Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >What is the knowledge about MySQL's SQL optimization, index optimization, lock mechanism, and master-slave replication?
What is the knowledge about MySQL's SQL optimization, index optimization, lock mechanism, and master-slave replication?
- PHPzforward
- 2023-06-05 17:30:501394browse

0 Storage engine introduction
myisam storage: If the table does not have high transaction requirements, both query and For adding mainly, we consider using the myisam storage engine, such as the posting table in bbs, and the reply table
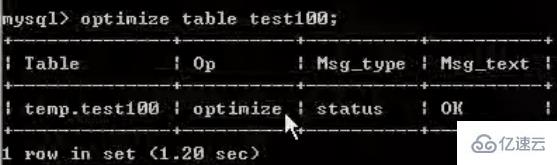
needs to be defragmented regularly (because the deleted data still exists):
optimize table table_name;
InnoDB storage: It has high transaction requirements and the saved data is important data. We recommend using INN0DB, such as order table, account table.
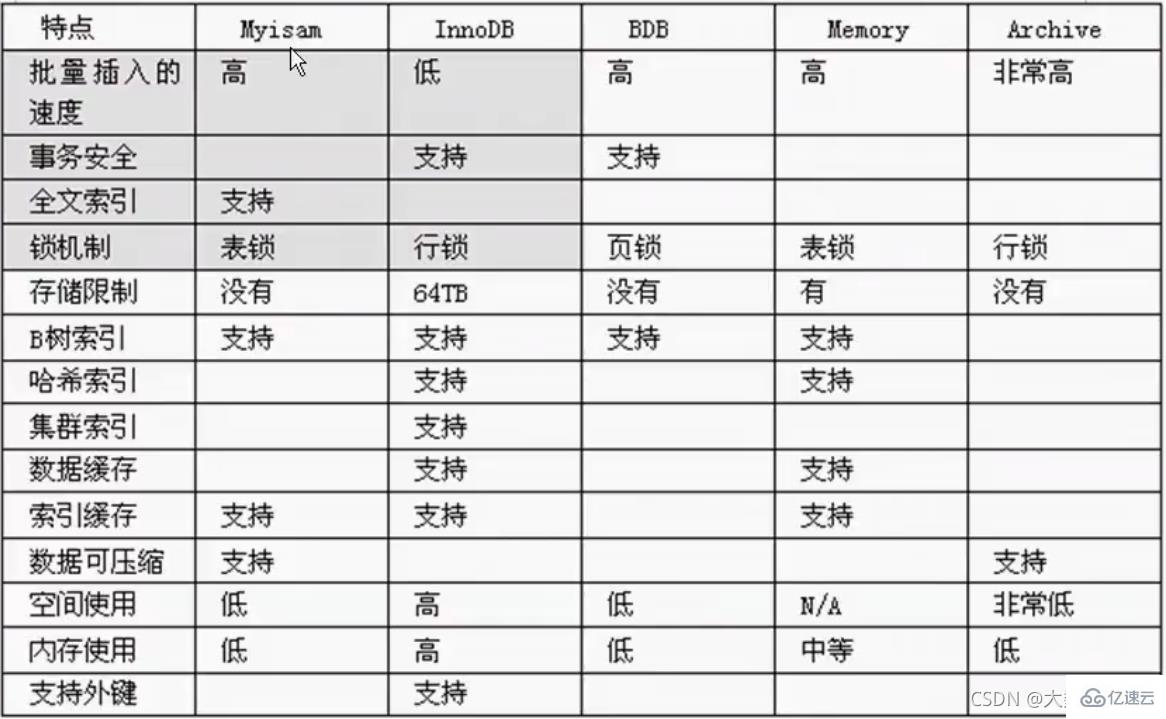
Interview asked about the difference between MyISAM and INNODB:
1.Transaction security
2. Query and add speed
3.Support full-text index
4.Lock mechanism
5. Foreign keys MyISAM does not support foreign keys, but INNODB supports foreign keys.
Mermoory storage: For example, our data changes frequently, There is no need to enter the database, and frequent queries and modifications are required. We consider using memory
to see what storage engines mysql provides:show engines;
View mysql's current default storage engine: show variables like '%storage_engine%';
1 SQL performance analysis
Reasons for SQL performance degradation:
1. Poorly written query statements
-
2. Index failure (data change)
3. Too many joins in related queries (design defects or unavoidable requirements)
4. Server tuning and various parameter settings (buffering, number of threads) etc.)
Usual SQL tuning process:
Observe, run for at least 1 day to see if the production is slow SQL situation.
Turn on the slow query log, set the threshold, for example, if it exceeds 5 seconds, it is slow SQL, and capture it.
explain Slow SQL analysis.
show profile.
Operation and maintenance manager or DBA, performs parameter tuning of the SQL database server.
##Summary:
- 1. Open and capture slow query
- 2. Explain slow SQL analysis
- 3. Show profile queries the execution details and life cycle of SQL in the Mysql server
- 4 , Parameter tuning of SQL database server
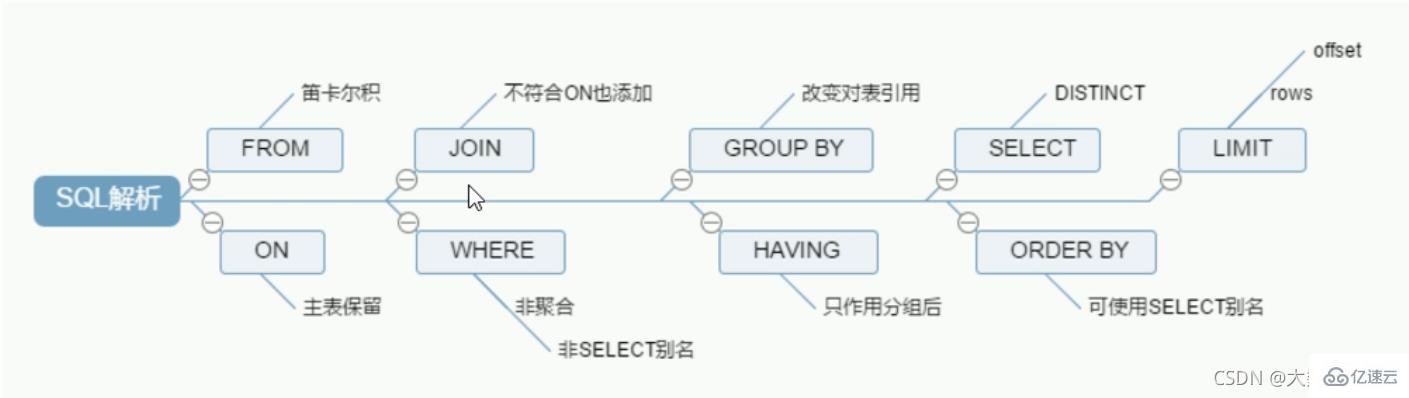
Handwriting order :
SELECT DISTINCT
<select_list>
FROM
<left_table> <join_type>
JOIN <right_table> on <join_codition> //join_codition:比如员工的部门ID和部门表的主键id相同
WHERE
<where_condition>
GROUP BY
<group_by_list>
HAVING
<having_condition>
ORDER BY
<order_by_condition>
LIMIT
<limit_number>
MySQL machine read order:
1 FROM <left_table> 2 ON <join_condition> 3 <join_type> JOIN <right_table> 4 WHERE <where_condition> 5 GROUP BY <group_by_list> 6 HAVING <having_condition> 7 SELECT 8 DISTINCT <select_list> 9 ORDER BY <order_by_condition> 10 LIMIT <limit_number>
Summary:
- ##Running order one Let’s take a look
 Seven ways to write JOIN
Seven ways to write JOIN
Create a table to insert data (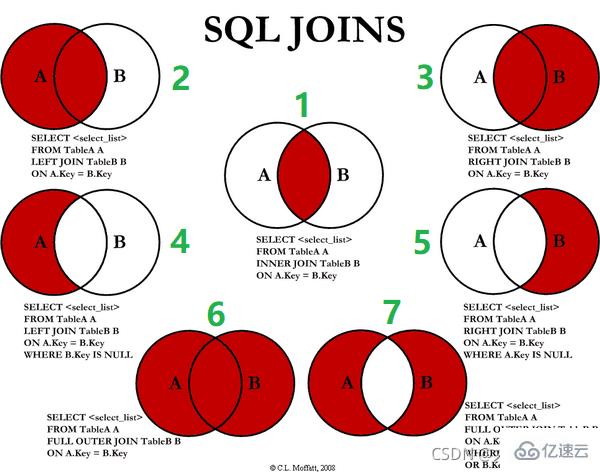 The left and right primary and foreign keys are connected
The left and right primary and foreign keys are connected
): <pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">CREATE TABLE tbl_dept(
id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
deptName VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL,
locAdd VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
)ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
//设置存储引擎,主键自动增长和默认文本字符集
CREATE TABLE tbl_emp (
id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL,
deptId INT(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id),
KEY fk_dept_Id (deptId)
#CONSTRAINT &#39;fk_dept_Id&#39; foreign key (&#39;deptId&#39;) references &#39;tbl_dept&#39;(&#39;Id&#39;)
)ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) VALUES(&#39;RD&#39;,11);
INSERT INTO tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) VALUES(&#39;HR&#39;,12);
INSERT INTO tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) VALUES(&#39;MK&#39;,13);
INSERT INTO tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) VALUES(&#39;MIS&#39;,14);
INSERT INTO tbl_dept(deptName,locAdd) VALUES(&#39;FD&#39;,15);
INSERT INTO tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) VALUES(&#39;z3&#39;,1);
INSERT INTO tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) VALUES(&#39;z4&#39;,1);
INSERT INTO tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) VALUES(&#39;z5&#39;,1);
INSERT INTO tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) VALUES(&#39;w5&#39;,2);
INSERT INTO tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) VALUES(&#39;w6&#39;,2);
INSERT INTO tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) VALUES(&#39;s7&#39;,3);
INSERT INTO tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) VALUES(&#39;s8&#39;,4);
INSERT INTO tbl_emp(NAME,deptId) VALUES(&#39;s9&#39;,51);
#查询执行后结果
mysql> select * from tbl_dept;
+----+----------+--------+
| id | deptName | locAdd |
+----+----------+--------+
| 1 | RD | 11 |
| 2 | HR | 12 |
| 3 | MK | 13 |
| 4 | MIS | 14 |
| 5 | FD | 15 |
+----+----------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from tbl_emp;
+----+------+--------+
| id | NAME | deptId |
+----+------+--------+
| 1 | z3 | 1 |
| 2 | z4 | 1 |
| 3 | z5 | 1 |
| 4 | w5 | 2 |
| 5 | w6 | 2 |
| 6 | s7 | 3 |
| 7 | s8 | 4 |
| 8 | s9 | 51 |
+----+------+--------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)</pre>
: only the common part of deptId and id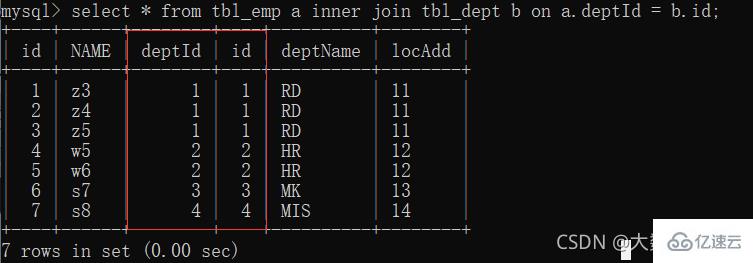
(All A): The first seven items share data; the eighth item has unique data in table a, and table b is filled with null
(all B): The first seven items share data; the eighth item has unique data in table b, and table a is filled with null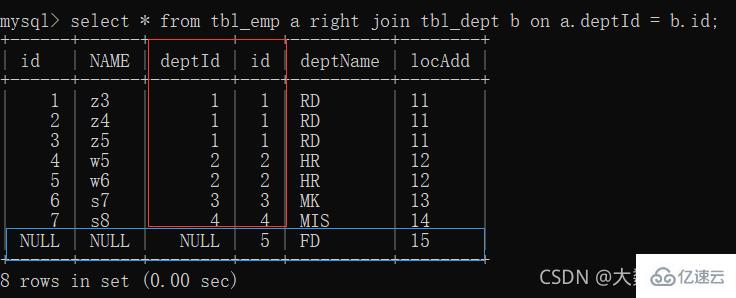 4. Left join only A
4. Left join only A
: unique part of table A 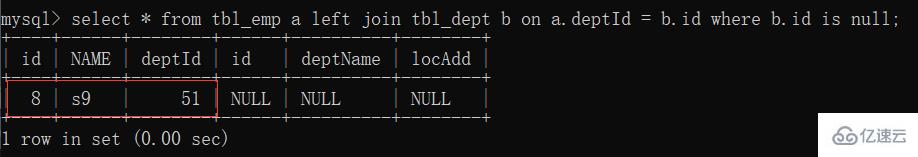 5. Right join unique B
5. Right join unique B
: The unique part of table B 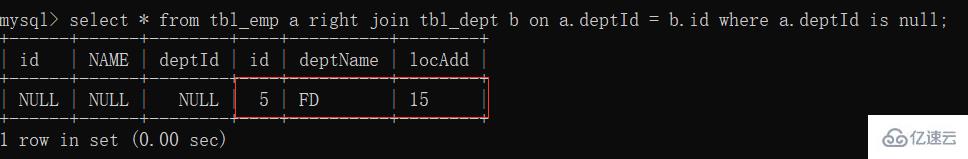 6. Full join
6. Full join
: MySQL does not support full join, use all a b. The middle part of union deduplication
- union keyword can be merged and deduplicated
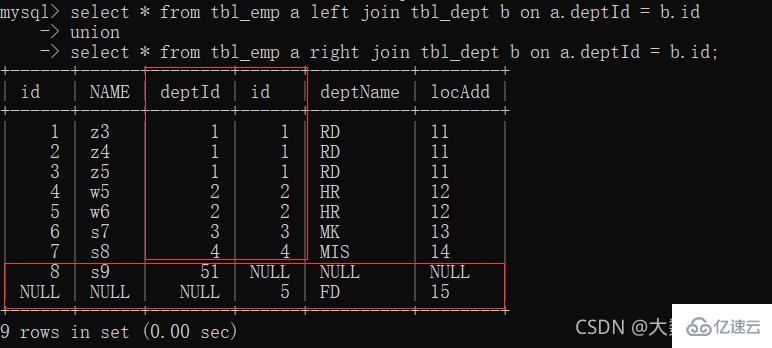
7、A、B各自独有集合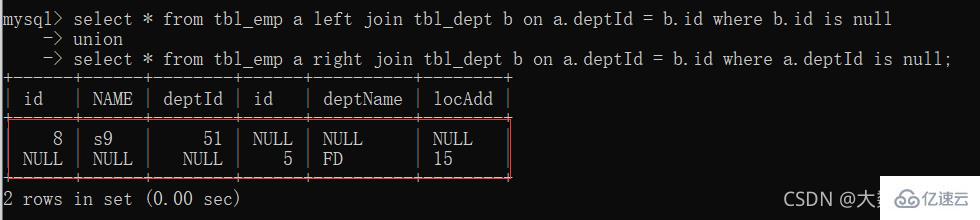
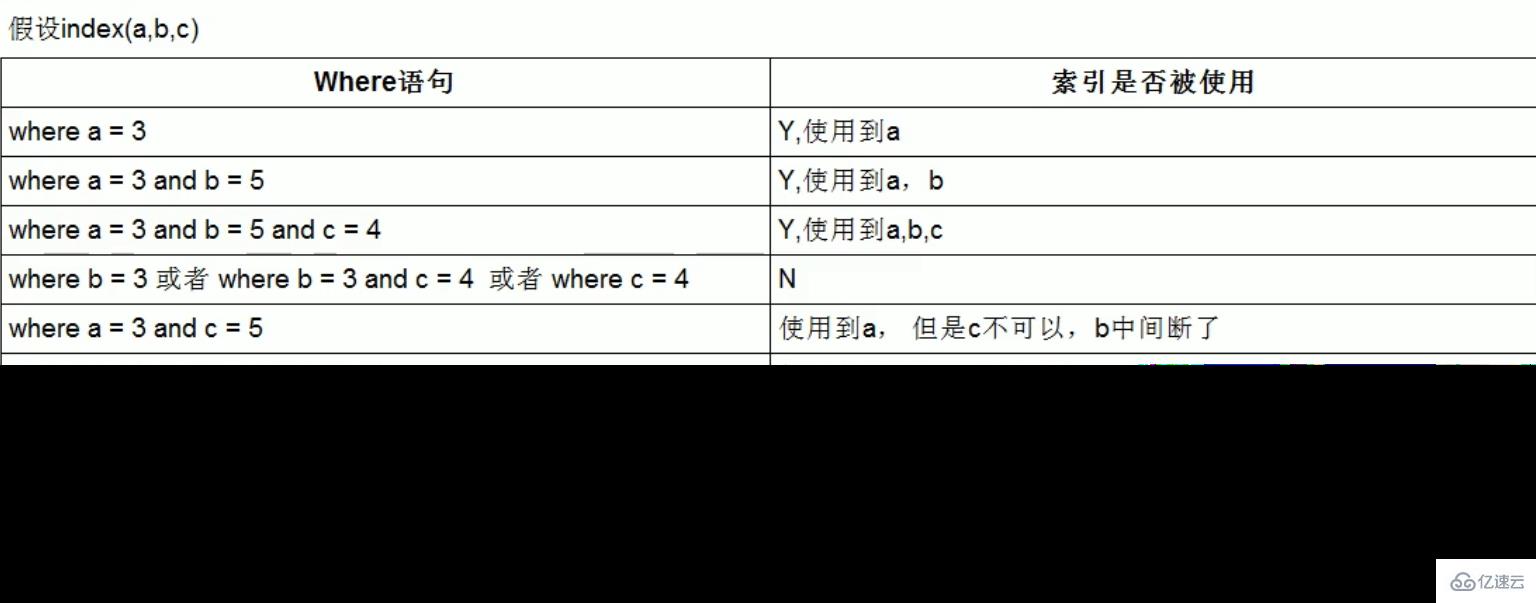
3 索引介绍
3.1 索引是什么
MySQL官方对索引的定义为:索引(Index)是帮助MySQL高效获取数据的数据结构(索引的本质是数据结构,排序+查询两种功能)。
索引的目的在于提高查询效率,可以类比字典。
如果要查“mysql”这个单词,我们肯定需要定位到m字母,然后从下往下找到y字母,再找到剩下的sql。
如果没有索引,那么你可能需要逐个逐个寻找,如果我想找到Java开头的单词呢?或者Oracle开头的单词呢?
是不是觉得如果没有索引,这个事情根本无法完成?
索引可以理解为:排好序的快速查找数据结构
下图就是一种可能的索引方式示例: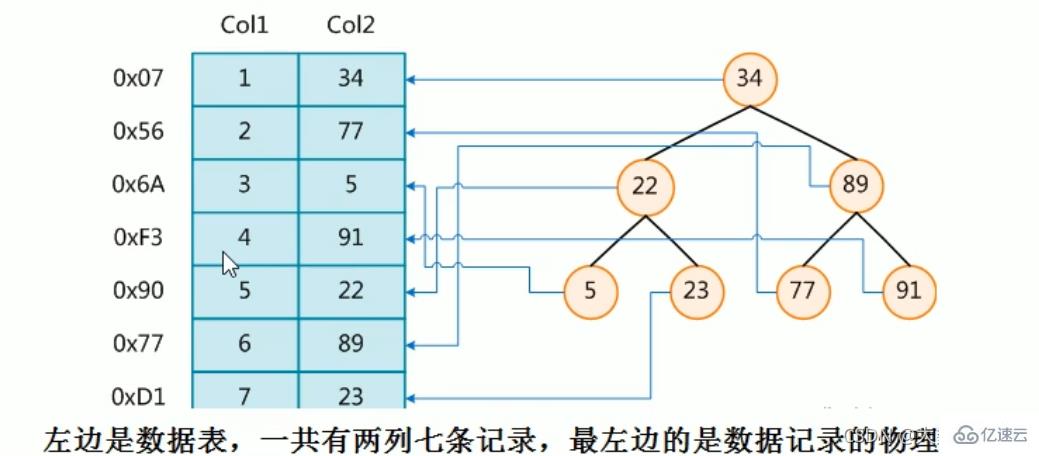
假如:找4号这本书,扫码得到对应的编号为91,91比34大往右边找,91比89大往右边找,然后找到(比较三次后就可以找到,然后检索出对应的物理地址)
为了加快Col2的查找,可以维护一个右边所示的二叉查找树,每个节点分别包含索引键值和一个指向对应数据记录物理地址的指针,这样就可以运用二叉查找在一定的复杂度内获取到相应数据,从而快速的检索出符合条件的记录
结论:在数据之外,数据库系统还维护着满足特定查找算法的数据结构,这些数据结构以某种方式引用(指向)数据,这样就可以在这些数据结构上实现高级查找算法。这种数据结构,就是索引
一般来说索引本身也很大,不可能全部存储在内存中,因此索引往往以索引文件的形式存储的磁盘上。
通常情况下,我们所说的索引都是指采用B树(一种多路搜索树,不一定是二叉树结构)组织的索引。这句话可以重写为:使用B+树索引的索引种类包括聚集索引、次要索引、覆盖索引、复合索引、前缀索引和唯一索引,它们被统称为索引。当然,除了B+树这种类型的索引之外,还有哈稀索引(hash index)等
3.2 索引优劣势
优势:
类似大学图书馆建书目索引,提高数据检索的效率,降低数据库的IO成本。
通过索引列对数据进行排序,降低数据排序的成本,降低了CPU的消耗。
劣势:
实际上索引也是一张表,该表保存了主键与索引字段,并指向实体表的记录,所以索引列也是要占用空间的(占空间)
虽然索引大大提高了查询速度,同时却会降低更新表的速度,如对表进行INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE。因为更新表时,MySQL不仅要保存数据,还要保存一下索引文件每次更新添加了索引列的字段,都会调整因为更新所带来的键值变化后的索引信息。
索引只是提高效率的一个因素,如果你的MysQL有大数据量的表,就需要花时间研究建立最优秀的索引,或优化查询
3.3 索引分类和建索引命令语句
主键索引:索引值必须是唯一的,且不能为NULL
第一种:
CREATE TABLE table_name(id int PRIMARY KEY aoto_increment,name varchar(10));第二种:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD PRIMARY KEY (columnName);
普通索引:索引值可出现多次
第一种:
CREATE INDEX index_name on table_name(columnName);第二种:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD INDEX index_name (columnName);
全文索引:主要是针对文本的检索,如:文章,全文索引只针对MyISAM引擎有效,并且只针对英文内容生效
-
建表时创建
#建表 CREATE TABLE articles( id INT UNSIGNED ATUO_INCREMENT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, title VARCHAR(200), body TEXT, FULLTEXT(title,body) )engine=myisam charset utf8; #指定引擎 #使用 select * from articles where match(title,body) against('英文内容'); #只针对英语内容生效 #说明 #1、在mysql中fultext索引只针对 myisam 生效 #2、mysq1自己提供的flltext只针对英文生效->sphinx (coreseek)技术处理中文工 #3、使用方法是match(字段名...) against(‘关键字') #4、全文索引一个叫停止词,因为在一个文本中创建索引是一个无穷大的数,因此对一些常用词和字符就不会创建,这些词称为停止词
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD FULLTEXT index_name (columnName);
唯一索引:索引列的值必须唯一,但允许有空值NULL,并可以有多个。
第一种:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name ON table_name(columnName);第二种:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD UNIQUE INDEX index_name ON (columnName);
单值索引:即一个索引只包含单个列,一个表可以有多个单列索引。
第一种:
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name(columnName);第二种:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD INDEX index_name ON (columnName);
select * from user where name=''; //经常查name字段,为其建索引 create index idx_user_name on user(name);
复合索引:即一个索引包含多个列
第一种:
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name(columnName1,columnName2...);第二种:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD INDEX index_name ON (columnName1,columnName2...);
select * from user where name='' and email=''; //经常查name和email字段,为其建索引 create index idx_user_name on user(name, email);
查询索引
第一种:
SHOW INDEX FROM table_name;第二种:
SHOW KEYS FROM table_name;
删除索引
第一种:
DROP INDEX index_name ON table_name;第二种:
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP INDEX index_name;删除主键索引:
ALTER TBALE table_name DROP PRIMARY KEY;
3.4 索引结构与检索原理
MySQL索引结构:
BTree索引
Hash索引
full-text全文索引
R-Tree索引

