 Software Tutorial
Software Tutorial Office Software
Office Software Print preview can display some pictures inserted in WORD but cannot be printed.
Print preview can display some pictures inserted in WORD but cannot be printed.
The part of the picture inserted in WORD cannot be printed, but the print preview can be seen. How to deal with it
1. Since you are working in normal view or outline view.
Workaround: To see where objects such as headers, footers, or graphic objects appear on the printed page, switch to Page view for accurate layout and typesetting. If you want to see how these objects appear in Web Layout view, switch to Web Layout view so you can adjust the style and alignment.
2. What is displayed on the screen may be the field code of the linked embedded graphic. Field codes are instructions enclosed in field characters ({}).
Workaround: To turn off field codes and display graphics, press Alt F9.
3. Open the "Picture Box" view option. If this option is checked, when a document containing a picture is opened, an outline will be used instead of the picture to speed up scrolling.
Workaround: Click Options on the Tools menu, click the View tab, and then clear the Picture Box check box.
4. The graphic to be viewed is a graphic object, such as a text box, AutoShape, clip art or WordArt. In normal view, graphic objects are not displayed.
Solution: Drawing and changing graphic objects must be done in page view, Web layout view or print preview.
5. Turn off the "Graphics" view option. Turning this option off increases scrolling speed when the document contains graphic objects, such as AutoShapes.
Workaround: Click Options on the Tools menu, click the View tab, and then select the Graphics check box.
Why can’t I print images in word2003
Maybe you have inserted several pictures into Word to achieve the effect of both pictures and text. But when you print the document, the graphics in the document are not printed. I hope the following methods can solve your problem:
Clear "Draft Output":
If Word is set to print in draft mode, Word will print the document with minimal formatting, that is, no formatting and most graphics will be printed. At this time, Word can only print the borders and graphics in the document if the "Draft Output" mode is cleared. How to clear "Draft Output" mode is:
Click "Tools" → "Options" → "Options" → "Print", clear the "Draft Output" check box, and click the "OK" button.
Select "Graphic Object":
If you created the graphics in the document using the tools on the Drawing toolbar, you should make sure the Graphics Object check box is selected. Because the Graphic Objects check box is cleared, Word does not print graphic objects created with tools on the Draw toolbar. Instead, it prints a blank box in the location of the graphic object. The method to select "Graphic Object" is:
Select the "Print" tab as described above and select the "Graphic Object" check box. Click the "OK" button.
Clear "Field Code":
If you insert a picture into the document as a link, the picture is actually located in a Word field. At this point, you should clear the Field Codes checkbox to ensure that Word prints the field results as the picture itself, rather than printing the field codes linked to the picture. To clear the Field Code checkbox:
Select the "Print" tab as described above, clear the "Field Code" checkbox, and click the "OK" button.
Fault caused by insufficient memory:
Sometimes, graphics in the document cannot be printed due to insufficient memory in Word or the operating system. At this time, please perform one or more of the following operations to free up more memory space:
Exit any other programs that are running, save the document you want to print, and then close any other windows that are open. Switch to page view, click "Tools" → "Options" → "View" tab, clear the "Picture Box", "Status Bar", "Vertical Ruler", "Horizontal Scroll Bar" and "Vertical Scroll Bar" check frame.
Switch to normal view, click "Tools" → "Options" → "View" tab, and type "0" in the "Style Area Width" box. Click the View→Toolbars command, and then clear all check boxes to hide the toolbars, which saves memory overhead.
Exit Word, disconnect any network connections, and then exit the program-resident program (TSR) and other common tools.
The above is the detailed content of Print preview can display some pictures inserted in WORD but cannot be printed.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Your Calculator App Can Be Replaced By Microsoft ExcelMar 06, 2025 am 06:01 AM
