Python crawler analyzes 'Wolf Warrior' movie review
| Introduction | As of August 20, the 25th day after "Wolf Warrior II" was released, its box office has exceeded 5 billion yuan, truly becoming the only Asian film to enter the top 100 box office in world film history. This article uses Python crawlers to obtain data, analyze Douban movie reviews, and create a cloud image of Douban movie reviews. Now, let’s take a look at what interesting subtexts are hidden in the reviews of “Wolf Warrior II”. |

Regardless of the explosive box office, the movie also aroused various emotions in the audience. Some people even said harshly: Anyone who dares to criticize "Wolf Warrior II" is either mentally retarded or a public enemy. It's as simple and crude as that.
Everyone has mixed reviews of "Wolf Warrior II" and have left comments on Douban to express their opinions on the movie. Although various comments were published and the media made a fuss, the audience still couldn't tell which opinion was more reliable.
So far, there have been more than 150,000 comments. When you read the comments, you may see most of them for a period of time, either praising or disparaging comments. So it’s hard to tell by browsing the comments what everyone’s overall opinion of this movie is. Now let’s use data analysis to see what interesting things happened in these comments!
This article obtains data through Python crawler, analyzes Douban movie reviews, and creates a cloud image of Douban movie reviews. Now, let’s take a look at what interesting subtexts are hidden in the reviews of “Wolf Warrior II”.
Data acquisitionThis article uses the data obtained by Python crawler. It mainly uses the requests package and the regular package re. This program does not process the verification code. I have crawled Douban's webpage before. At that time, because the crawled content was small, I did not encounter the verification code. When I wrote this crawler, I thought there would be no verification code, but when about 15,000 comments were crawled, the verification code popped up.
Then I thought, isn’t it just 120,000? At most, I only entered the verification code about a dozen times, so I didn’t have to deal with the verification code. But what happened next was a bit confusing for me. When I crawled about 15,000 comments and entered the verification code, I thought it would crawl to about 30,000, but after crawling about 3,000, it didn’t work. I still had to enter the verification code. .
Then it has been like this, stumbling, sometimes crawling for a long time before requiring a verification code, sometimes not. But in the end, the comments were crawled. The content crawled is mainly: user name, whether you have seen it, the number of stars of the comment, the time of the comment, the number of people who found it useful, and the content of the comment. The following is the code of the Python crawler:
import requests<br>
import re<br>
import pandas as pd<br>
url_first='https://movie.douban.com/subject/26363254/comments?start=0'<br>
head={'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Ubuntu Chromium/59.0.3071.109 Chrome/59.0.3071.109 Safari/537.36'}<br>
html=requests.get(url_first,headers=head,cookies=cookies)<br>
cookies={'cookie':'your own cookie'} #That is, find the cookie corresponding to your account<br>
reg=re.compile(r'') #Next page<br>
ren=re.compile(r'<span>(.*?)</span>.*?comment">(.*?).*?.*?<span .>(.*?).*?<span> (.*?)</span>.*?title="(.*?)"></span>.*?title="(.*?)">.*?class=""> (.*?) \n',re.S) #Comments and other content<br>
while html.status_code==200:<br>
url_next='https://movie.douban.com/subject/26363254/comments' re.findall(reg,html.text)[0]<br>
zhanlang=re.findall(ren,html.text)<br>
data=pd.DataFrame(zhanlang)<br>
data.to_csv('/home/wajuejiprince/document/zhanlang/zhanlangpinglun.csv', header=False,index=False,mode='a ') #Write a csv file, 'a ' is the append mode<br>
data=[]<br>
zhanlang=[]<br>
html=requests.get(url_next,cookies=cookies,headers=head)
In the above code, please set your own User-Agent, Cookie, CSV saving path, etc., and save the crawled content into a CSV format file.
This article uses R language to process data. Although we have paid great attention to the structure of the crawled content when crawling, it is inevitable that there are some values that are not what we want. For example, some comment content will appear in the commenter item, so it is still necessary to clean the data.
First load all the packages to be used:
library(data.table)<br>
library(plotly)<br>
library(stringr)<br>
library(jiebaR)<br>
library(wordcloud2)<br>
library(magrittr)
Import data and clean it:
dt
Let’s first take a look at the situation of comments based on the number of stars:
plot_ly(my_dt[,.(.N),by=.(five-star number)],type = 'bar',x=~five-star number,y=~N)
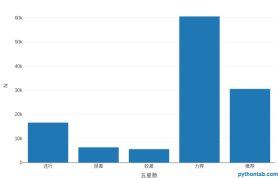
The number of five-pointed stars corresponds to 5 levels, 5 stars means highly recommended, 4 stars means recommended, 3 stars means okay, 2 stars means poor, and 1 star means very poor.
It is obvious from the reviews of Pentagram that we have reason to believe that the vast majority of viewers will be satisfied with this film.
First we should segment the comments:
wk <br>
Overall comment cloud display: <br>
<code>words�ta.table()<br>
setnames(words,"N","pinshu")<br>
words[pinshu>1000] #Remove lower frequency words (less than 1000)<br>
wordcloud2(words[pinshu>1000], size = 2, fontFamily = "Microsoft Yahei", color = "random-light", backgroundColor = "grey")
Because there was too much data, my broken computer froze, so I removed words with frequencies lower than 1,000 when making the cloud chart. The cloud chart results are as follows:

Overall, everyone’s comments on this movie are pretty good! Topics such as plot, action, and patriotism are the focus of discussion.
Evaluation keywords: Wu Jing, personal heroism, main theme, China, protagonist aura, Secretary Dakang, very burning.
It can be seen that "Ran" was not the most popular response after watching it. The audience was more interested in admiring Wu Jing himself and commenting on patriotism and individualism.
Cloud image display of different comment levelsBut what would it look like if the comments of people with different ratings were displayed separately? That is to create a cloud chart for the review content of five levels (strongly recommended, recommended, okay, poor, very poor), the code is as follows (just change the code to "strongly recommended" to other).
1. Comment cloud of highly recommended reviewers




Judging from the word segmentation results of different comments, they all have a common topic: patriotism.
The number of patriotic topics in highly recommended comments may be higher than in poorly recommended comments. In highly recommended comments, people are more willing to discuss things other than patriotic topics. Most of the negative comments were about patriotic topics. And their proportion is very interesting. From those who highly recommend it to those who comment poorly, the proportion of patriotic topics gradually increases.
We cannot subjectively think who is right and who is wrong. We can only say that they stand from different perspectives, so the results they see are also different. When we disagree with others, it is often from different perspectives. People with bad comments may be thinking more about patriotic topics (this is just a discussion of patriotic topics, not who loves or dislikes the country)! !
After the analysis, the fundamental reason why this "Wolf Warrior 2" has been supported by so many people is that it has achieved an American blockbuster-level scene in production that "Wolf Warrior 1" did not have, and at the same time, it also embodies patriotism. It aroused resonance and aroused people's hearts.
The above is the detailed content of Python crawler analyzes 'Wolf Warrior' movie review. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Compare and contrast the security models of Linux and Windows.Apr 24, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Compare and contrast the security models of Linux and Windows.Apr 24, 2025 am 12:03 AMThe security models of Linux and Windows each have their own advantages. Linux provides flexibility and customizability, enabling security through user permissions, file system permissions, and SELinux/AppArmor. Windows focuses on user-friendliness and relies on WindowsDefender, UAC, firewall and BitLocker to ensure security.
 How does hardware compatibility differ between Linux and Windows?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:15 AM
How does hardware compatibility differ between Linux and Windows?Apr 23, 2025 am 12:15 AMLinux and Windows differ in hardware compatibility: Windows has extensive driver support, and Linux depends on the community and vendors. To solve Linux compatibility problems, you can manually compile drivers, such as cloning RTL8188EU driver repository, compiling and installing; Windows users need to manage drivers to optimize performance.
 What are the differences in virtualization support between Linux and Windows?Apr 22, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
What are the differences in virtualization support between Linux and Windows?Apr 22, 2025 pm 06:09 PMThe main differences between Linux and Windows in virtualization support are: 1) Linux provides KVM and Xen, with outstanding performance and flexibility, suitable for high customization environments; 2) Windows supports virtualization through Hyper-V, with a friendly interface, and is closely integrated with the Microsoft ecosystem, suitable for enterprises that rely on Microsoft software.
 What are the main tasks of a Linux system administrator?Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AM
What are the main tasks of a Linux system administrator?Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AMThe main tasks of Linux system administrators include system monitoring and performance tuning, user management, software package management, security management and backup, troubleshooting and resolution, performance optimization and best practices. 1. Use top, htop and other tools to monitor system performance and tune it. 2. Manage user accounts and permissions through useradd commands and other commands. 3. Use apt and yum to manage software packages to ensure system updates and security. 4. Configure a firewall, monitor logs, and perform data backup to ensure system security. 5. Troubleshoot and resolve through log analysis and tool use. 6. Optimize kernel parameters and application configuration, and follow best practices to improve system performance and stability.
 Is it hard to learn Linux?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:23 AM
Is it hard to learn Linux?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:23 AMLearning Linux is not difficult. 1.Linux is an open source operating system based on Unix and is widely used in servers, embedded systems and personal computers. 2. Understanding file system and permission management is the key. The file system is hierarchical, and permissions include reading, writing and execution. 3. Package management systems such as apt and dnf make software management convenient. 4. Process management is implemented through ps and top commands. 5. Start learning from basic commands such as mkdir, cd, touch and nano, and then try advanced usage such as shell scripts and text processing. 6. Common errors such as permission problems can be solved through sudo and chmod. 7. Performance optimization suggestions include using htop to monitor resources, cleaning unnecessary files, and using sy
 What is the salary of Linux administrator?Apr 17, 2025 am 12:24 AM
What is the salary of Linux administrator?Apr 17, 2025 am 12:24 AMThe average annual salary of Linux administrators is $75,000 to $95,000 in the United States and €40,000 to €60,000 in Europe. To increase salary, you can: 1. Continuously learn new technologies, such as cloud computing and container technology; 2. Accumulate project experience and establish Portfolio; 3. Establish a professional network and expand your network.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AMThe main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 Does the internet run on Linux?Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Does the internet run on Linux?Apr 14, 2025 am 12:03 AMThe Internet does not rely on a single operating system, but Linux plays an important role in it. Linux is widely used in servers and network devices and is popular for its stability, security and scalability.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)





