
RMSprop is a widely used optimizer for updating the weights of neural networks. It was proposed by Geoffrey Hinton et al. in 2012 and is the predecessor of the Adam optimizer. The emergence of the RMSprop optimizer is mainly to solve some problems encountered in the SGD gradient descent algorithm, such as gradient disappearance and gradient explosion. By using the RMSprop optimizer, the learning rate can be effectively adjusted and the weights adaptively updated, thereby improving the training effect of the deep learning model.
The core idea of the RMSprop optimizer is to perform a weighted average of gradients so that gradients at different time steps have different effects on the update of weights. Specifically, RMSprop computes an exponentially weighted average of the squared gradients of each parameter and divides it by the square root of the average gradient. This square root serves as the denominator to normalize the historical gradient of each parameter, thereby making the update amount of each parameter smoother. In addition, RMSprop can also adjust the learning rate so that it gradually decreases during the training process to improve the model's convergence speed and generalization ability. In this way, RMSprop can effectively handle changes in gradients and help the model better adapt to different data distributions and optimization goals.
Specifically, the update formula of the RMSprop optimizer is as follows:
\begin{aligned}
v_t&=\gamma v_{t-1}+(1-\gamma)(\nabla J(\theta_t))^2\
\theta_{t+1}&=\theta_t-\frac{\eta}{\sqrt{v_t}+\epsilon}\nabla J(\theta_t)
\end{aligned}
Where, v_t represents the The exponentially weighted average of the squared gradients of t time steps, usually calculated using the decay rate \gamma=0.9. The learning rate \eta is used to control the step size of parameter update, and \epsilon is a small constant used to prevent division by 0 from occurring. These parameters play an important role in the gradient descent algorithm. By adjusting their values, the optimization process can be finely adjusted and optimized.
The main advantage of the RMSprop optimizer is that it can adaptively adjust the learning rate of each parameter, thereby reducing oscillations and instability during the training process. Compared with traditional gradient descent algorithms, RMSprop can converge faster and have better generalization capabilities. In addition, RMSprop can also handle sparse gradients, making it more efficient when processing large data sets.
However, RMSprop also has some shortcomings. First, the learning rate of RMSprop may be too small, causing the model to converge slowly. Second, RMSprop may be affected by noisy gradients, resulting in poor model performance. In addition, the performance of RMSprop is also affected by hyperparameters such as initial learning rate, decay rate, constant $\epsilon$, etc., and requires empirical parameter adjustment.
Can the rmsprop optimizer prevent overfitting?
The RMSprop optimizer can help alleviate overfitting problems in some cases , but it does not completely solve overfitting. The RMSprop optimizer adaptively adjusts the learning rate of each parameter to converge to the optimal solution faster. This helps prevent the model from overfitting on the training set, but does not guarantee that the model will not overfit on the test set. Therefore, in order to effectively alleviate the overfitting problem, other techniques such as regularization, dropout, etc. are usually required.
Usage of rmsprop optimizer
The RMSprop optimizer is a common gradient descent optimizer that can be used to train neural networks. The following are the general steps for using the RMSprop optimizer:
1. Import the required libraries and datasets
2. Build the neural network model
3. Initialize the RMSprop optimizer, specify the learning rate and other hyperparameters
4. Compile the model, specify the loss function and evaluation indicators
5. Train the model, specify the training data set, batch size, number of training cycles and other parameters
6. Evaluate the model performance and use the test Data set for evaluation
7. Adjust model architecture, hyperparameters, etc. to further improve model performance
The following is an implementation using Keras API Example of RMSprop optimizer:
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.optimizers import RMSprop
from keras.datasets import mnist
# Load MNIST dataset
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = mnist.load_data()
# Preprocess the data
train_images = train_images.reshape((60000, 784))
train_images = train_images.astype('float32') / 255
test_images = test_images.reshape((10000, 784))
test_images = test_images.astype('float32') / 255
# Build the model
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, activation='relu', input_shape=(784,)))
model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax'))
# Initialize RMSprop optimizer
optimizer = RMSprop(lr=0.001, rho=0.9)
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer,
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Train the model
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=5, batch_size=128)
# Evaluate the model
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels)
print('Test accuracy:', test_acc)In the above code, we first load the MNIST dataset and preprocess it. We then use Keras to build a neural network model with two fully connected layers and optimize it using the RMSprop optimizer. We specified a learning rate of 0.001 and a rho parameter of 0.9. Next, we compile the model using cross-entropy as the loss function and accuracy as the evaluation metric. We then trained the model using the training dataset, specifying the number of training epochs as 5 and the batch size as 128. Finally, we evaluate the model performance using the test dataset and output the test accuracy.
The above is the detailed content of Improved RMSprop algorithm. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AM
Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis article explores the growing concern of "AI agency decay"—the gradual decline in our ability to think and decide independently. This is especially crucial for business leaders navigating the increasingly automated world while retainin
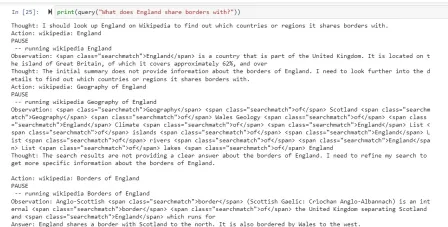 How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AM
How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AMEver wondered how AI agents like Siri and Alexa work? These intelligent systems are becoming more important in our daily lives. This article introduces the ReAct pattern, a method that enhances AI agents by combining reasoning an
 Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM"I think AI tools are changing the learning opportunities for college students. We believe in developing students in core courses, but more and more people also want to get a perspective of computational and statistical thinking," said University of Chicago President Paul Alivisatos in an interview with Deloitte Nitin Mittal at the Davos Forum in January. He believes that people will have to become creators and co-creators of AI, which means that learning and other aspects need to adapt to some major changes. Digital intelligence and critical thinking Professor Alexa Joubin of George Washington University described artificial intelligence as a “heuristic tool” in the humanities and explores how it changes
 Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AM
Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AMLangChain is a powerful toolkit for building sophisticated AI applications. Its agent architecture is particularly noteworthy, allowing developers to create intelligent systems capable of independent reasoning, decision-making, and action. This expl
 What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AM
What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AMRadial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs): A Comprehensive Guide Radial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs) are a powerful type of neural network architecture that leverages radial basis functions for activation. Their unique structure make
 The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AMBrain-computer interfaces (BCIs) directly link the brain to external devices, translating brain impulses into actions without physical movement. This technology utilizes implanted sensors to capture brain signals, converting them into digital comman
 Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis "Leading with Data" episode features Ines Montani, co-founder and CEO of Explosion AI, and co-developer of spaCy and Prodigy. Ines offers expert insights into the evolution of these tools, Explosion's unique business model, and the tr
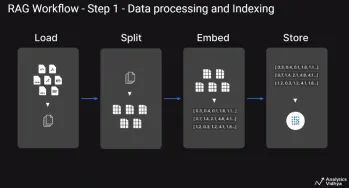 A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AMThis article explores Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems and how AI agents can enhance their capabilities. Traditional RAG systems, while useful for leveraging custom enterprise data, suffer from limitations such as a lack of real-time dat


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools