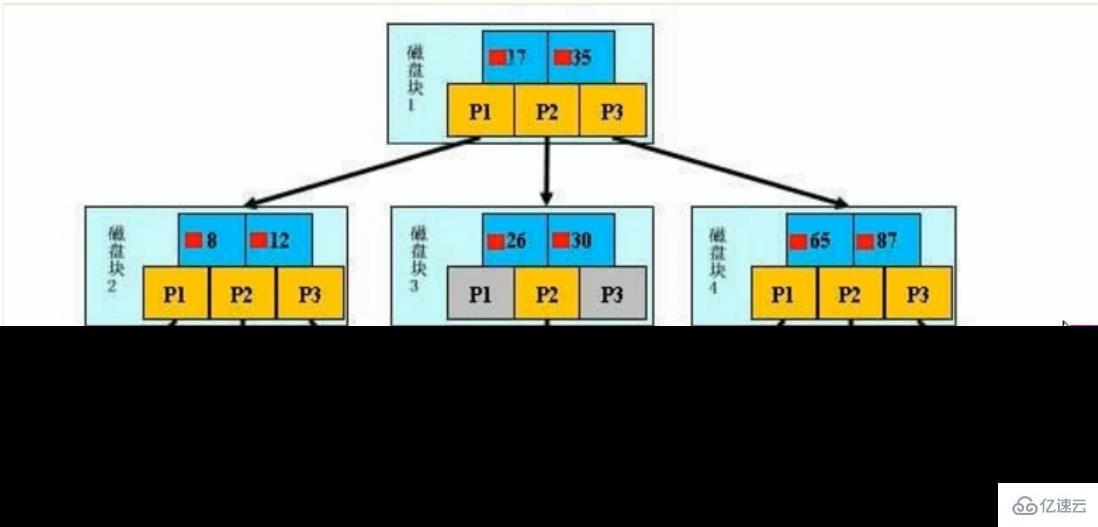
初始化介绍
一颗b+树,浅蓝色的块我们称之为一个磁盘块,可以看到每个磁盘块包含几个数据项(深蓝色所示)和指针(黄色所示),如磁盘块1包含数据项17和35,包含指针P1、P2、P3,
P1表示小于17的磁盘块,P2表示在17和35之间的磁盘块,P3表示大于35的磁盘块。
真实的数据存在于叶子节点:3、5、9、10、13、15、28、29、36、60、75、79、90、99。
非叶子节点只不存储真实的数据,只存储指引搜索方向的数据项,如17、35并不真实存在于数据表中。
查找过程
如果要查找数据项29,那么首先会把磁盘块1由磁盘加载到内存,此时发生一次IO。在内存中用二分查找确定 29 在 17 和 35 之间,锁定磁盘块1的P2指针,内存时间因为非常短(相比磁盘的IO)可以忽略不计,通过磁盘块1的P2指针的磁盘地址把磁盘块3由磁盘加载到内存,发生第二次IO,29 在 26 和 30 之间,锁定磁盘块3的P2指针,通过指针加载磁盘块8到内存,发生第三次IO,同时内存中做二分查找找到29,结束查询,总计三次IO
真实的情况是,3层的b+树可以表示上百万的数据,如果上百万的数据查找只需要三次IO,性能提高将是巨大的,如果没有索引,每个数据项都要发生一次IO,那么总共需要百万次的IO,显然成本非常非常高
3.5 哪些情况适合建索引
主键自动建立唯一索引
频繁作为查询条件的字段应该创建索引
查询中与其它表关联的字段,外键关系建立索引
单键/组合索引的选择问题,who?(在高并发下倾向创建组合索引)
查询中排序的字段,排序字段若通过索引去访问将大大提高排序速度
查询中统计或者分组字段
3.6 哪些情况不适合建索引
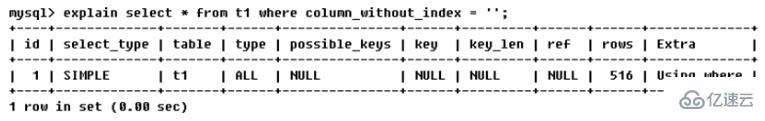
Where条件里用不到的字段不创建索引
表记录太少(300w以上建)
经常增删改的表(提高了查询速度,同时却会降低更新表的速度,如对表进行INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE。因为更新表时,MySQL不仅要保存数据,还要保存一下索引文件)
为了优化数据库查询性能,应该只对经常被查询和排序的数据列建立索引,这些数据也需要在表中有重复且均匀的分布。注意,如果某个数据列包含许多重复的内容,为它建立索引就没有太大的实际效果。(比如:国籍、性别)
假如一个表有10万行记录,有一个字段A只有T和F两种值,且每个值的分布概率天约为50%,那么对这种表A字段建索引一般不会提高数据库的查询速度。
索引的选择性是指索引列中不同值的数目与表中记录数的比。如果一个表中有2000条记录,表索引列有1980个不同的值,那么这个索引的选择性就是1980/2000=0.99。一个索引的选择性越接近于1,这个索引的效率就越高
4 性能分析
4.1 性能分析前提知识
MySQL Query Optimizer(查询优化器)[ˈkwɪəri] [ˈɒptɪmaɪzə]
Mysql中专门负责优化SELECT语句的优化器模块,主要功能:通过计算分析系统中收集到的统计信息,为客户端请求的Query提供他认为最优的执行计划(他认为最优的数据检索方式,但不见得是DBA认为是最优的,这部分最耗费时间)
当客户端向MySQL请求一条Query,命令解析器模块完成请求分类,区别出是SELECT并转发给MySQL Query Optimizer时,MySQL Query Optimizer首先会对整条Query进行优化,处理掉一些常量表达式的预算直接换算成常量值。简化和转换Query中的查询条件,例如删除或调整一些毫无意义或显然的条件。然后分析Query 中的 Hint信息(如果有),看显示Hint信息是否可以完全确定该Query的执行计划。如果没有Hint 或Hint信息还不足以完全确定执行计划,则会读取所涉及对象的统计信息,根据Query进行写相应的计算分析,然后再得出最后的执行计划
MySQL常见瓶颈:
CPU:CPU在饱和的时候一般发生在数据装入内存或从磁盘上读取数据时候
IO:磁盘I/O瓶颈发生在装入数据远大于内存容量的时候
服务器硬件的性能瓶颈:top,free,iostat和vmstat来查看系统的性能状态
4.2 Explain使用简介
使用EXPLAIN关键字可以模拟优化器执行SQL查询语句,从而知道MySQL是如何处理你的SQL语句的。分析你的查询语句或是表结构的性能瓶颈
官网地址
Explain的作用:
表的读取顺序
数据读取操作的操作类型
哪些索引可以使用
哪些索引被实际使用
表之间的引用
每张表有多少行被优化器查询
使用Explain:
explain + sql语句
执行计划包含的信息(
重点) :| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
mysql> select * from tbl_emp; +----+------+--------+ | id | NAME | deptId | +----+------+--------+ | 1 | z3 | 1 | | 2 | z4 | 1 | | 3 | z5 | 1 | | 4 | w5 | 2 | | 5 | w6 | 2 | | 6 | s7 | 3 | | 7 | s8 | 4 | | 8 | s9 | 51 | +----+------+--------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from tbl_emp; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | tbl_emp | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 8 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
4.3 执行计划包含的信息字段解释(重中之重)
执行计划包含的信息(重点) :| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
面试重点:id、type、key、rows、Extra
id(表的读取顺序)
select查询的序列号,包含一组数字,表示查询中执行select子句或操作表的顺序
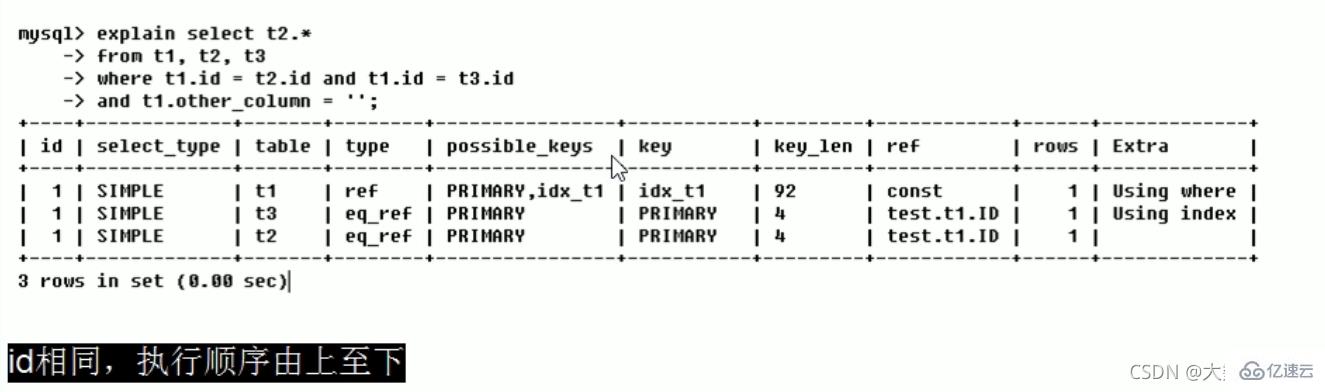
三种情况:
1、id相同,执行顺序由上至下(t1、t3、t2)

2、id不同,如果是子查询,id的序号会递增,id值越大优先级越高,越先被执行(t3、t1、t2)

3、id相同不同,同时存在。先走数字大的,数字相同的由上至下(t3、s1、t2)

select_type( 数据读取操作的操作类型)
查询的类型,主要是用于区别普通查询、联合查询、子查询等的复杂查询。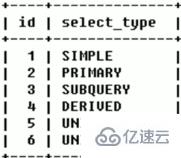
SIMPLE [ˈsɪnpl] :简单的select查询,查询中不包含子查询或者UNION
PRIMARY:查询中若包含任何复杂的子部分,最外层查询则被标记为(最后加载的那个)
SUBQUERY [ˈkwɪəri] :在SELECT或WHERE列表中包含了子查询
DERIVED [dɪˈraɪvd]:在FROM列表中包含的子查询被标记为DERIVED(衍生)MySQL会递归执行这些子查询,把结果放在临时表里
UNION [ˈjuːniən]: If the second SELECT appears after UNION, it will be marked as UNION; if UNION is included in the subquery of the FROM clause, the outer SELECT will be marked as: DERIVED
UNION RESULT [rɪˈzʌlt]: SELECT to obtain the result from the UNION table (two select statements are merged with UNION)
table (displays the executed Table name)
Shows which table this row of data is about
type (access type arrangement)
Shows what type is used in the query
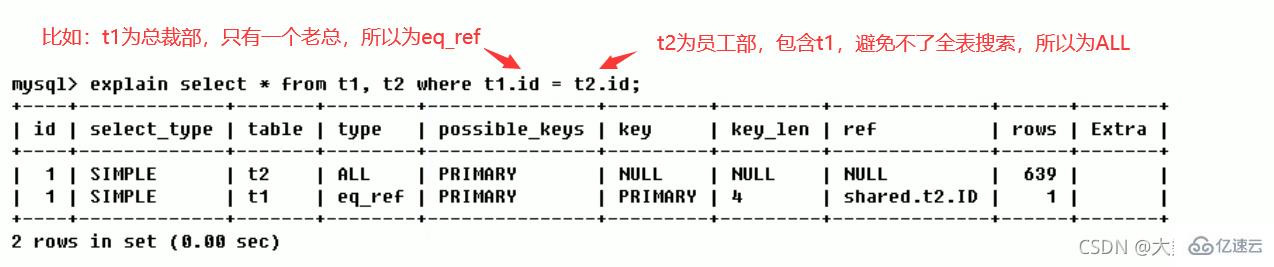
Access type arrangement:system > const > eq_ref > ref > fulltext > ref_or_null > index_merge > unique_subquery > index_subquery > range > index >ALL
typeThere are eight commonly used types:
The result values from best to worst are (key points)::system > const > eq_ref > ref > range > index > ALL
## Generally speaking, you must ensure that the query reaches at least the range level, preferably Can reach ref
Detailed description
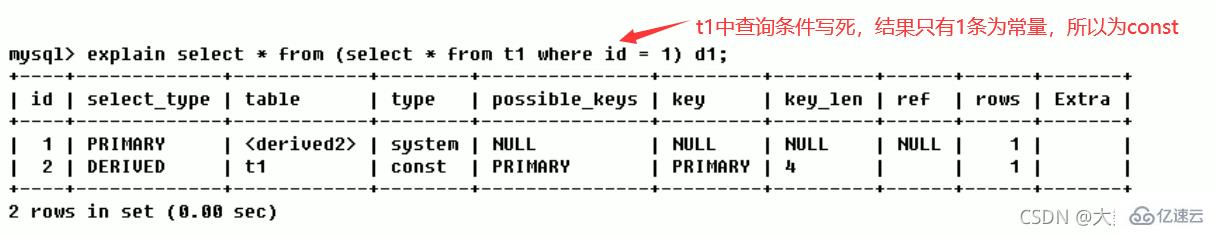
- ##system
: The table has only one row of records (equal to the system table), This is a special column of the const type, which does not usually appear, and can be ignored.
- const
: Indicates that it is found through the index once. Const is used to compare the primary key or unique index. Because only one row of data is matched, MySQL can quickly convert the query into a constant if the primary key is placed in the where list.

