 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI LightSim: An autonomous driving lighting simulation platform launched at NeurIPS 2023 to achieve a realistic, controllable and scalable simulation experience
LightSim: An autonomous driving lighting simulation platform launched at NeurIPS 2023 to achieve a realistic, controllable and scalable simulation experienceLightSim: An autonomous driving lighting simulation platform launched at NeurIPS 2023 to achieve a realistic, controllable and scalable simulation experience
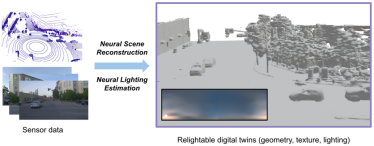
Recently, researchers from Waabi AI, University of Toronto, University of Waterloo and MIT proposed a new autonomous driving lighting simulation platform LightSim at NeurIPS 2023. Researchers have proposed methods to generate paired illumination training data from real data, solving the problems of missing data and model migration loss. LightSim uses neural radiation fields (NeRF) and physics-based deep networks to render vehicle driving videos, achieving lighting simulation of dynamic scenes on large-scale real data for the first time. 

Project website: https://waabi.ai/lightsim Paper link: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=mcx8IGneYw

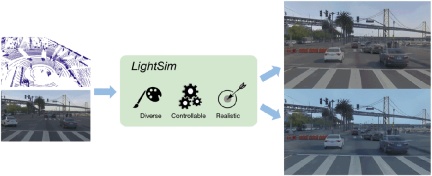
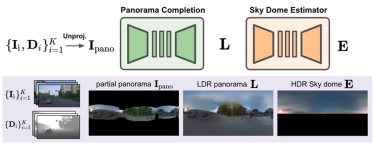
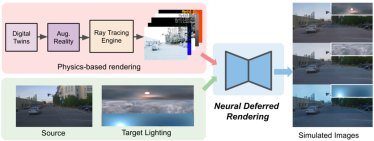
 LightSim can perform batch relighting of scenes, generating new time-consistent and 3D-aware lighting changes of the same scene from estimated and real HDR environment maps.
LightSim can perform batch relighting of scenes, generating new time-consistent and 3D-aware lighting changes of the same scene from estimated and real HDR environment maps. 
 LightSim can also perform shadow editing in batches.
LightSim can also perform shadow editing in batches. 


 Another example is shown in the video below, where a new set of vehicles has been added after a new road obstacle has been inserted. Using simulated lighting built with LightSim, newly added vehicles can be seamlessly integrated into the scene.
Another example is shown in the video below, where a new set of vehicles has been added after a new road obstacle has been inserted. Using simulated lighting built with LightSim, newly added vehicles can be seamlessly integrated into the scene. 
The above is the detailed content of LightSim: An autonomous driving lighting simulation platform launched at NeurIPS 2023 to achieve a realistic, controllable and scalable simulation experience. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How can Simpson's Paradox Uncover Hidden Trends in Data? - Analytics VidhyaApr 23, 2025 am 09:20 AM
How can Simpson's Paradox Uncover Hidden Trends in Data? - Analytics VidhyaApr 23, 2025 am 09:20 AMSimpson's Paradox: Unveiling Hidden Trends in Data Have you ever been misled by statistics? Simpson's Paradox demonstrates how aggregated data can obscure crucial trends, revealing the importance of analyzing data at multiple levels. This concise gui
 What is Nominal Data? - Analytics VidhyaApr 23, 2025 am 09:13 AM
What is Nominal Data? - Analytics VidhyaApr 23, 2025 am 09:13 AMIntroduction Nominal data forms the bedrock of data analysis, playing a crucial role in various fields like statistics, computer science, psychology, and marketing. This article delves into the characteristics, applications, and distinctions of nomi
 What is One-Shot Prompting? - Analytics VidhyaApr 23, 2025 am 09:12 AM
What is One-Shot Prompting? - Analytics VidhyaApr 23, 2025 am 09:12 AMIntroduction In the dynamic world of machine learning, efficiently generating precise responses using minimal data is paramount. One-shot prompting offers a powerful solution, enabling AI models to execute specific tasks using just a single example
 Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AMSince 2008, I've championed the shared-ride van—initially dubbed the "robotjitney," later the "vansit"—as the future of urban transportation. I foresee these vehicles as the 21st century's next-generation transit solution, surpas
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
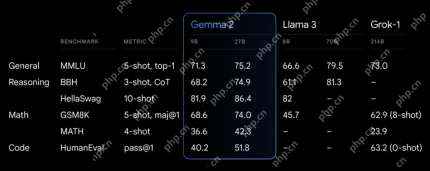 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!




