the CVPR 2023 UG2+ and VizWiz competitions, and his paper was selected as TIPNetEase Fuxi won the CVPR 2023 UG2+ and VizWiz competitions, and his paper was selected as TIP
Recently, the results of the CVPR 2023 competition were announced. NetEase Fuxi Lab achieved first place in the CVPR 2023 UG2 Haze Target Recognition Challenge and VizWiz Few-Sample Target Recognition Challenge. Their related papers have also been accepted by TIP, the top international journal. This shows that NetEase Fuxi's top technological innovation capabilities in the field of computer vision have been highly recognized internationally.

From February to June 2023, IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR), as the top conference in the field of international computer vision and pattern recognition, cooperates with authoritative academic institutions and well-known enterprises around the world , held a number of challenges. These challenges have attracted widespread participation from many AI research teams. Recently, CVPR has successively announced the award results and issued award certificates. As a top AI academic conference hosted by IEEE, CVPR has extremely high academic influence and social recognition.

In the CVPR 2023 UG2 Object Detection in Haze Challenge and the CVPR 2023 VizWiz Few-Shot Object Recognition Challenge, NetEase Fuxi teamed up with teacher Yu Jun from the University of Science and Technology of China and achieved first place. This cooperation mainly focuses on two aspects: target detection and few-sample target recognition in the field of computer vision. These technologies can be widely used in vision tasks in various fields. Especially in industrial applications, few-sample target detection is of great value and significance in scenarios where data acquisition and annotation are difficult. Through the success of this competition, we have demonstrated NetEase Fuxi’s research strength and innovation capabilities in the field of computer vision. We will continue to be committed to promoting the development of computer vision technology and providing more accurate and efficient solutions for practical applications.
The goal of UG2 is to advance the analysis of "difficult" images by applying image restoration and enhancement algorithms to improve analysis performance. Contestants are tasked with developing new algorithms to improve the analysis of images captured under problematic conditions. VizWiz's goal is to make more people aware of the technology needs and interests of people with visual impairments and to encourage artificial intelligence researchers to develop new algorithms to remove accessibility barriers. Competitions typically include tasks such as identifying objects in images, identifying text in images, and answering questions about images. The following is a brief overview of NetEase Fuxi’s award-winning paper:
Full-frequency Channel-selection Representations for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection
Omni-frequency Channel-selection Representations for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection
Keywords: Unsupervised image anomaly detection
Anomaly detection plays an important role in visual image understanding and is used to determine whether a given image deviates from a preset normal state. It is widely used in novelty detection, industrial image-based product quality monitoring, automatic defect repair, human health monitoring and video surveillance. Currently, there are three main types of mainstream unsupervised anomaly detection methods, including density-based methods, classification-based methods and reconstruction-based methods. These methods achieve anomaly detection by analyzing the statistical characteristics of images, learning normal samples, and reconstructing images, providing reliable tools and technical support for various applications.
Among them, the reconstruction-based method is rarely mentioned due to poor reconstruction ability and low performance, but it does not require a large amount of additional training samples for unsupervised training. More practical in industrial applications. To this end, this study focuses on improving the reconstruction-based method and proposes a new full-frequency channel selective reconstruction network (OCR-GAN), which is the first to handle the sensory anomaly detection task from the perspective of frequency. A large number of experiments have proved the effectiveness and superiority of this method compared to other methods. For example, without additional training data, new SOTA performance is achieved on the MVTec AD dataset, with an AUC of 98.3, significantly exceeding the reconstruction-based method baseline of 38.1 and the current SOTA method by 0.3.

The paper proposes an innovative solution to solve the UI anomaly problem in smart game compatibility testing. This solution uses artificial intelligence technology to automatically detect UI anomalies that occur when the game is running, and realizes the automation of game compatibility testing. By using image anomaly detection technology, we automatically detect a large number of generated game interface screenshots from the perspective of computer vision, obtain UI abnormal pictures from them, and assist game developers to quickly and accurately locate the cause of the problem, thus effectively saving game testing. The labor cost of experts.

This paper, in collaboration with the team of Professor Liu Yong of Zhejiang University, was selected for publication in the IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP) journal. TIP is the top journal in the field of image processing research under IEEE. It is a journal in the SCI area of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and a Category A journal in the field of computer graphics and multimedia (CCF A) recommended by the China Computer Society. The journal's impact factor in 2022-2023 reaches 11.041.
The above is the detailed content of NetEase Fuxi won the CVPR 2023 UG2+ and VizWiz competitions, and his paper was selected as TIP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AMSince 2008, I've championed the shared-ride van—initially dubbed the "robotjitney," later the "vansit"—as the future of urban transportation. I foresee these vehicles as the 21st century's next-generation transit solution, surpas
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
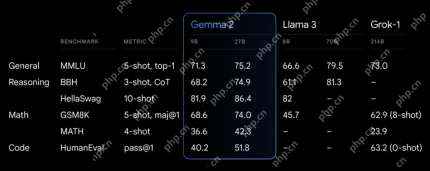 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version