- eq_ref
: Unique index scan, for each index key, only one record in the table matches it. Commonly seen in primary key or unique index scans.

- ref
: Non-unique index scan, returns all rows matching a single value, which is essentially an index access. It returns all rows that match a single value, however, it may find multiple matching rows, so it should be a mixture of find and scan

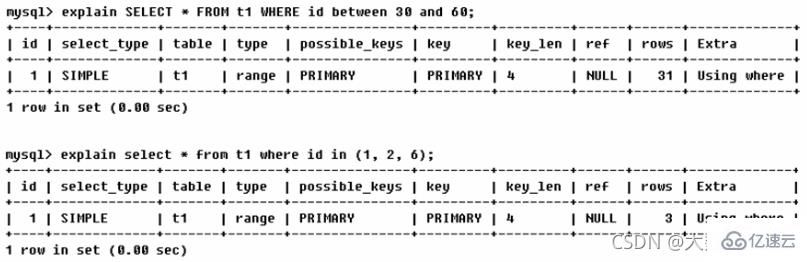
- range
: Retrieve only rows in a given range, using an index to select rows. The key column shows which index is used. Generally, queries such as between, , in, etc. appear in your where statement. This range scan index scan is better than a full table scan because it only needs to start at a certain point in the index and end at another point, without scanning the entire index

- index
: Full Index Scan, the difference between index and ALL is that the index type only traverses the index column. This is usually faster than ALL because index files are usually smaller than data files (that is, although all and Index both read the entire table, index reads from the index, while all reads from the hard disk)

- all
: Full Table Scan, will traverse the entire table to find matching rows
Work case: Manager this I ran an Explain analysis on the SQL statement. There may be an ALL full table scan on the system. It is recommended to try optimization. I changed this SQL and wrote it like this after optimization. The effect has changed from ALL to... possible_keys (which indexes can be used)
possible_keys (which indexes can be used)
Displays one or more indexes that may be applied to this table. If there is an index for the fields involved in the query, the index will be listed, but
may not be actually used by the query(the system believes that theoretically some indexes will be used) key ( Which indexes are actually used)
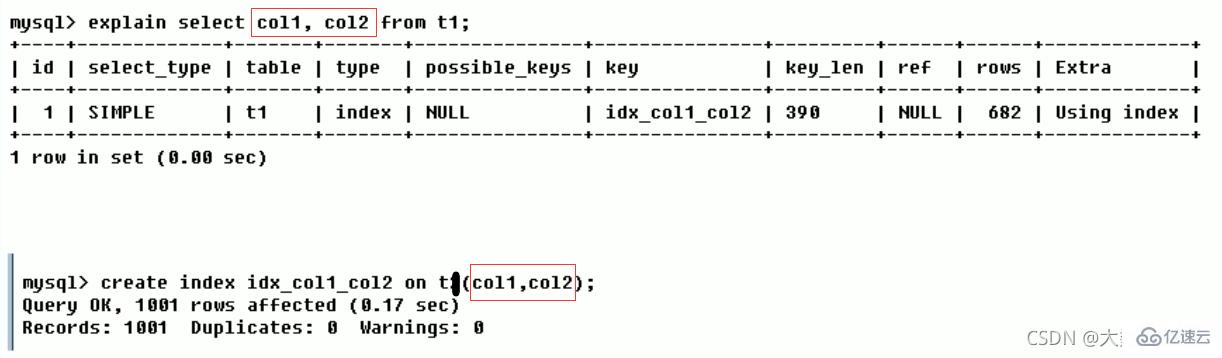
Indexes actually used. If it is NULL, the index is not used (either it is not built, or it is invalid)
If a covering index is used in the query, the index will only appear in the key list
Covering index: The created index fields are consistent with the queried fields, as shown below
key_len (number of bytes consumed)
Indicates the number of bytes used in the index. This column can be used to calculate the length of the index used in the query. Without losing accuracy, the shorter the length, the better
The value displayed by key_len is the maximum possible length of the index field, not the actual length used, that is, key_len is calculated based on the table definition, not through the table The retrieved

ref (reference between tables)
shows which column of the index is used, if possible, is a constant. Which columns or constants are used to find the value on the index column. 
rows (how many rows in each table are queried by the optimizer)
Based on the table statistics and index selection, roughly estimate the time required to find the required records Number of rows read (the smaller the better)
Before indexing : 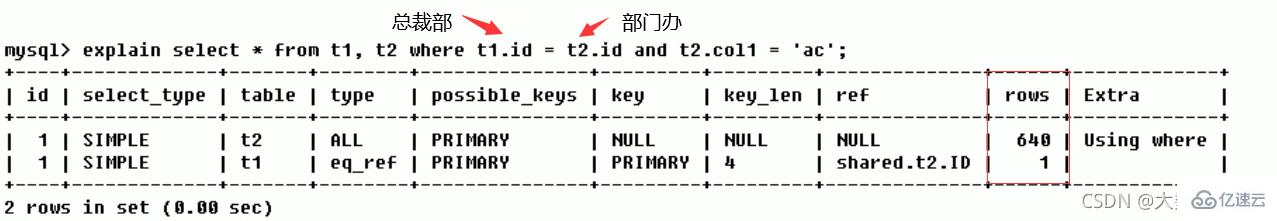
After indexing : Number of rows scanned Reduce
Extra [ˈekstrə]
Contains important extra information that is not suitable for display in other columns
Types of information: Using filesort, Using temporary , Using index , Using where , Using join buffer , impossible where , select tables optimized away , distinct
Using filesort(needs optimization)
MySQL will use external indexes To sort the data instead of reading it in the order of the index in the table. When MySQL cannot use the index to complete the sorting operation, it is called "file sorting"
Using temporary(requires optimization)
MySQL will use Temporary tables sort query results to hold intermediate results. Commonly used in sort order by and group query group by
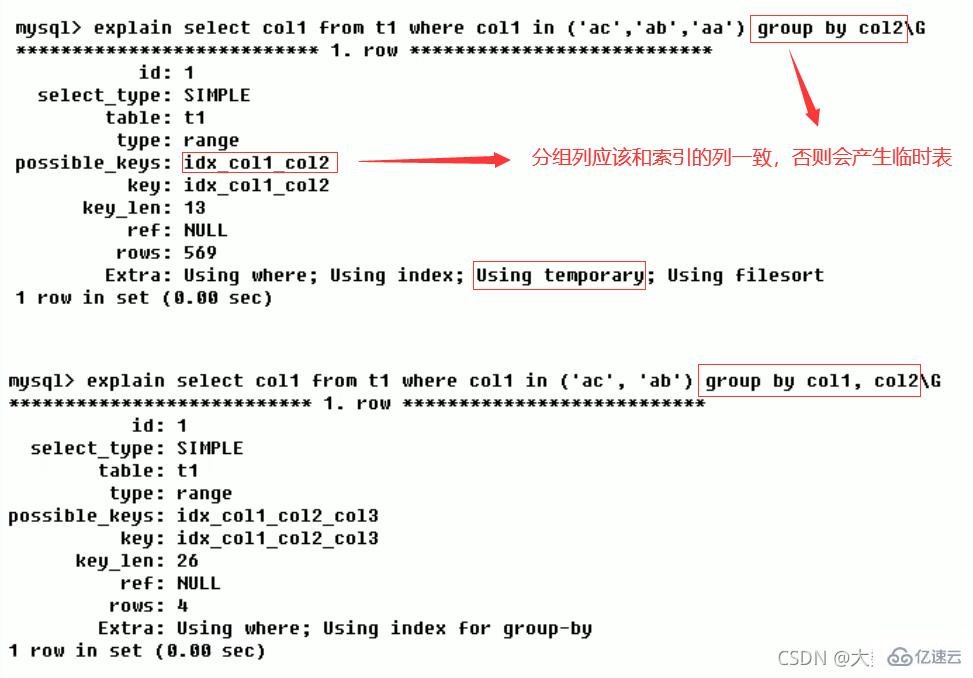
Using index(good)
indicates that it is used in the corresponding select operation Covering Index avoids accessing the data rows of the table, which is very efficient!
Situation one:

Situation two:

Covering Index/Index Covering (Covering Index).
Understanding method one: The data columns of the select can only be obtained from the index without reading the data rows. MySQL can use the index to return the fields in the select list without having to read the data rows. The index reads the data file again, in other words the query column must be covered by the built index.

Understanding method two: Index is a way to find rows efficiently, but general databases can also use indexes to find data in a column, so it does not have to read the entire OK. Since the index leaf nodes store data index information, the required data can be obtained by reading the index without having to read each row of data. An index that contains (or covers) data that satisfies the query results is called a covering index.
Note:
If you want to use a covering index, be sure to take out only the required columns from the select list. Cannot select*
Because if all fields are indexed together, the index file will be too large and the query performance will be reduced
Using where : Indicates that where filtering is used.
Using join buffer: The connection cache is used 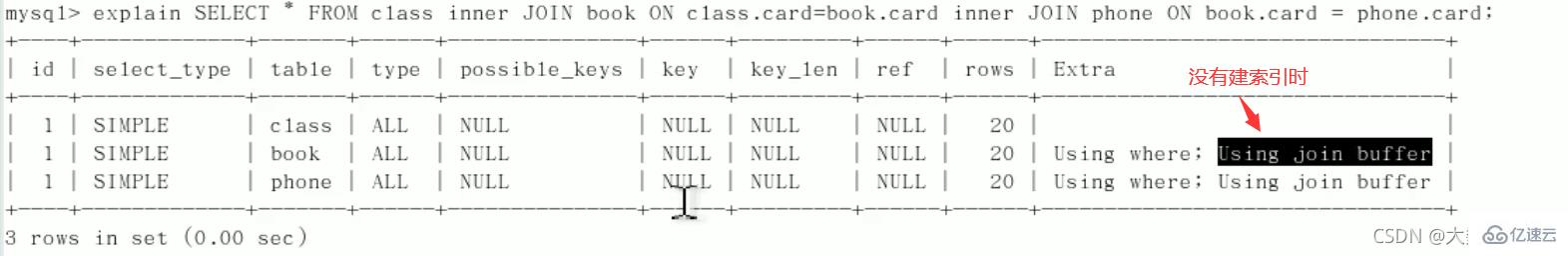
impossible where: The value of the where clause is always false, Cannot be used to get any tuple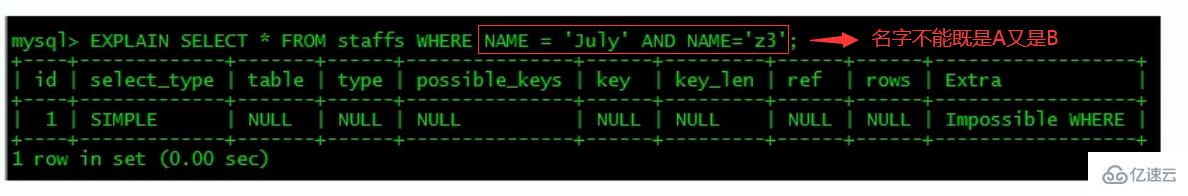
select tables optimized away
在没有GROUPBY子句的情况下,基于索引优化MIN/MAX操作,或者对于MyISAM存储引擎优化COUNT(*)操作,不必等到执行阶段再进行计算,查询执行计划生成的阶段即完成优化。
distinct
优化distinct操作,在找到第一匹配的元组后即停止找同样值的动作。
练习
写出下图的表的执行顺序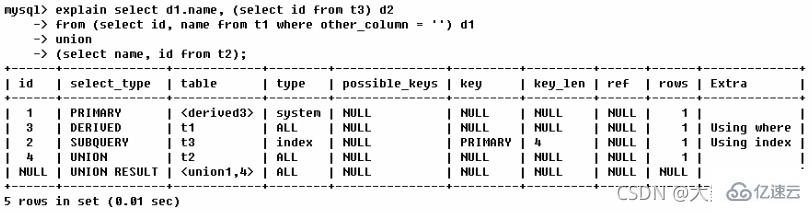
第一行(执行顺序4):id列为1,表示是union里的第一个select,select_type列的primary表示该查询为外层查询,table列被标记为,表示查询结果来自一个衍生表,其中derived3中3代表该查询衍生自第三个select查询,即id为3的select。【select d1.name… 】
第三个select在整个查询中排在第二位,其id为3。因查询包含在from中,所以为derived。【select id,namefrom t1 where other_column=’’】
第三行(执行顺序3):select列表中的子查询select_type为subquery,为整个查询中的第二个select。【select id from t3】
第四行(执行顺序1):select_type为union,说明第四个select是union里的第二个select,最先执行【select name,id from t2】
第五行(执行顺序5):代表从union的临时表中读取行的阶段,table列的
5 索引优化
5.1 索引单表优化案例
建表:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS article( id INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, author_id INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, category_id INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, views INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, comments INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, content TEXT NOT NULL ); INSERT INTO article(author_id,category_id,views,comments,title,content) VALUES (1,1,1,1,'1','1'), (2,2,2,2,'2','2'), (1,1,3,3,'3','3'); //查询 mysql> select * from article; +----+-----------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+---------+ | id | author_id | category_id | views | comments | title | content | +----+-----------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+---------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | +----+-----------+-------------+-------+----------+-------+---------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
案例
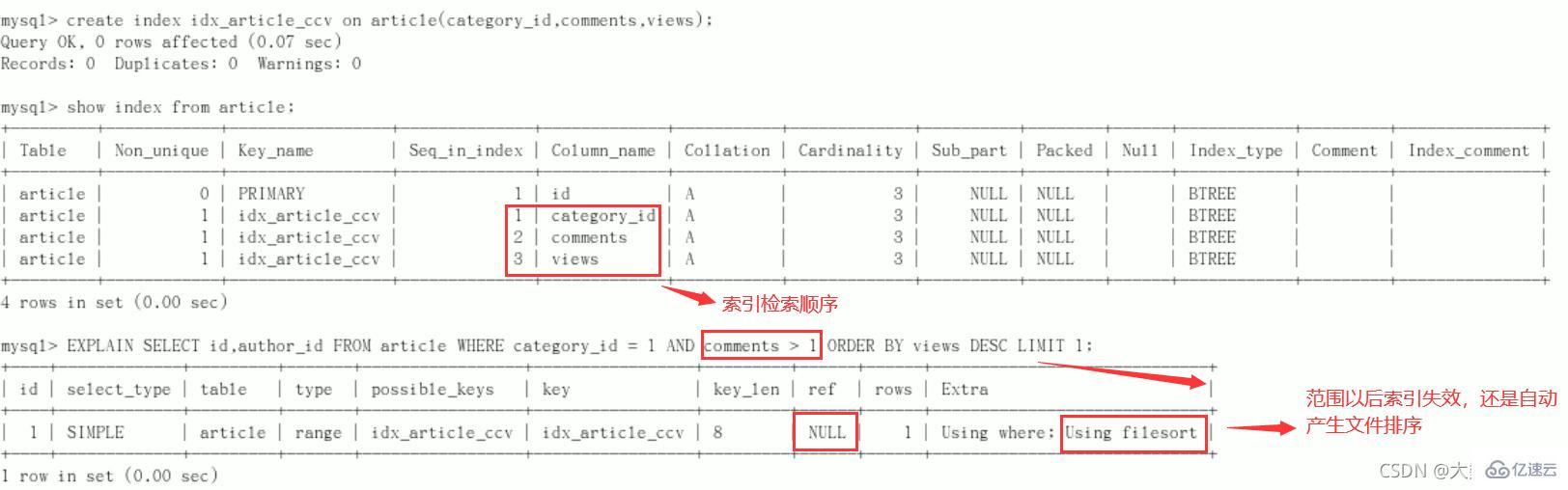
要求:查询 category_id 为 1 且 comments 大于1 的情况下,views 最多的 article_id
//功能实现 mysql> SELECT id, author_id FROM article WHERE category_id = 1 AND comments > 1 ORDER BY views DESC LIMIT 1; +----+-----------+ | id | author_id | +----+-----------+ | 3 | 1 | +----+-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) //explain分析 mysql> explain SELECT id, author_id FROM article WHERE category_id = 1 AND comments > 1 ORDER BY views DESC LIMIT 1; +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | article | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where; Using filesort | +----+-------------+---------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
结论:很显然,type是ALL,即最坏的情况。Extra里还出现了Using filesort,也是最坏的情况。优化是必须的
开始优化
新建索引(给WHERE语句后使用的字段添加索引)
创建方式:
create index idx_article_ccv on article(category_id,comments,views);ALTER TABLE 'article' ADD INDEX idx_article_ccv ( 'category_id , 'comments', 'views' );
索引用处不大,删除:DROP INDEX idx_article_ccv ON article;
结论:
type变成了range,这是可以忍受的。仍然不能接受extra中使用Using filesort。
但是我们已经建立了索引,为啥没用呢?
这是因为按照BTree索引的工作原理,先排序category_id,如果遇到相同的category_id则再排序comments,如果遇到相同的comments 则再排序views。
当comments字段在联合索引里处于中间位置时,因comments > 1条件是一个范围值(所谓range),MySQL无法利用索引再对后面的views部分进行检索,即
range类型查询字段后面的索引无效。
改进
上次创建索引相比,这次不为comments字段创建索引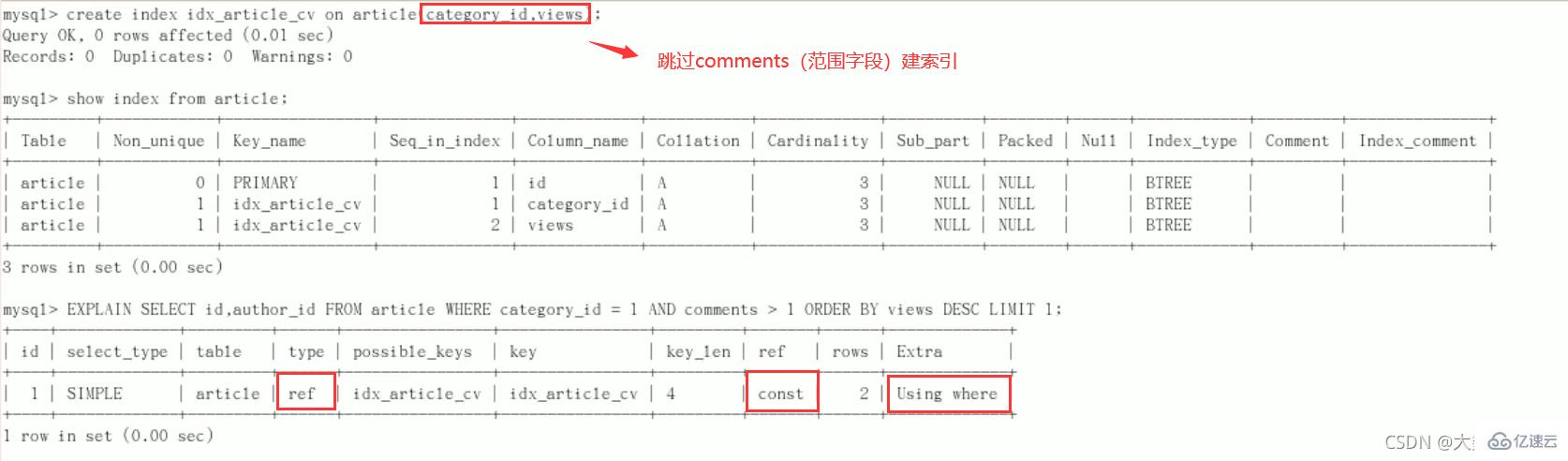
结论:type变为了ref,ref 中是 const,Extra 中的 Using filesort也消失了,结果非常理想
5.2 索引两表优化案例
建表:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS class( id INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, card INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(id) ); CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS book( bookid INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, card INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(bookid) ); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO class(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO book(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); //查询 mysql> select * from class; +----+------+ | id | card | +----+------+ | 1 | 17 | | 2 | 2 | | 3 | 18 | | 4 | 4 | | 5 | 4 | | 6 | 8 | | 7 | 9 | | 8 | 1 | | 9 | 18 | | 10 | 6 | | 11 | 15 | | 12 | 15 | | 13 | 12 | | 14 | 15 | | 15 | 18 | | 16 | 2 | | 17 | 18 | | 18 | 5 | | 19 | 7 | | 20 | 1 | | 21 | 2 | +----+------+ 21 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from book; +--------+------+ | bookid | card | +--------+------+ | 1 | 8 | | 2 | 14 | | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 16 | | 5 | 8 | | 6 | 12 | | 7 | 17 | | 8 | 8 | | 9 | 10 | | 10 | 3 | | 11 | 4 | | 12 | 12 | | 13 | 9 | | 14 | 7 | | 15 | 6 | | 16 | 8 | | 17 | 3 | | 18 | 11 | | 19 | 5 | | 20 | 11 | +--------+------+ 20 rows in set (0.00 sec)
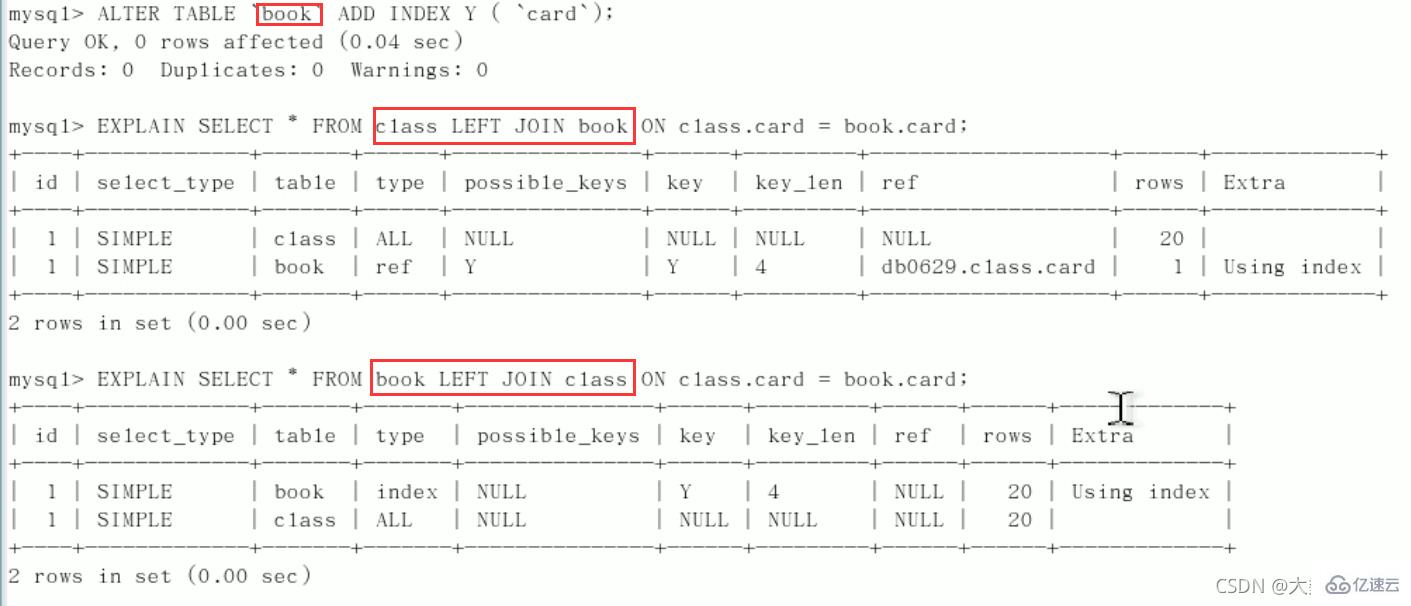
开始Explain分析:type都是all,需要优化(总有一个表来添加索引驱动)
左连接为左表加索引

