 Web Front-end
Web Front-end H5 Tutorial
H5 Tutorial HTML5 graphic tutorial on making a cool audio player plug-in_html5 tutorial skills
HTML5 graphic tutorial on making a cool audio player plug-in_html5 tutorial skillsHTML5 graphic tutorial on making a cool audio player plug-in_html5 tutorial skills
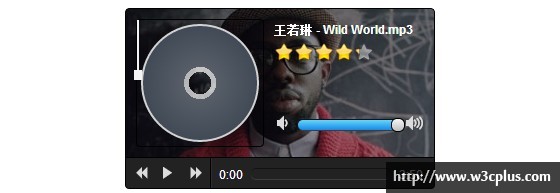
The picture above is the UI interface diagram of this audio player, which also hides a playlist of songs. The entire player UI is drawn with CSS and font-face except for the background portrait and the star rating of the song, which are all drawn with CSS and font-face. The only areas that seem to be difficult are the production of CDs and disc players. In the song Both the CD and the disc player have animated interactive effects during playback, which will be explained in a later section. Click on the CD in the player to open the playlist~
Because this tutorial is mainly to demonstrate the use of the new
Main functions:1. Play, pause, previous song, next song, volume increase or decrease
2. Click CD to open and close the playlist
3. You can drag local music files to the player to play
Html structure
audio tag
In the above structure we can find the new audio tag in HTML5, which has a controls attribute. As the name suggests, it is the controller of the player. The controls attribute specifies that the browser provides playback controls for audio, such as in the chrome browser If you set this attribute in the audio tag under

However, due to the different rendering effects of audio tags under different browsers, this simple method is not suitable for use under cross-browsers, and the functions provided by the browser's default player control are really too limited. Less. . Therefore, we usually hide the browser's default playback controls by not setting this attribute, and manually add additional tags and styles to customize the player's UI interface.
Playback ControlsAfter the UI interface of the player is drawn, the first thing we need to do is to add corresponding event listeners for the three main control buttons: play, previous song, and next song.
var myAudio = $("#myAudio audio ")[0];
var $sourceList = $("#myAudio source");
var currentSrcIndex = 0;
var currentSr = "";
$(".btn_play").click (function(){
if (myAudio.paused) {
myAudio.play();
} else {
myAudio.pause();
}
});
$(".btn_next").click(function(){
currentSrcIndex > $sourceList.length - 1 && (currentSrcIndex = 0);
currentSrc = $("#myAudio source").eq (currentSrcIndex).prop("src");
myAudio.src = currentSrc;
myAudio.play();
});
$(".btn_previous").click(function( ){
--currentSrcIndex currentSrc = $("#myAudio source").eq(currentSrcIndex).prop("src");
myAudio.src = currentSrc;
myAudio.play();
});
In the above button click event monitoring, we control the play and pause of the audio by calling the play() and pause() methods of the original audio element. In addition, the audio element provides the currentSrc attribute, which represents the file source of the currently playing file. We control the currently playing song track by setting this attribute.
Volume controlNext, let’s add event monitoring to the two small speakers on both sides of the volume bar, so that the volume of the current playback can be reduced and increased by clicking on the two small speakers on the left and right. To set the volume of the player, we can call the volume attribute provided in the audio element. The maximum volume value is 1 and the minimum is 0. Here we control the volume by increasing or decreasing the volume by 0.1 each time we click the speaker. Of course you can also use other values. But it should be noted that the JavaScript language cannot provide precise control over decimals, so each time the volume is reduced by 0.1, the volume actually reduced is slightly greater than 0.1, which results in 0.09 remaining when the volume reduction button is clicked 9 times in a row. xxxx volume, and then you will find out why the player cannot be muted. . . Of course this problem is easy to fix (shown below), just a little reminder.
$(".volume_control .decrease") .click(function() {
var volume = myAudio.volume - 0.1;
volume myAudio.changeVolumeTo(volume);
});
$(".volume_control .increase").click(function() {
var volume = myAudio.volume 0.1;
volume > 1 && (volume = 1);
myAudio.changeVolumeTo( volume);
});
In addition, we also need to implement the function of using the slider or clicking a certain position of the volume bar to control the volume. With the above foundation, this is easy to complete. . First, let's take a look at the function of clicking a certain position of the volume bar to control the volume: click a certain position of the volume bar, calculate the length value from the starting point of the volume bar to that position, and then divide this value by the total length of the volume bar. (Here it is 100) Get the percentage value, then multiply the percentage value by the maximum volume value 1 to get the volume value you want to jump to, and then assign it to volume. The method of controlling the volume through a slider is similar to this. The main thing is to know how to calculate the position value of the slider on the volume bar. I won’t explain it in detail here. If you have any questions, please leave a message below.