Your Calculator App Can Be Replaced By Microsoft ExcelMar 06, 2025 am 06:01 AMDitch the Calculator: Why and How to Use Excel for All Your Calculations I haven't touched a calculator in ages. Why? Because Microsoft Excel handles all my calculations with ease, and it can do the same for you. Why Excel Trumps a Calculator While
 Don't Create Tables in Word: Use Excel InsteadMar 06, 2025 am 03:04 AM
Don't Create Tables in Word: Use Excel InsteadMar 06, 2025 am 03:04 AMCreating tables in Word, although improved, is still cumbersome and sometimes brings more problems. This is why you should always create tables in Microsoft Excel. Why is it better to create tables in Excel? In short, Word is a word processor, while Excel is a data processor. So Word is not built for the best table creation, but its similar product, Excel. Here are just some of the reasons why creating tables in Excel is better than using Microsoft Word: Although it is surprising that you can use many Excel-like features in Microsoft Word tables, in Excel you
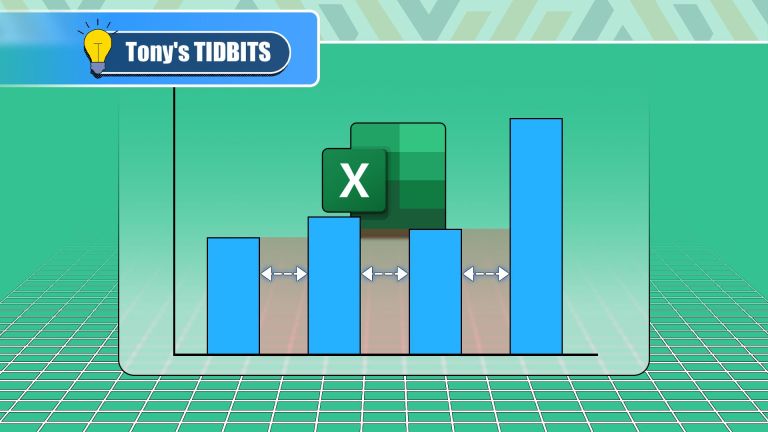 How to Reduce the Gaps Between Bars and Columns in Excel Charts (And Why You Should)Mar 08, 2025 am 03:01 AM
How to Reduce the Gaps Between Bars and Columns in Excel Charts (And Why You Should)Mar 08, 2025 am 03:01 AMEnhance Your Excel Charts: Reducing Gaps Between Bars and Columns Presenting data visually in charts significantly improves spreadsheet readability. Excel excels at chart creation, but its extensive menus can obscure simple yet powerful features, suc
 5 Things You Can Do in Excel for the Web Today That You Couldn't 12 Months AgoMar 22, 2025 am 03:03 AM
5 Things You Can Do in Excel for the Web Today That You Couldn't 12 Months AgoMar 22, 2025 am 03:03 AMExcel web version features enhancements to improve efficiency! While Excel desktop version is more powerful, the web version has also been significantly improved over the past year. This article will focus on five key improvements: Easily insert rows and columns: In Excel web, just hover over the row or column header and click the " " sign that appears to insert a new row or column. There is no need to use the confusing right-click menu "insert" function anymore. This method is faster, and newly inserted rows or columns inherit the format of adjacent cells. Export as CSV files: Excel now supports exporting worksheets as CSV files for easy data transfer and compatibility with other software. Click "File" > "Export"
 How to Use the AVERAGEIF and AVERAGEIFS Functions in ExcelMar 07, 2025 am 06:03 AM
How to Use the AVERAGEIF and AVERAGEIFS Functions in ExcelMar 07, 2025 am 06:03 AMQuick View of AVERAGEIF and AVERAGEIFS Functions in Excel Excel's AVERAGEIF and AVERAGEIFS functions can be used to calculate the average value of a dataset. However, unlike simpler AVERAGE functions, they are able to include or exclude specific values in the calculation. How to use the AVERAGEIF function in Excel Excel's AVERAGEIF function allows you to calculate the average value of a filtered dataset based on a single condition set. AVERAGEIF function syntax The AVERAGEIF function contains three parameters: =AVERAGEIF(x,y,z)
 Microsoft Excel Keyboard Shortcuts: Printable Cheat SheetMar 14, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Microsoft Excel Keyboard Shortcuts: Printable Cheat SheetMar 14, 2025 am 12:06 AMMaster Microsoft Excel with these essential keyboard shortcuts! This cheat sheet provides quick access to the most frequently used commands, saving you valuable time and effort. It covers essential key combinations, Paste Special functions, workboo
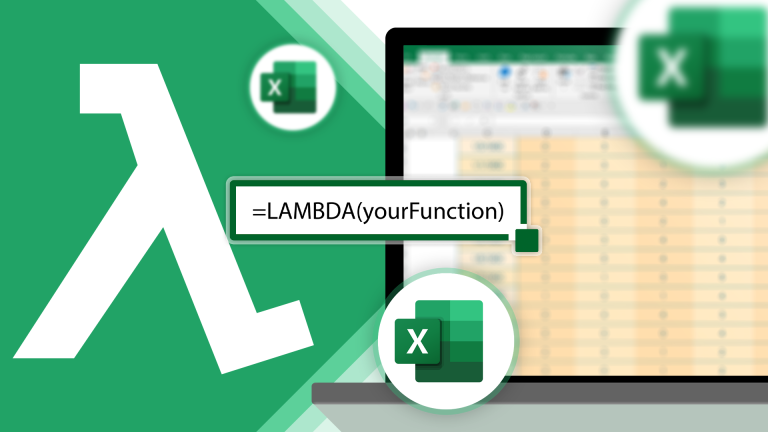 How to Use LAMBDA in Excel to Create Your Own FunctionsMar 21, 2025 am 03:08 AM
How to Use LAMBDA in Excel to Create Your Own FunctionsMar 21, 2025 am 03:08 AMExcel's LAMBDA Functions: An easy guide to creating custom functions Before Excel introduced the LAMBDA function, creating a custom function requires VBA or macro. Now, with LAMBDA, you can easily implement it using the familiar Excel syntax. This guide will guide you step by step how to use the LAMBDA function. It is recommended that you read the parts of this guide in order, first understand the grammar and simple examples, and then learn practical applications. The LAMBDA function is available for Microsoft 365 (Windows and Mac), Excel 2024 (Windows and Mac), and Excel for the web. E
 If You Don't Use Excel's Hidden Camera Tool, You're Missing a TrickMar 25, 2025 am 02:48 AM
If You Don't Use Excel's Hidden Camera Tool, You're Missing a TrickMar 25, 2025 am 02:48 AMQuick Links Why Use the Camera Tool?


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.