删除索引:drop index y on class;
左连接为右表添加索引

删除索引:drop index Y on book;
案例:如果别人建的索引位置不对,只需要自己查询时调整左右表的顺序即可

结论:
第二行的type变为了ref,rows也变少了,优化比较明显。这是由左连接特性决定的。LEFT JOIN条件用于确定如何从右表搜索行,左边一定都有,
所以右边是我们的关键点,一定需要在右表建立索引(小表驱动大表)。左连接,右表加索引同理:右连接,左表加索引
5.3 索引三表优化案例
建表:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS phone( phoneid INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, card INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(phoneid) )ENGINE=INNODB; INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); INSERT INTO phone(card) VALUES(FLOOR(1+(RAND()*20))); //查询 mysql> select * from phone; +---------+------+ | phoneid | card | +---------+------+ | 1 | 10 | | 2 | 13 | | 3 | 17 | | 4 | 5 | | 5 | 12 | | 6 | 7 | | 7 | 15 | | 8 | 17 | | 9 | 17 | | 10 | 14 | | 11 | 19 | | 12 | 13 | | 13 | 5 | | 14 | 8 | | 15 | 2 | | 16 | 8 | | 17 | 11 | | 18 | 14 | | 19 | 13 | | 20 | 5 | +---------+------+ 20 rows in set (0.00 sec)
用上一节两个表,删除他们的索引:
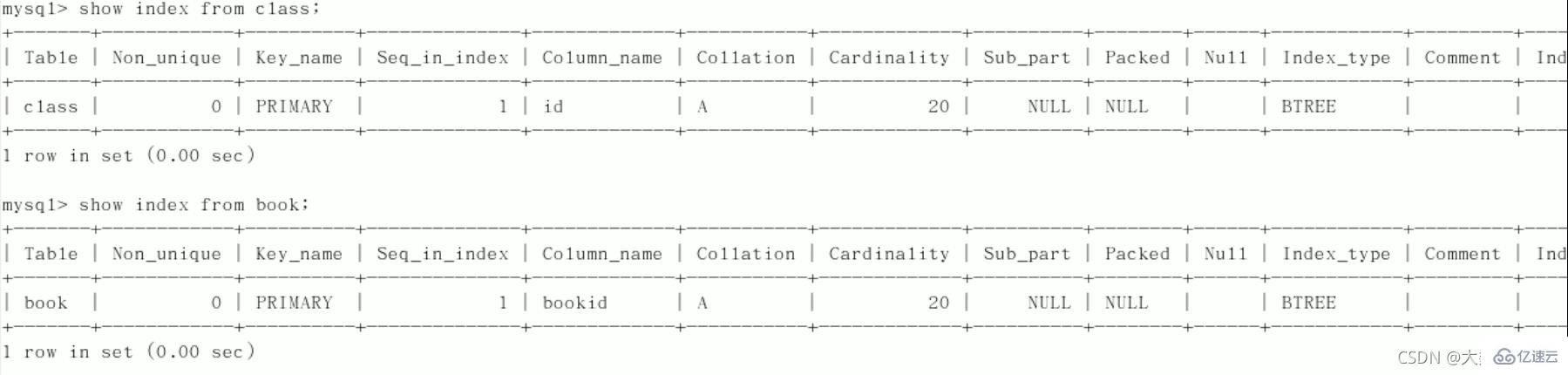
三表查询语句应为:SELECT * FROM class LEFT JOIN book ON class.card = book.card LEFT JOIN phone ON book.card = phone.card;
创建索引:
-
应该为第一个LFET JOIN 的右表 book 建索引
alter table `book` add index Y(`card`);
-
应该为第二个LFET JOIN 的右表 phone 建索引
alter table `phone` add index z(`card`);
Explain分析: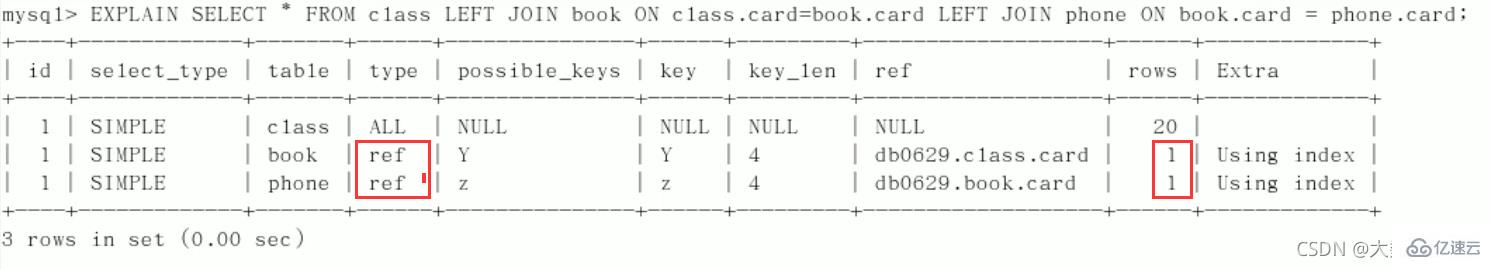
后2行的 type 都是ref且总 rows优化很好,效果不错。因此索引最好设置在需要经常查询的字段中
结论:
Join语句的优化
尽可能减少Join语句中的NestedLoop的循环总次数:“
永远用小结果集驱动大的结果集(比如:书的类型表驱动书的名称表)”。优先优化NestedLoop的内层循环,保证Join语句中被驱动表上Join条件字段已经被索引。
当无法保证被驱动表的Join条件字段被索引且内存资源充足的前提下,不要太吝惜JoinBuffer的设置
5.4 索引失效
建表:
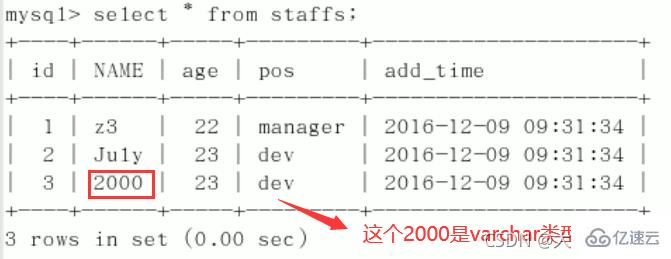
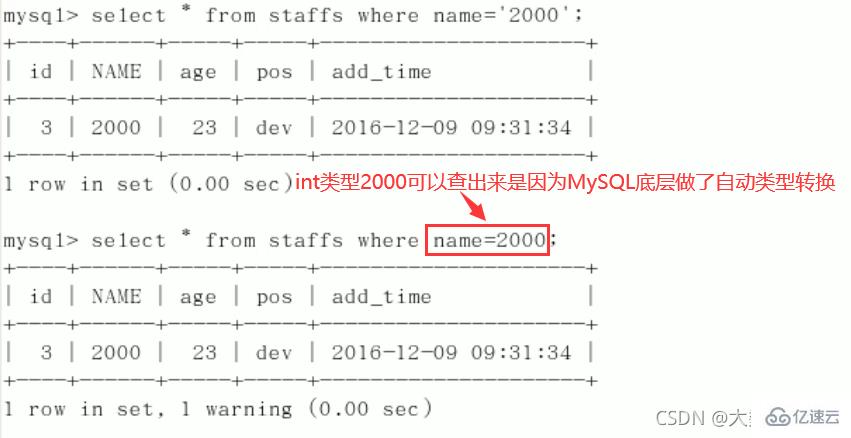
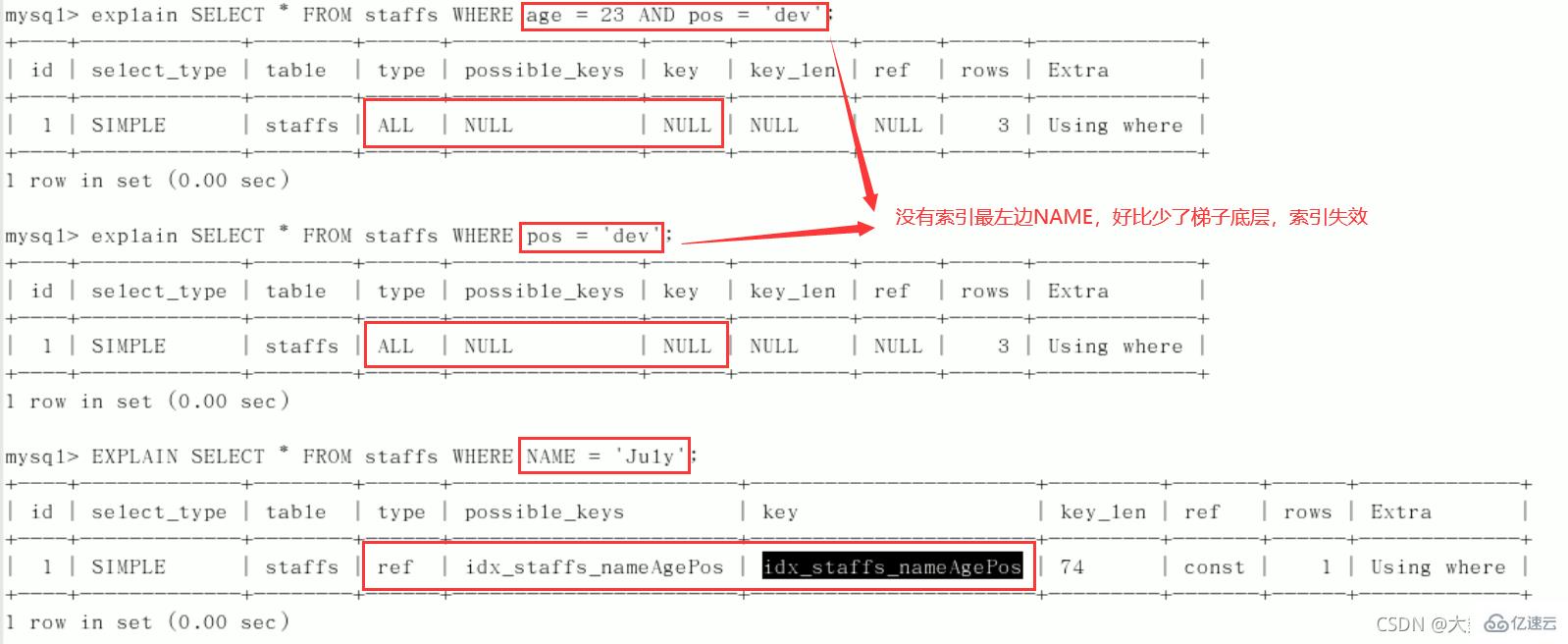
CREATE TABLE staffs( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` VARCHAR(24) NOT NULL DEFAULT'' COMMENT'姓名', `age` INT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT'年龄', `pos` VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT'' COMMENT'职位', `add_time` TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT'入职时间' )CHARSET utf8 COMMENT'员工记录表'; INSERT INTO staffs(`name`,`age`,`pos`,`add_time`) VALUES('z3',22,'manager',NOW()); INSERT INTO staffs(`name`,`age`,`pos`,`add_time`) VALUES('July',23,'dev',NOW()); INSERT INTO staffs(`name`,`age`,`pos`,`add_time`) VALUES('2000',23,'dev',NOW()); ALTER TABLE staffs ADD INDEX index_staffs_nameAgePos(`name`,`age`,`pos`);
索引失效案例:
1、全值匹配我最爱