$(".volume_control .base_bar").mousedown(function(ev){
var posX = ev.clientX;
var targetLeft = $(this).offset().left;
var volume = (posX - targetLeft)/100;
volume > 1 && (volume = 1);
volume myAudio.changeVolumeTo(volume );
});
$(".volume_control .slider").mousedown(starDrag = function(ev) {
ev.preventDefault();
var origLeft = $(this). position().left; /*Initial position of slider*/
var origX = ev.clientX; /*Initial position of mouse*/
var target = this;
var progress_bar = $(".volume_control .progress_bar")[0];
$(document).mousemove(doDrag = function(ev){
ev.preventDefault();
var moveX = ev.clientX - origX; /*Calculate mouse Moving distance*/
var curLeft = origLeft moveX; /*Use the distance moved by the mouse to represent the moving distance of the slider*/
(curLeft (curLeft > 93) && (curLeft = 93);
target.style.left = curLeft "px";
progress_bar.style.width = curLeft 7 "%";
myAudio.changeVolumeTo(( curLeft 7)/100);
});
$(document).mouseup(stopDrag = function(){
$(document).unbind("mousemove",doDrag);
$ (document).unbind("mouseup",stopDrag);
});
});
Time Control
Okay, now the player is basically working, but we also want to be able to directly skip a part of the audio to a specific time point. So how to achieve it? ? ! The committee members who formulate the standard are not fools. Such commonly used functions cannot be omitted. So quickly browse the API and you will find that the audio element provides an attribute called currentTime, which is a very concise and easy-to-understand name. (In fact, most attributes are easy to understand). Setting this attribute can set the current playback time point.
Here, we also need to use another attribute of audio, duration, which refers to the total time length of the currently playing file. So depending on the volume control implementation, we can do this:
1. Click a certain position of the progress bar, and calculate the percentage value of the length from the starting point of the progress bar to that position to the total length of the progress bar (for example, click on the middle position of the progress bar, then the length from the starting point of the progress bar to that position will be The length of the position accounts for 50% of the total progress bar length), recorded as percentage.
2. Then multiply the percentage by the total duration of the file to get the value of the time point you want to jump to, and then assign the value to currentTime to complete the function to be implemented.
$(".time_line .base_bar") .mousedown(function(ev){
var posX = ev.clientX;
var targetLeft = $(this).offset().left;
var percentage = (posX - targetLeft)/140 * 100 ;
myAudio.currentTime = myAudio.duration * percentage / 100;
});
At this point, the player has basically taken shape. There are some insignificant UI interaction implementations left (actually, they are the most important to me, haha). If you are interested, you can check it out in the source code. If you have any questions, you can leave a comment below. I hope we can communicate and learn more.
 The Connection Between H5 and HTML5: Similarities and DifferencesApr 24, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Connection Between H5 and HTML5: Similarities and DifferencesApr 24, 2025 am 12:01 AMH5 and HTML5 are different concepts: HTML5 is a version of HTML, containing new elements and APIs; H5 is a mobile application development framework based on HTML5. HTML5 parses and renders code through the browser, while H5 applications need to run containers and interact with native code through JavaScript.
 The Building Blocks of H5 Code: Key Elements and Their PurposeApr 23, 2025 am 12:09 AM
The Building Blocks of H5 Code: Key Elements and Their PurposeApr 23, 2025 am 12:09 AMKey elements of HTML5 include,,,,,, etc., which are used to build modern web pages. 1. Define the head content, 2. Used to navigate the link, 3. Represent the content of independent articles, 4. Organize the page content, 5. Display the sidebar content, 6. Define the footer, these elements enhance the structure and functionality of the web page.
 HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AMThere is no difference between HTML5 and H5, which is the abbreviation of HTML5. 1.HTML5 is the fifth version of HTML, which enhances the multimedia and interactive functions of web pages. 2.H5 is often used to refer to HTML5-based mobile web pages or applications, and is suitable for various mobile devices.
 HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AMHTML5 is the latest version of the Hypertext Markup Language, standardized by W3C. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, multimedia support and form enhancements, improving web structure, user experience and SEO effects. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, such as, ,, etc., to make the web page structure clearer and the SEO effect better. HTML5 supports multimedia elements and no third-party plug-ins are required, improving user experience and loading speed. HTML5 enhances form functions and introduces new input types such as, etc., which improves user experience and form verification efficiency.
 H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AM
H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AMHow to write clean and efficient HTML5 code? The answer is to avoid common mistakes by semanticizing tags, structured code, performance optimization and avoiding common mistakes. 1. Use semantic tags such as, etc. to improve code readability and SEO effect. 2. Keep the code structured and readable, using appropriate indentation and comments. 3. Optimize performance by reducing unnecessary tags, using CDN and compressing code. 4. Avoid common mistakes, such as the tag not closed, and ensure the validity of the code.
 H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AMH5 improves web user experience with multimedia support, offline storage and performance optimization. 1) Multimedia support: H5 and elements simplify development and improve user experience. 2) Offline storage: WebStorage and IndexedDB allow offline use to improve the experience. 3) Performance optimization: WebWorkers and elements optimize performance to reduce bandwidth consumption.
 Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AMHTML5 code consists of tags, elements and attributes: 1. The tag defines the content type and is surrounded by angle brackets, such as. 2. Elements are composed of start tags, contents and end tags, such as contents. 3. Attributes define key-value pairs in the start tag, enhance functions, such as. These are the basic units for building web structure.
 Understanding H5 Code: The Fundamentals of HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Understanding H5 Code: The Fundamentals of HTML5Apr 17, 2025 am 12:08 AMHTML5 is a key technology for building modern web pages, providing many new elements and features. 1. HTML5 introduces semantic elements such as, , etc., which enhances web page structure and SEO. 2. Support multimedia elements and embed media without plug-ins. 3. Forms enhance new input types and verification properties, simplifying the verification process. 4. Offer offline and local storage functions to improve web page performance and user experience.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),