2、
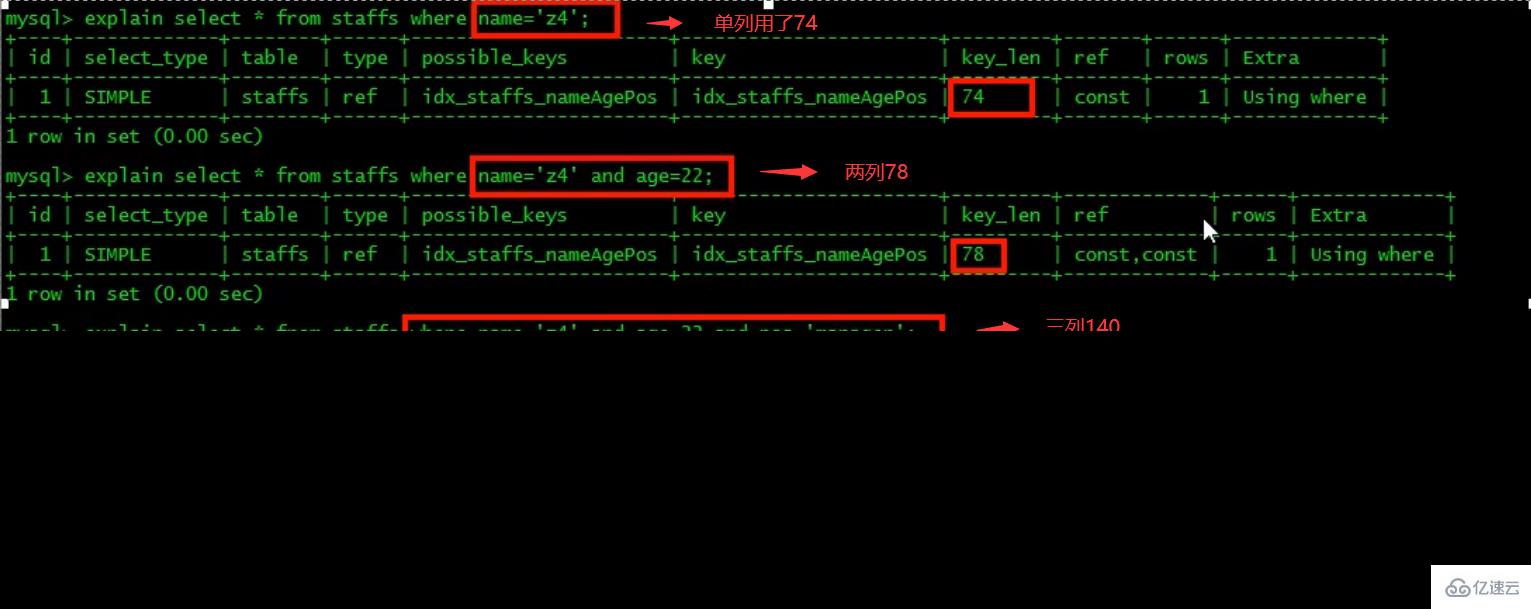
最佳左前缀法则(重要!):如果索引了多列,要遵守最左前缀法则。指的是查询从索引的最左前列开始并且不跳过复合索引中间列。 中间列不能断:
中间列不能断:
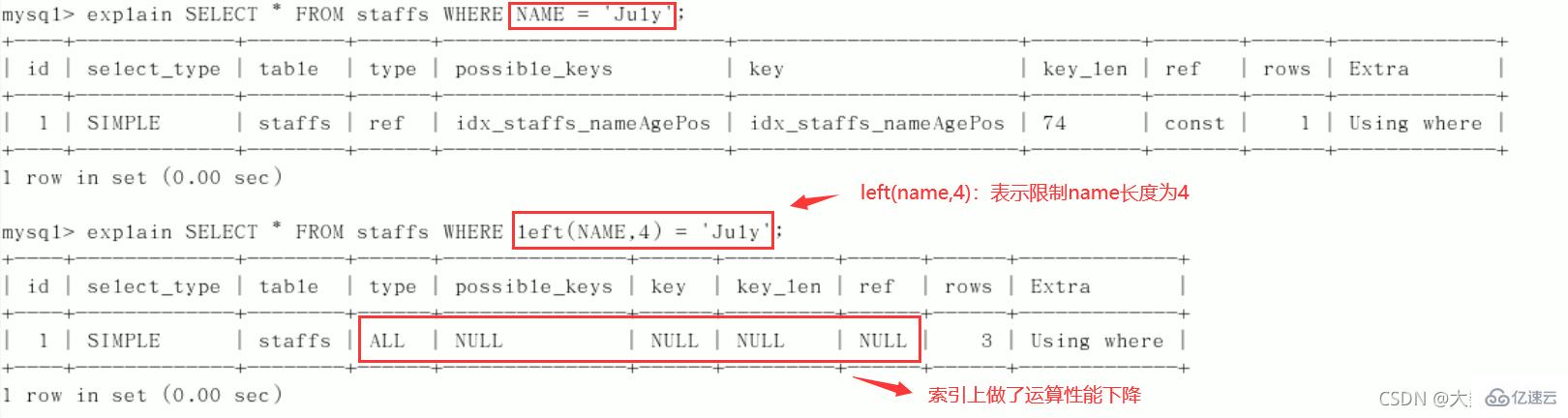
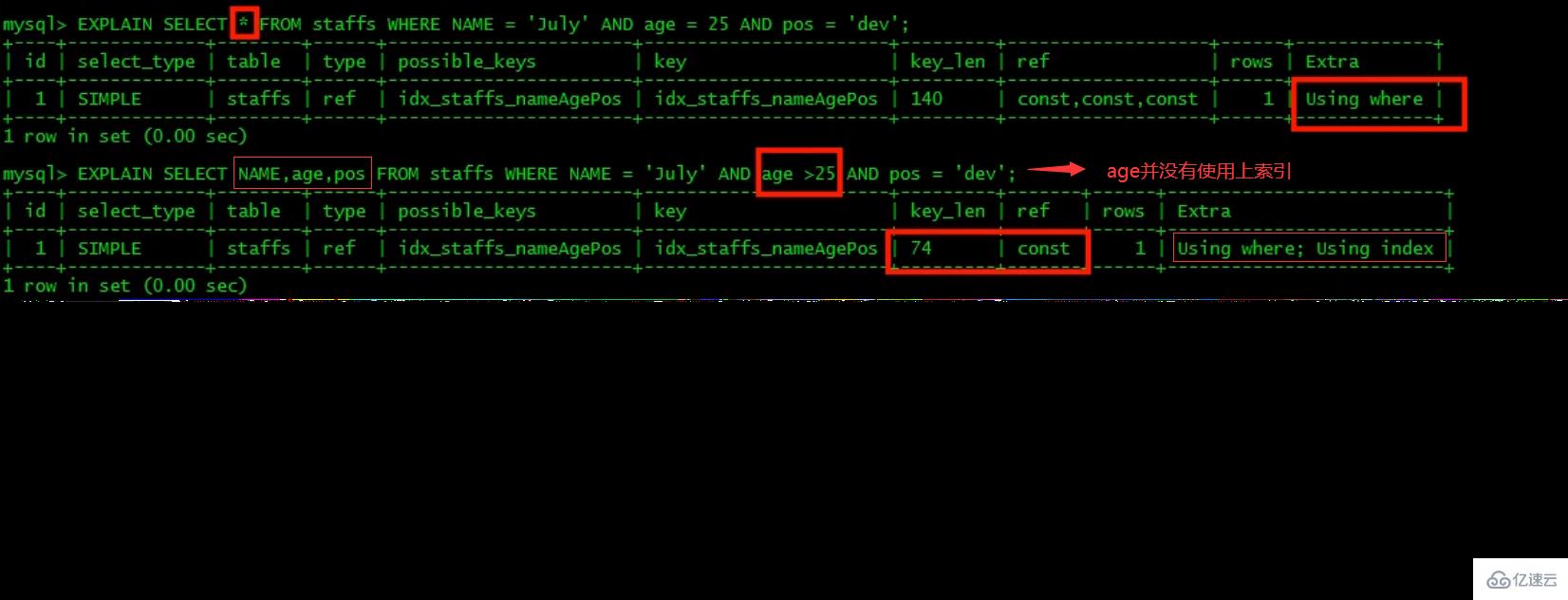
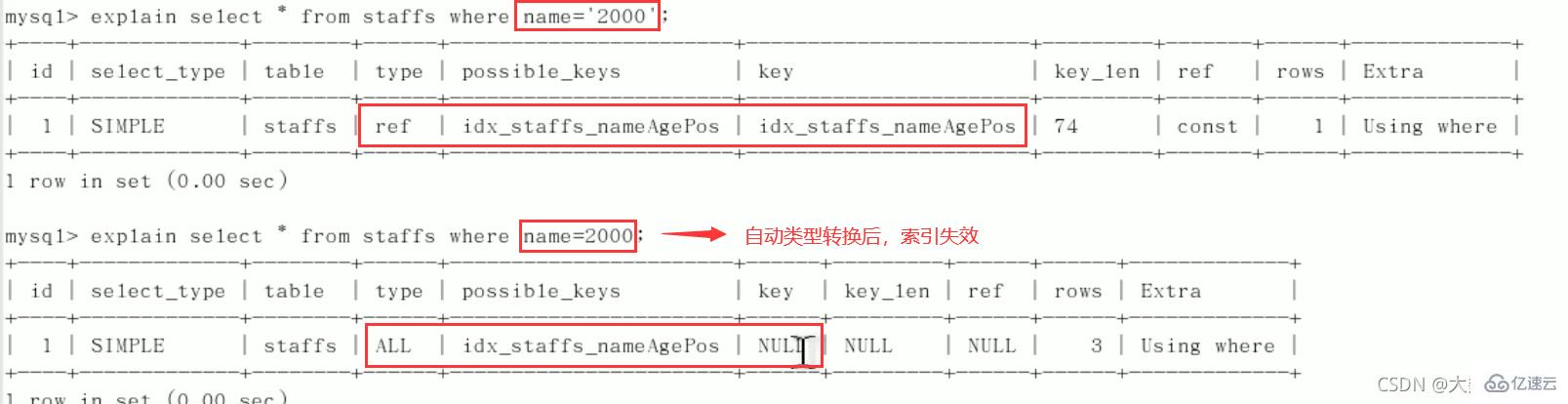
3、不在索引列上做任何操作(计算、函数、(自动or手动)类型转换),会导致索引失效而转向全表扫描。

4、存储引擎不能使用索引中范围条件右边的列(范围之后全失效,范围列并不是做的查询而是排序)。

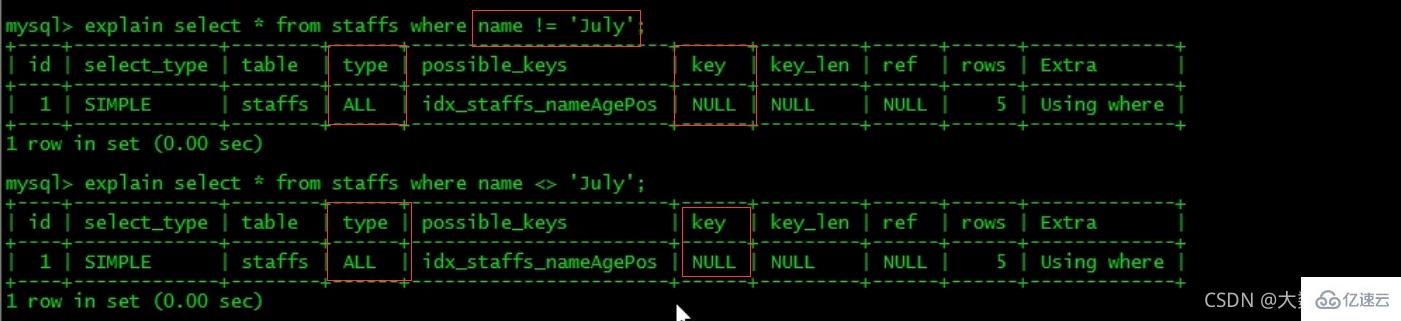
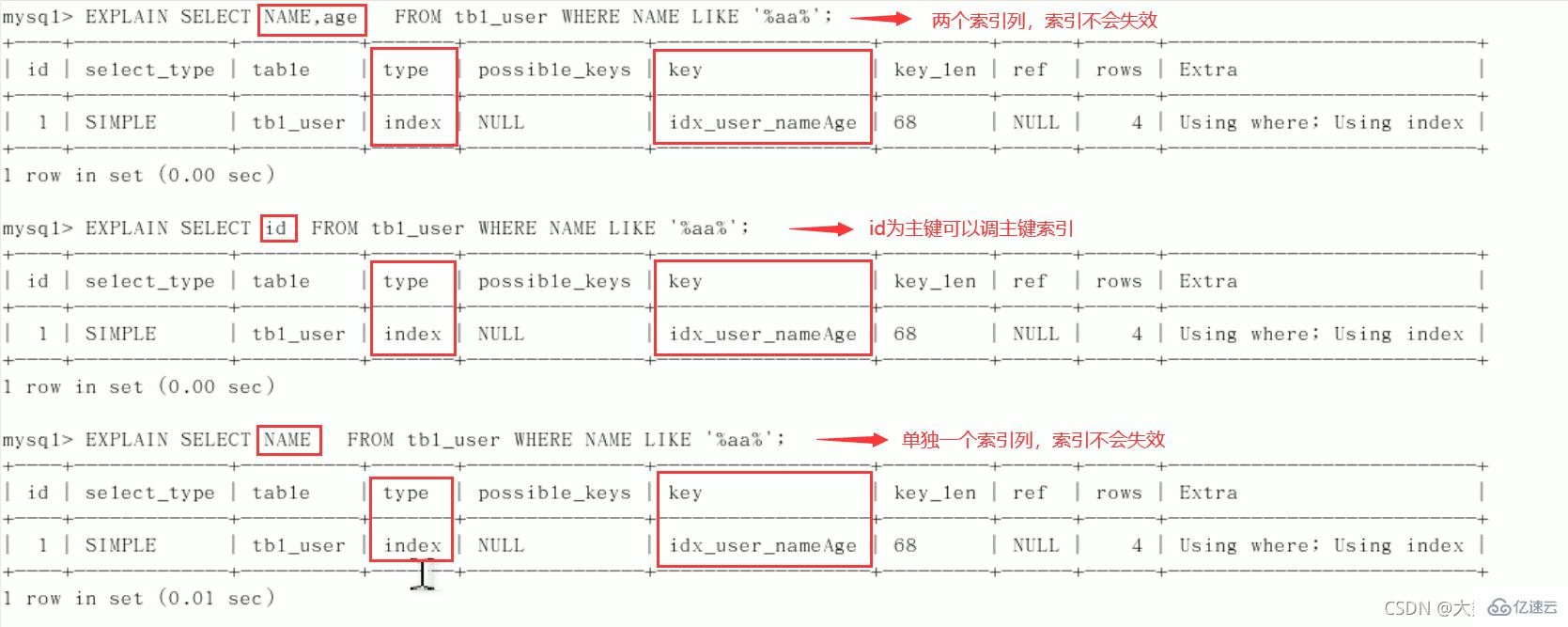
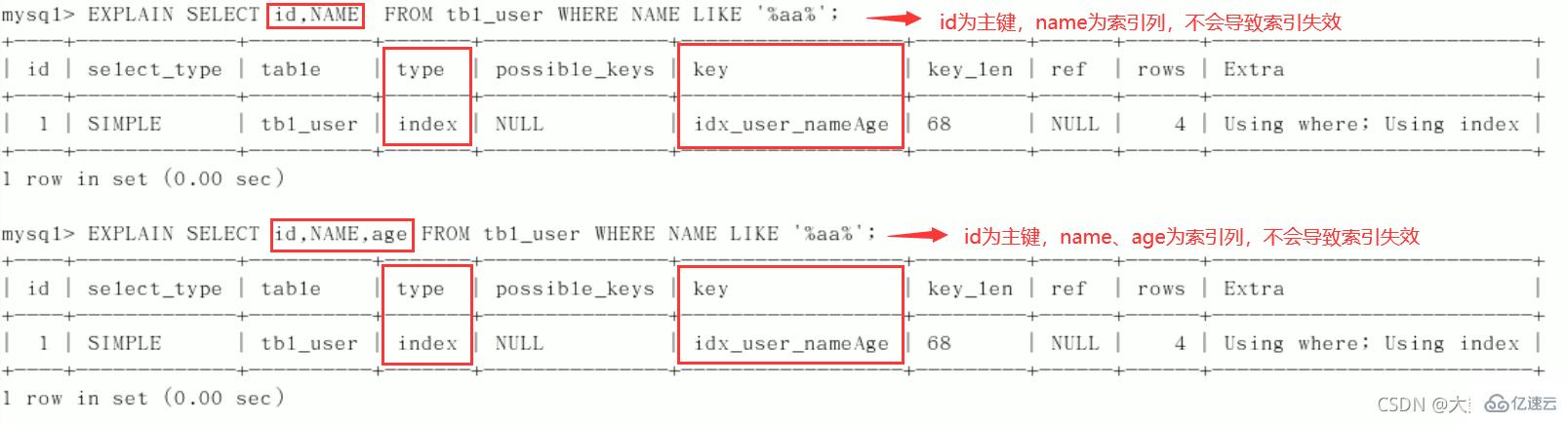
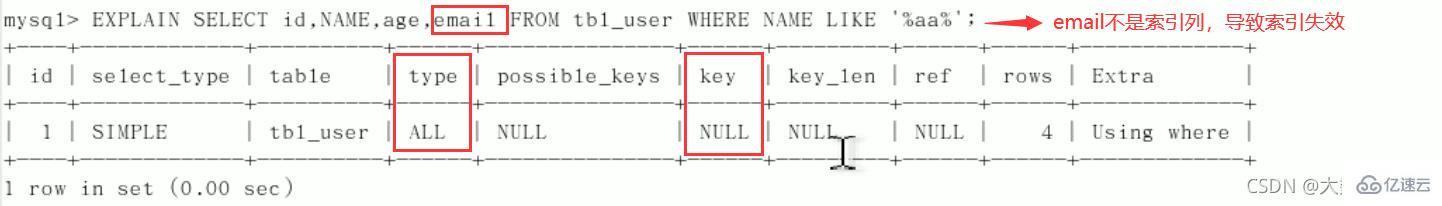
5、尽量使用覆盖索引(只访问索引的查询(索引列和查询列一致)),减少select *。

6、mysql在使用不等于(!=或者)的时候无法使用索引会导致全表扫描。

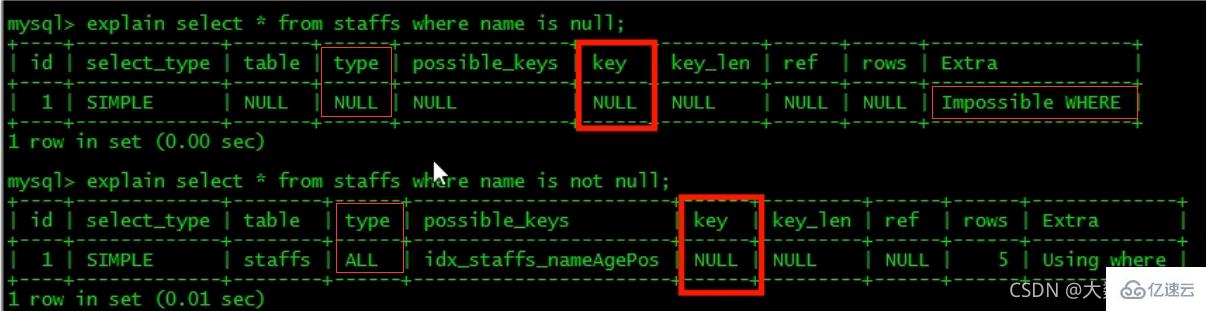
7、is null, is not null 也无法使用索引。

-
8、like以通配符开头(’%abc…’),mysql索引失效会变成全表扫描的操作(%写在最右边索引不会失效,或覆盖索引)。

问题:解决like '%字符串%'时索引不被使用的方法? 采用覆盖索引的方法!
建表:CREATE TABLE `tbl_user`( `id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL, `age`INT(11) DEFAULT NULL, `email` VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(`id`) )ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO tbl_user(`name`,`age`,`email`)VALUES('1aa1',21,'a@163.com'); INSERT INTO tbl_user(`name`,`age`,`email`)VALUES('2bb2',23,'b@163.com'); INSERT INTO tbl_user(`name`,`age`,`email`)VALUES('3cc3',24,'c@163.com'); INSERT INTO tbl_user(`name`,`age`,`email`)VALUES('4dd4',26,'d@163.com'); //查询 mysql> select * from tbl_user; +----+------+------+-----------+ | id | name | age | email | +----+------+------+-----------+ | 1 | 1aa1 | 21 | a@163.com | | 2 | 2bb2 | 23 | b@163.com | | 3 | 3cc3 | 24 | c@163.com | | 4 | 4dd4 | 26 | d@163.com | +----+------+------+-----------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
创建索引:
CREATE INDEX idx_user_nameAge ON tbl_user(NAME,age);
索引成功使用:


索引失效:

总结:%写在最右边,如果非要写在最左边,就使用覆盖索引 9、字符串不加单引号索引失效。


Explain分析:
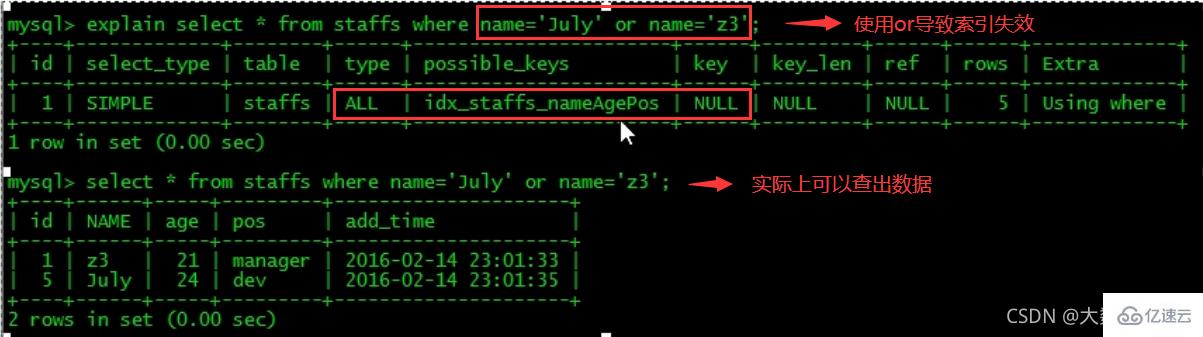
10、少用or,用它来连接时会索引失效

5.5 索引面试题分析
建表:
create table test03(
id int primary key not null auto_increment,
c1 char(10),
c2 char(10),
c3 char(10),
c4 char(10),
c5 char(10)
);
insert into test03(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values ('a1','a2','a3','a4','a5');
insert into test03(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values ('b1','b2','b3','b4','b5');
insert into test03(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values ('c1','c2','c3','c4','c5');
insert into test03(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values ('d1','d2','d3','d4','d5');
insert into test03(c1,c2,c3,c4,c5) values ('e1','e2','e3','e4','e5');
//查看表结构
mysql> select * from test03;
+----+------+------+------+------+------+
| id | c1 | c2 | c3 | c4 | c5 |
+----+------+------+------+------+------+
| 1 | a1 | a2 | a3 | a4 | a5 |
| 2 | b1 | b2 | b3 | b4 | b5 |
| 3 | c1 | c2 | c3 | c4 | c5 |
| 4 | d1 | d2 | d3 | d4 | d5 |
| 5 | e1 | e2 | e3 | e4 | e5 |
+----+------+------+------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)建索引:
create index idx_test03_c1234 on test03(c1,c2,c3,c4); //查看索引 mysql> show index from test03; +--------+------------+------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | +--------+------------+------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | test03 | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 2 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | | test03 | 1 | idx_test03_c1234 | 1 | c1 | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | | test03 | 1 | idx_test03_c1234 | 2 | c2 | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | | test03 | 1 | idx_test03_c1234 | 3 | c3 | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | | test03 | 1 | idx_test03_c1234 | 4 | c4 | A | 5 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | +--------+------------+------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
1)逐一增加列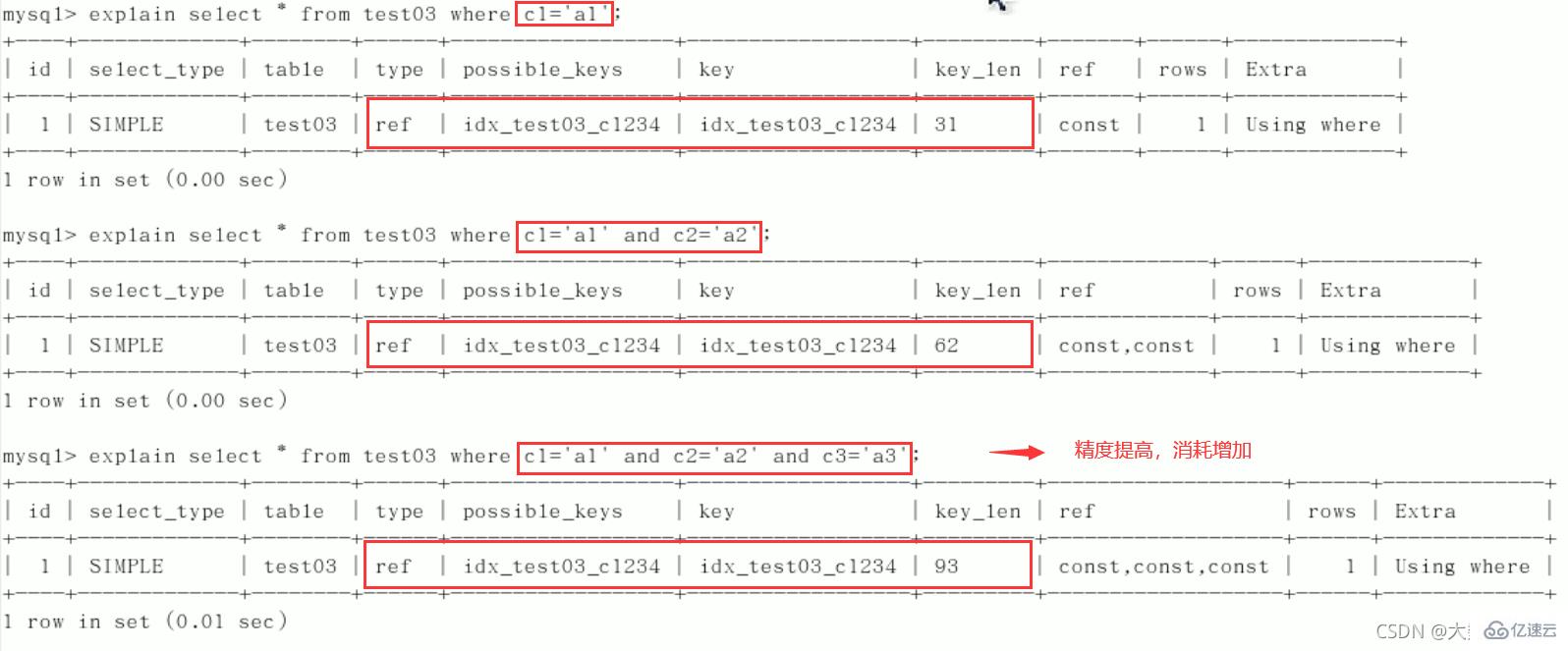
2)交换条件顺序不影响索引,但最好按照建索引顺序来写SQL
3) 限定范围

4)order by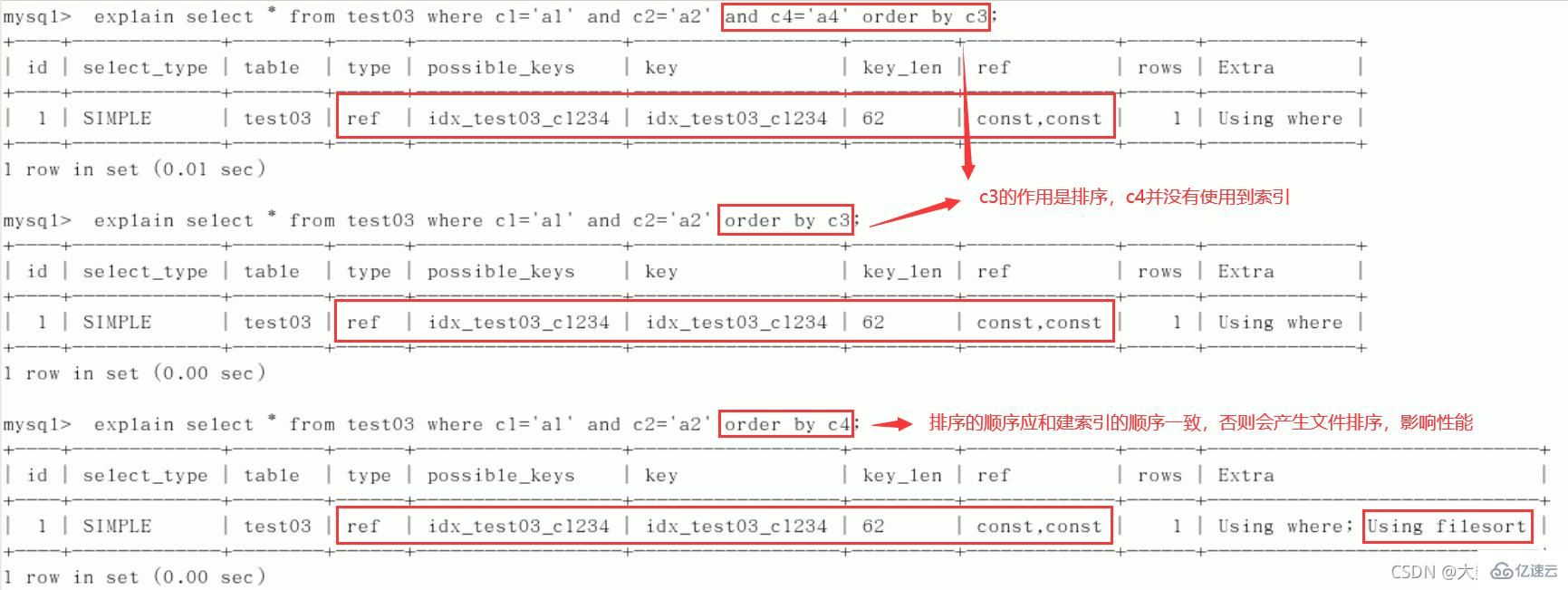
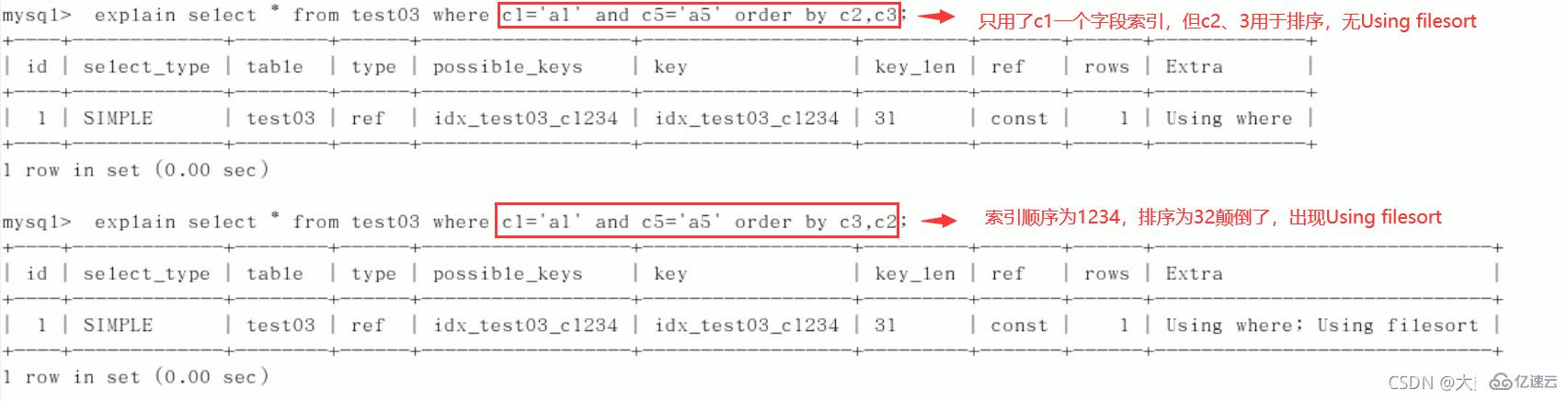
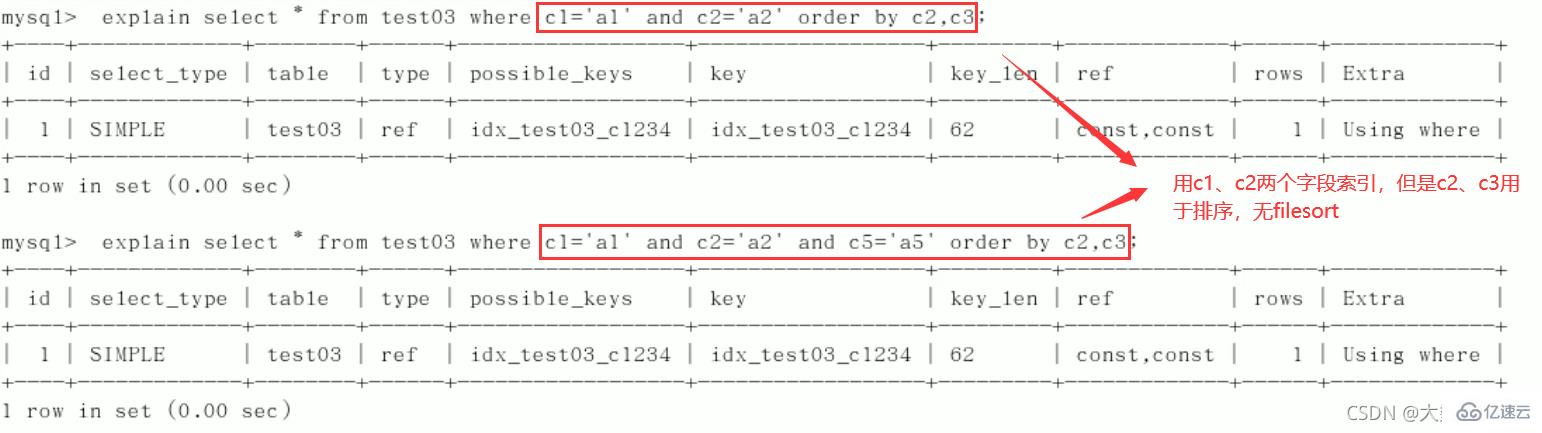
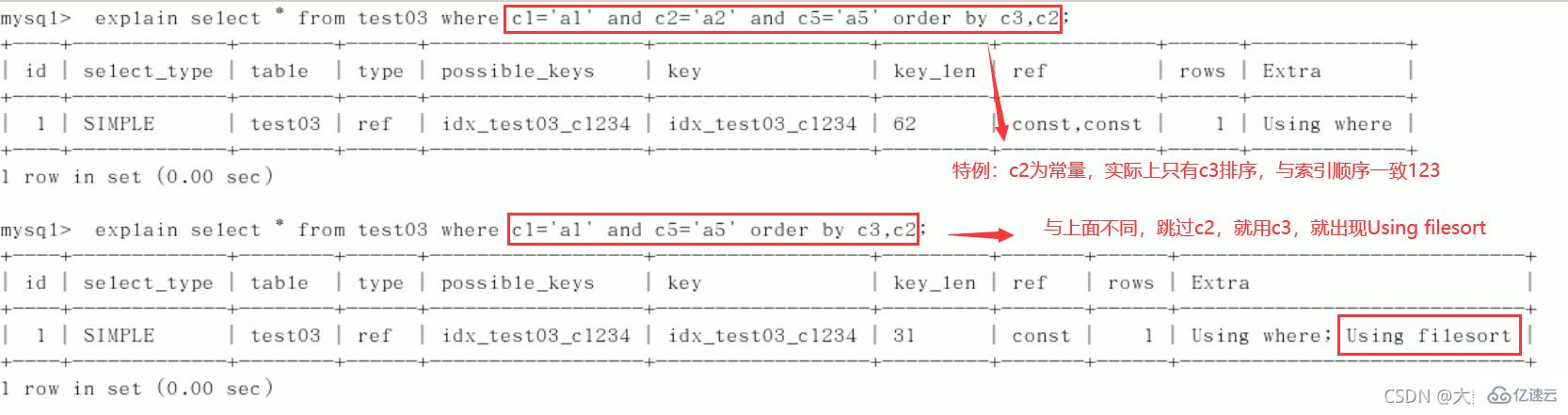
5)group by
定值、范围还是排序,一般order by是给个范围
group by基本上都需要进行排序,会有临时表产生
建议:
对于单值索引,尽量选择针对当前query过滤性更好的索引。
在选择组合索引的时候,当前Query中过滤性最好的字段在索引字段顺序中,位置越靠左越好。
在选择组合索引的时候,尽量选择可以能够包含当前query中的where字句中更多字段的索引。
尽可能通过分析统计信息和调整query的写法来达到选择合适索引的目的。
5.6 总结


优化总结口诀
全值匹配我最爱, 最左前缀要遵守;
带头大哥不能死, 中间兄弟不能断;
索引列上少计算, 范围之后全失效;
LIKE 百分写最右, 覆盖索引不写 *;
不等空值还有OR, 索引影响要注意;
VAR 引号不可丢, SQL 优化有诀窍。
6 查询截取分析
6.1 小表驱动大表

EXISTS [ɪɡˈzɪsts]语法:SELECT ...FROM table WHERE EXISTS (subquery)
该语法可以理解为:将主查询的数据,放到子查询中做条件验证,根据验证结果(TRUE或FALSE)来决定主查询的数据结果是否得以保留
提示:
EXSTS(subquey) 只返回TRUE或FALSE,因此子查询中的SELECT * 也可以是 SELECT 1 或select ‘X’,官方说法是实际执行时会忽略SELECT清单,因此没有区别。
EXISTS子查询的实际执行过程可能经过了优化而不是我们理解上的逐条对比,如果担忧效率问题,可进行实际检验以确定是否有效率问题。
具体问题具体分析,对于存在子查询,通常可以使用条件表达式、其他子查询或JOIN来替代,最优的使用方式需要根据具体情况进行评估
in和exists用法:
6.2 Order by 关键字排序优化
1、ORDER BY之后子句,尽量使用Index方式排序,避免使用FileSort方式排序
建表:
create table tblA(
#id int primary key not null auto_increment,
age int,
birth timestamp not null
);
insert into tblA(age, birth) values(22, now());
insert into tblA(age, birth) values(23, now());
insert into tblA(age, birth) values(24, now());
create index idx_A_ageBirth on tblA(age, birth);
//查询
mysql> select * from tblA;
+------+---------------------+
| age | birth |
+------+---------------------+
| 22 | 2021-04-04 19:31:45 |
| 23 | 2021-04-04 19:31:45 |
| 24 | 2021-04-04 19:31:45 |
+------+---------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show index from tblA;
+-------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment |
+-------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
| tbla | 1 | idx_A_ageBirth | 1 | age | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | |
| tbla | 1 | idx_A_ageBirth | 2 | birth | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | |
+-------+------------+----------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)关注点:是order by之后会不会产生Using filesort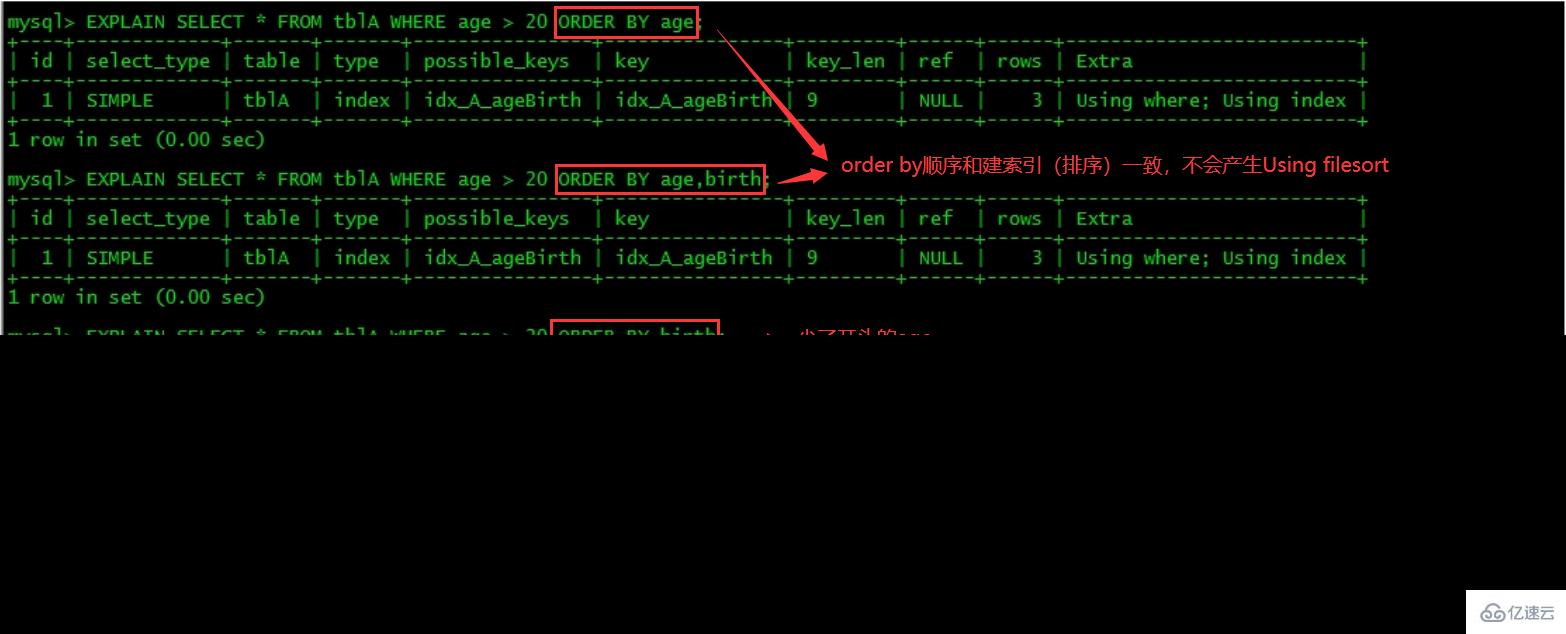
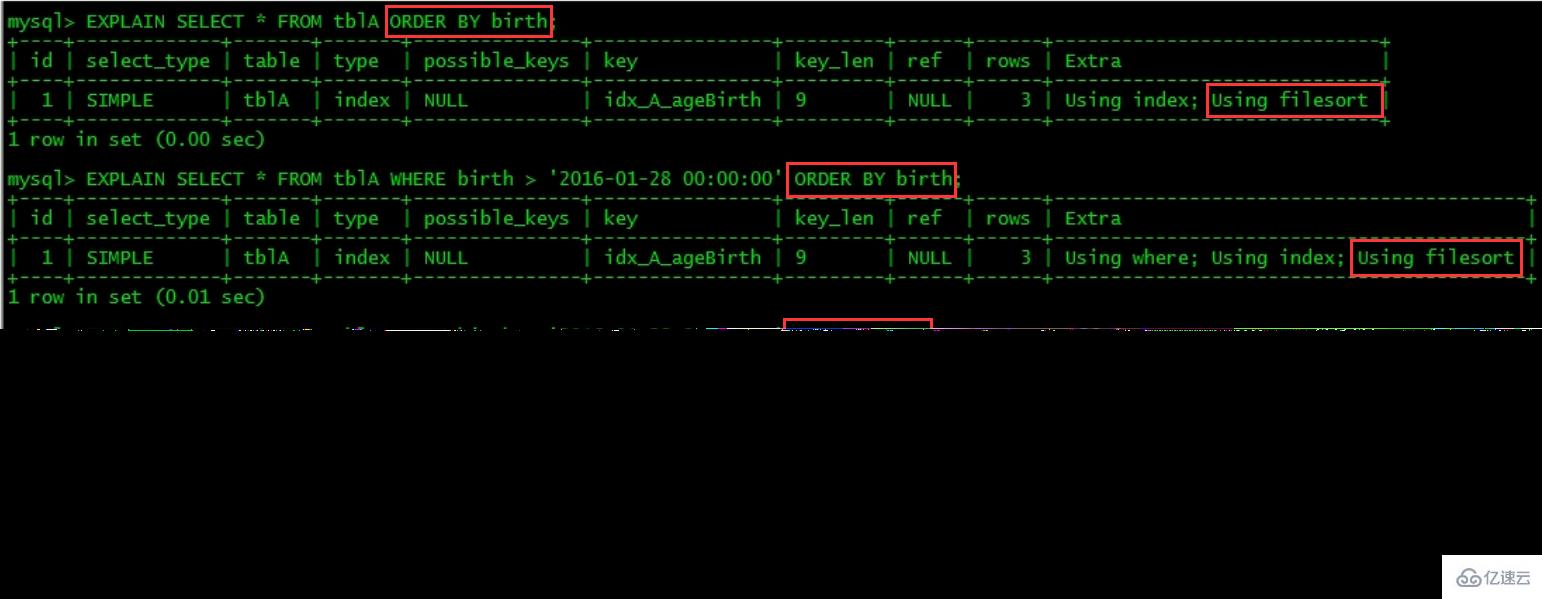
MySQL支持二种方式的排序,FileSort和lIndex,Index效率高,它指MySQL扫描索引本身完成排序。FileSort方式效率较低。
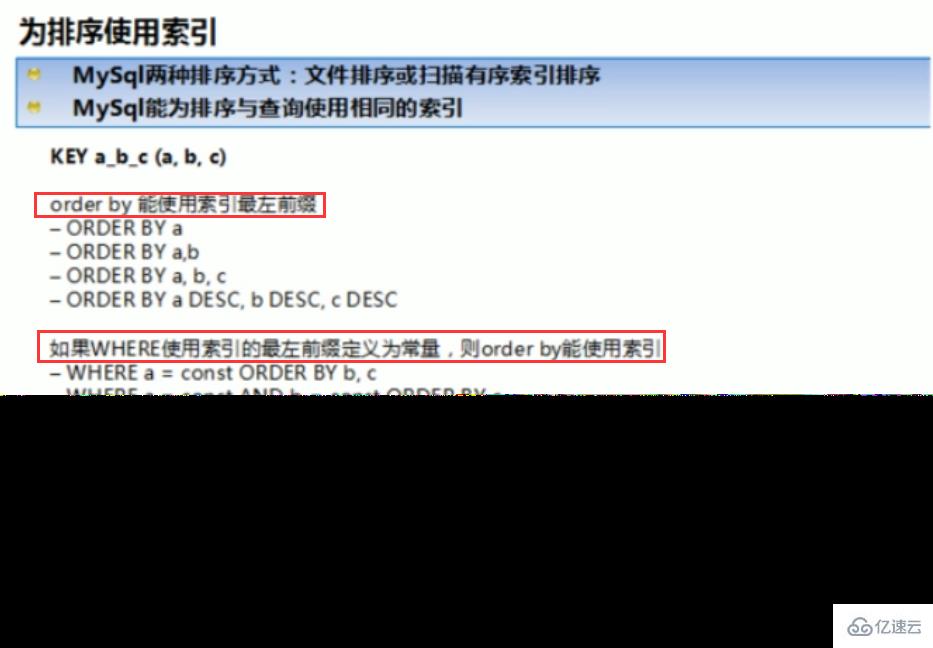
ORDER BY满足两情况,会使用Index方式排序:
ORDER BY语句使用索引最左前列。
使用where子句与Order BY子句条件列组合满足索引最左前列。
2、尽可能在索引上完成排序操作,遵照建索引的最佳左前缀
3、如果不在索引列上,mysql的filesort有两种算法(自动启动)
-
双路排序
MySQL4.1之前是使用双路排序,字面意思就是两次扫描磁盘,最终得到数据,读取行指针和OrderBy列,对他们进行排序,然后扫描已经排序好的列表,按照列表中的值重新从列表中读对应的数据输出。
从磁盘取排序字段,在buffer进行排序,再从磁盘取其他字段。
取一批数据,要对磁盘进行了两次扫描,众所周知,I\O是很耗时的,所以在mysql4.1之后,出现了第二种改进的算法,就是单路排序
-
单路排序
从磁盘读取查询需要的所有列,按照order by列在buffer对它们进行排序,然后扫描排序压的列表进行输出,它的效率更快一些,避免了第二次读取数据。尽管它将随机IO转换为顺序IO,但会占用更多的空间,因为它会将每一行都存储在内存中
-
结论及引申出的问题
由于单路是后出的,总体而言好过双路
但是用单路有问题,在sort_buffer中,方法B比方法A要多占用很多空间,因为方法B是把所有字段都取出,所以有可能取出的数据的总大小超出了sort_buffer的容量,导致每次只能取sort_buffer容量大小的数据,进行排序(创建tmp文件,多路合并),排完再取取
sort_buffer容量大小,再排……从而多次I/O。本来想省一次I/O操作,反而导致了大量的I/O操作,反而得不偿失
4、优化策略
增大sort_buffer_size参数的设置
增大max_length_for_sort_data参数的设置
Why?

5、小总结:
6.3 Group by 优化
group by实质是先排序后进行分组,遵照索引建的最佳左前缀。
当无法使用索引列,增大max_length_for_sort_data参数的设置 + 增大sort_buffer_size参数的设置。
where高于having,能写在where限定的条件就不要去having限定了
6.4 慢查询日志(重点)
介绍:
MySQL的慢查询日志是MySQL提供的一种日志记录,它用来记录在MySQL中响应时间超过阀值的语句,具体指运行时间超过long_query_time值的SQL,则会被记录到慢查询日志中。
如果SQL的运行时间超过long_query_time值,那么它会被记录到慢查询日志中。long_query_time的默认值为10,意思是运行10秒以上的语句。
由他来查看哪些SQL超出了我们的最大忍耐时间值,比如一条sql执行超过5秒钟,我们就算慢SQL,希望能收集超过5秒的sql,结合之前explain进行全面分析
操作说明:
默认情况下,MySQL数据库没有开启慢查询日速,需要我们手动来设置这个参数。
除非需要进行性能调优,一般不建议启用该参数,因为启用慢查询日志可能会带来一定的性能影响。慢查询日志支持将日志记录写入文件。
查看是否开启及如何开启:
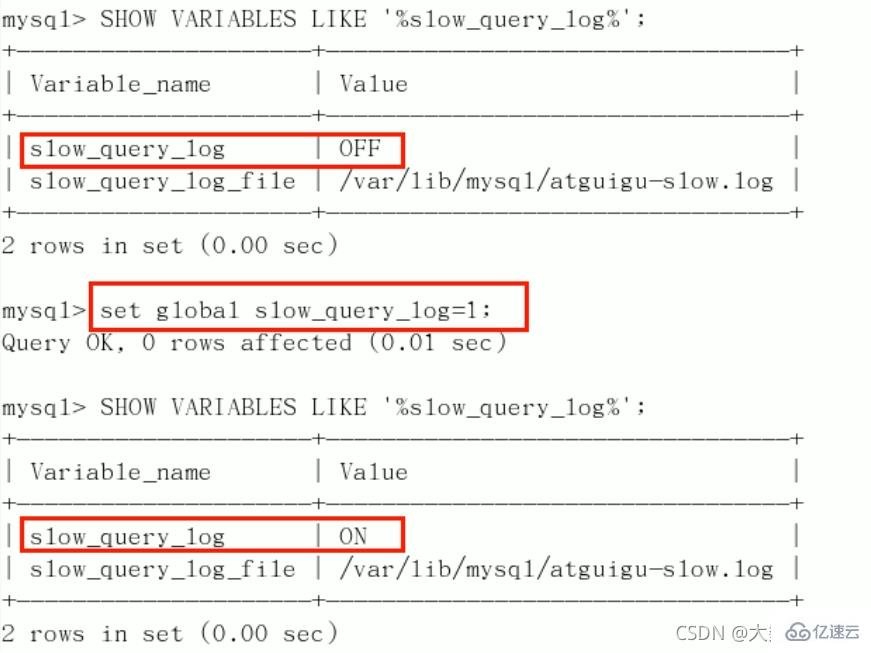
默认:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%slow_query_log%';[ˈveəriəbls]开启:
set global slow_query_log=1;,只对当前数据库生效,如果MySQL重启后则会失效
如果要永久生效,就必须修改配置文件my.cnf(其它系统变量也是如此)
修改my.cnf文件,[mysqld] 下增加或修改参数slow_query_log和slow_query_log_file后,然后重启MySQL服务器。也即将如下两行配置进my.cnf文件
slow_query_log =1slow_query_log_file=/var/lib/mysqatguigu-slow.log
关于慢查询的参数slow_query_log_file,它指定慢查询日志文件的存放路径,系统默认会给一个缺省的文件host_name-slow.log(如果没有指定参数slow_query_log_file的话)
开启了慢查询日志后,什么样的SQL才会记录到慢查询日志里面呢?
这个是由参数long_query_time控制,默认情况下long_query_time的值为10秒,命令:SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'long_query_time%';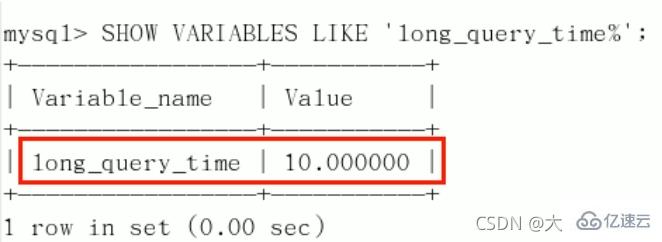
可以使用命令修改,也可以在my.cnf参数里面修改。
假如运行时间正好等于long_query_time的情况,并不会被记录下来。也就是说,在mysql源码里是判断大于long_query_time,而非大于等于。
命名修改慢SQL阈值时间:set global long_query_time=3; [ˈɡləʊbl]
看不到修改情况的话,重开连接,或者换一个语句:show global variables like 'long_query_time';
记录慢SQL并后续分析:
假设我们成功设置慢SQL阈值时间为3秒(set global long_query_time=3;)。
模拟超时SQL:select sleep(4);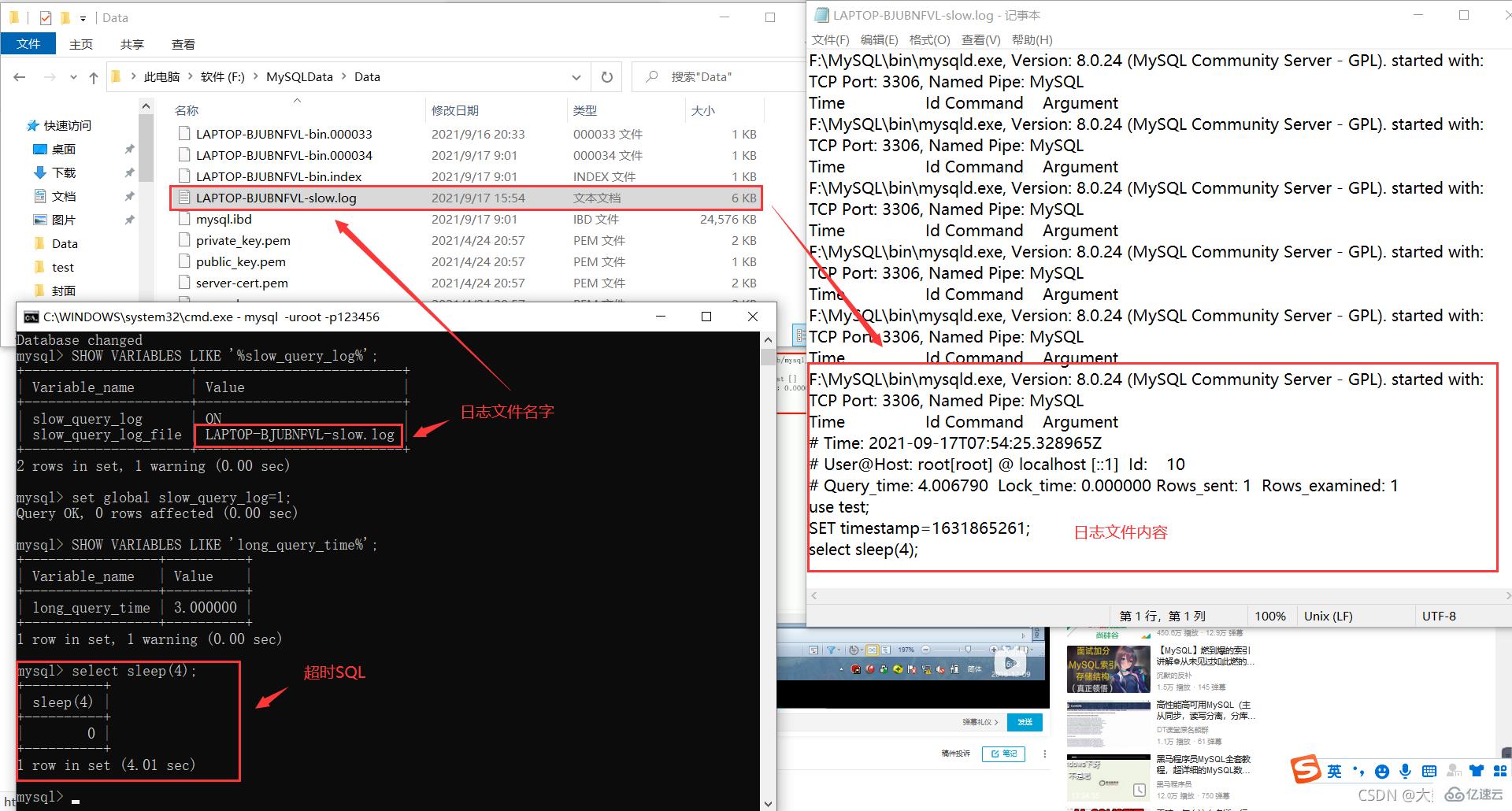
查询当前系统中有多少条慢查询记录:show global status like '%Slow_queries%'; [ˈsteɪtəs]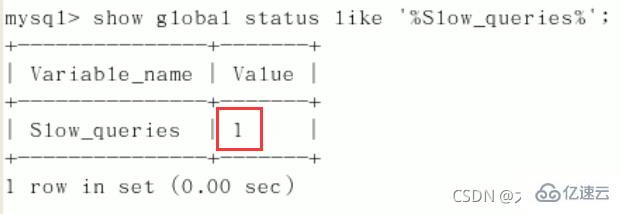
在配置文件中设置慢SQL阈值时间(永久生效):
#[mysqld]下配置:slow_query_log=1;slow_query_log_file=/var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.log long_query_time=3;log_output=FILE;
日志分析工具mysqldumpslow
在生产环境中,如果要手工分析日志,查找、分析SQL,显然是个体力活,MySQL提供了日志分析工具mysqldumpslow。
查看mysqldumpslow的帮助信息,mysqldumpslow --help。
常用mysqldumpslow帮助信息:
s:是表示按照何种方式排序
c:访问次数
l:锁定时间
r:返回记录
t:查询时间
al:平均锁定时间
ar:平均返回记录数
at:平均查询时间
t:即为返回前面多少条的数据
g:后边搭配一个正则匹配模式,大小写不敏感的
工作常用参考:
得到返回记录集最多的10个SQL:
mysqldumpslow -s r -t 10 /var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.log得到访问次数最多的10个SQL:
mysqldumpslow -s c -t 10 /var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.log得到按照时间排序的前10条里面含有左连接的查询语句:
mysqldumpslow -s t -t 10 -g "left join" /var/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.log另外建议在使用这些命令时结合│和more 使用,否则有可能出现爆屏情况:`mysqldumpslow -s r-t 10 /ar/lib/mysql/atguigu-slow.log | more
6.5 批量插入数据脚本
1、建表:
create database bigData;use bigData;//部门表CREATE TABLE dept(
id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
deptno MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
dname VARCHAR(20)NOT NULL DEFAULT "",
loc VARCHAR(13) NOT NULL DEFAULT "")ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;//员工表CREATE TABLE emp(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
empno mediumint unsigned not null default 0, //编号
ename varchar(20) not null default "", //名字
job varchar(9) not null default "", //工作
mgr mediumint unsigned not null default 0, //上级编号
hiredate date not null, //入职时间
sal decimal(7,2) not null, //薪水
comm decimal(7,2) not null, //红利
deptno mediumint unsigned not null default 0 //部门编号)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;2、设置参数log_bin_trust_function_creators
创建函数,假如报错:This function has none of DETERMINISTIC…
由于开启过慢查询日志,因为我们开启了bin-log,我们就必须为我们的function指定一个参数
show variables like 'log_bin_trust_function_creators';set global log_bin_trust_function_creators=1;
这样添加了参数以后,如果mysqld重启,上述参数又会消失,永久方法:
windows下:my.ini[mysqld] 加上
log_bin_trust_function_creators=1linux下:/etc/my.cnf 下my.cnf[mysqld] 加上
log_bin_trust_function_creators=1
3、创建函数,保证每条数据都不同
-
随机产生字符串
delimiter $$ #为了存储过程能正常运行,修改命令结束符,两个 $$ 表示结束create function rand_string(n int) returns varchar(255)begin declare chars_str varchar(100) default 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'; declare return_str varchar(255) default ''; declare i int default 0; while i < n do set return_str = concat(return_str,substring(chars_str,floor(1+rand()*52),1)); set i=i+1; end while; return return_str;end $$ -
随机产生部门编号
delimiter $$create function rand_num() returns int(5)begin declare i int default 0; set i=floor(100+rand()*10); return i;end $$
4、创建存储过程
-
创建往emp表中插入数据的存储过程
delimiter $$create procedure insert_emp(in start int(10),in max_num int(10)) #max_num:表示插入多少条数据begin declare i int default 0; set autocommit = 0; #关闭自动提交,避免写一个insert提交一次,50w条一次性提交 repeat set i = i+1; insert into emp(empno,ename,job,mgr,hiredate,sal,comm,deptno) values((start+i),rand_string(6),'salesman',0001,curdate(),2000,400,rand_num()); until i=max_num end repeat; commit;end $$ -
创建往dept表中插入数据的存储过程
delimiter $$create procedure insert_dept(in start int(10),in max_num int(10))begin declare i int default 0; set autocommit = 0; repeat set i = i+1; insert into dept(deptno,dname,loc) values((start+i),rand_string(10),rand_string(8)); until i=max_num end repeat; commit;end $$
5、调用存储过程
-
往dept表中插入数据
mysql> DELIMITER ; # 修改默认结束符号为(;),之前改成了## mysql> CALL insert_dept(100, 10); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
-
往emp表中插入50万数据
mysql> DELIMITER ; mysql> CALL insert_emp(100001, 500000); Query OK, 0 rows affected (27.00 sec)
-
查看运行结果
mysql> select * from dept; +----+--------+---------+--------+ | id | deptno | dname | loc | +----+--------+---------+--------+ | 1 | 101 | mqgfy | ck | | 2 | 102 | wgighsr | kbq | | 3 | 103 | gjgdyj | brb | | 4 | 104 | gzfug | p | | 5 | 105 | keitu | cib | | 6 | 106 | nndvuv | csue | | 7 | 107 | cdudl | tw | | 8 | 108 | aafyea | aqq | | 9 | 109 | zuqezjx | dpqoyo | | 10 | 110 | pam | cses | +----+--------+---------+--------+ 10 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from emp limit 10; #查看前10条数据(50W太多了) +----+--------+-------+----------+-----+------------+---------+--------+--------+ | id | empno | ename | job | mgr | hiredate | sal | comm | deptno | +----+--------+-------+----------+-----+------------+---------+--------+--------+ | 1 | 100002 | xmbva | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 108 | | 2 | 100003 | aeq | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 109 | | 3 | 100004 | cnjfz | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 105 | | 4 | 100005 | wwhd | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 100 | | 5 | 100006 | e | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 107 | | 6 | 100007 | yjfr | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 108 | | 7 | 100008 | xlp | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 102 | | 8 | 100009 | mp | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 102 | | 9 | 100010 | tcdl | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 107 | | 10 | 100011 | akw | salesman | 1 | 2021-04-05 | 2000.00 | 400.00 | 106 | +----+--------+-------+----------+-----+------------+---------+--------+--------+ 10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
6.6 Show Profile进行sql分析(重中之重)
MySQL的Show Profile命令可用于分析当前会话中语句的资源消耗情况。可以用于SQL的调优的测量
官网文档
默认情况下,参数处于关闭状态,并保存最近15次的运行结果
分析步骤:
-
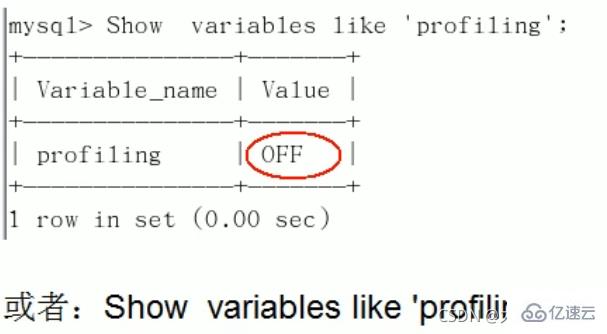
1、是否支持,看看当前的mysql版本是否支持:
show variables like 'profiling';
默认是关闭,使用前需要开启
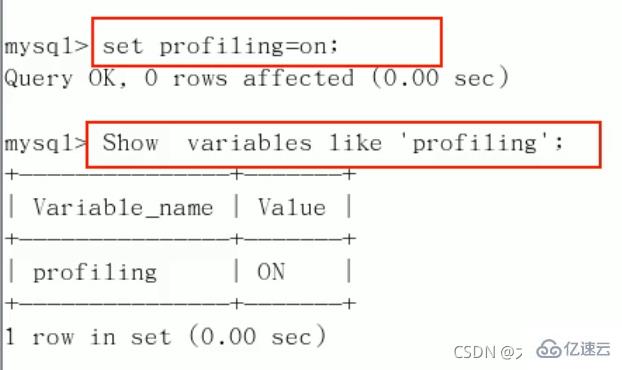
2、开启功能,默认是关闭,使用前需要开启:
set profiling=on;
-
3、运行SQL(随便运行用来测试)
mysql> select * from emp group by id%10 limit 150000; mysql> select * from emp group by id%20 order by 5;
-
4、查看结果:
show profiles;mysql> show profiles; +----------+------------+-----------------------------------------------+ | Query_ID | Duration | Query | +----------+------------+-----------------------------------------------+ | 1 | 0.00204000 | show variables like 'profiling' | | 2 | 0.55134250 | select * from emp group by id%10 limit 150000 | | 3 | 0.56902000 | select * from emp group by id%20 order by 5 | +----------+------------+-----------------------------------------------+ 3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
-
5、诊断SQL,
show profile cpu,block io for query ID号;(ID号为第4步Query_ID列中数字)mysql> show profile cpu,block io for query 3; +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ | Status | Duration | CPU_user | CPU_system | Block_ops_in | Block_ops_out | +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ | starting | 0.000049 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | checking permissions | 0.000005 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | Opening tables | 0.000012 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | init | 0.000021 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | System lock | 0.000009 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | optimizing | 0.000003 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | statistics | 0.000017 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | preparing | 0.000008 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | Creating tmp table | 0.000045 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | Sorting result | 0.000004 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | executing | 0.000002 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | Sending data | 0.568704 | 0.546875 | 0.046875 | NULL | NULL | | Creating sort index | 0.000048 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | end | 0.000003 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | query end | 0.000005 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | removing tmp table | 0.000006 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | query end | 0.000003 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | closing tables | 0.000004 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | freeing items | 0.000061 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | | cleaning up | 0.000015 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | NULL | NULL | +----------------------+----------+----------+------------+--------------+---------------+ 20 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
参数备注(写在代码中):
show profile cpu,block io for query 3;(如此代码中的cpu,block) ALL:显示所有的开销信息。
BLOCK IO:显示块lO相关开销。
CONTEXT SWITCHES :上下文切换相关开销。
CPU:显示CPU相关开销信息。
IPC:显示发送和接收相关开销信息。
MEMORY:显示内存相关开销信息。
PAGE FAULTS:显示页面错误相关开销信息。
SOURCE:显示和Source_function,Source_file,Source_line相关的开销信息。
SWAPS:显示交换次数相关开销的信息。
6、
日常开发需要注意的结论(Status列中的出现此四个问题严重)converting HEAP to MyISAM:查询结果太大,内存都不够用了往磁盘上搬了。
Creating tmp table:创建临时表,拷贝数据到临时表,用完再删除
Copying to tmp table on disk:把内存中临时表复制到磁盘,危险!
locked:锁了
6.7 全局查询日志
永远不要在生产环境开启这个功能,只能在测试环境使用!
-
第一种:配置文件启用。在mysq l的 my.cnf 中,设置如下:
#开启general_log=1#记录日志文件的路径general_log_file=/path/logfile#输出格式log_output=FILE
第二种:编码启用。命令如下:
set global general_log=1;set global log_output='TABLE';
此后,你所编写的sql语句,将会记录到mysql库里的geneial_log表,可以用下面的命令查看:
mysql> select * from mysql.general_log; +----------------------------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+ | event_time | user_host | thread_id | server_id | command_type | argument | +----------------------------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+ | 2021-04-05 19:57:28.182473 | root[root] @ localhost [::1] | 5 | 1 | Query | select * from mysql.general_log | +----------------------------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+--------------+---------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
7 MySQL锁机制
7.1 概述
定义:
锁是计算机协调多个进程或线程并发访问某一资源的机制。
在数据库中,除传统的计算资源(如CPU、RAM、I/O等)的争用以外,数据也是一种供许多用户共享的资源。如何保证数据并发访问的一致性、有效性是所有数据库必须解决的一个问题,锁冲突也是影响数据库并发访问性能的一个重要因素。从这个角度来说,锁对数据库而言显得尤其重要,也更加复杂
例子:京东购物
打个比方,我们到京东上买一件商品,商品只有一件库存,这个时候如果还有另一个人买,那么如何解决是你买到还是另一个人买到的问题?
这里肯定要用到事务,我们先从库存表中取出物品数量,然后插入订单,付款后插入付款表信息,然后更新商品数量。使用锁可以保护有限的资源,在处理隔离和并发之间的冲突时起着作用
锁的分类:
从对数据操作的类型(读\写)分
读锁(共享锁):针对同一份数据,多个读操作可以同时进行而不会互相影响。
写锁(排它锁):当前写操作没有完成前,它会阻断其他写锁和读锁。
从对数据操作的粒度分
表锁
行锁
7.2 表锁(偏读)
特点:偏向MyISAM存储引擎,开销小,加锁快;无死锁;锁定粒度大,发生锁冲突的概率最高,并发度最低。
读锁案例讲解1
案例分析
建表表
create table mylock (
id int not null primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) default ''
) engine myisam;
insert into mylock(name) values('a');
insert into mylock(name) values('b');
insert into mylock(name) values('c');
insert into mylock(name) values('d');
insert into mylock(name) values('e');
#查询
mysql> select * from mylock;
+----+------+
| id | name |
+----+------+
| 1 | a |
| 2 | b |
| 3 | c |
| 4 | d |
| 5 | e |
+----+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)手动增加表锁:lock table 表名字 read(write), 表名字2 read(write), 其他;
mysql> lock table mylock read;Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
查看表上加过的锁:show open tables;
mysql> show open tables; +--------------------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ | Database | Table | In_use | Name_locked | +--------------------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_by_user_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_global_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_transactions_summary_global_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | replication_connection_status | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone_leap_second | 0 | 0 | | mysql | columns_priv | 0 | 0 | | my | test03 | 0 | 0 | | bigdata | mylock | 1 | 0 | # In_use为1时表示已上锁
释放锁:unlock tables;
mysql> unlock tables; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) # 再次查看 mysql> show open tables; +--------------------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ | Database | Table | In_use | Name_locked | +--------------------+------------------------------------------------------+--------+-------------+ | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_by_user_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_waits_summary_global_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | events_transactions_summary_global_by_event_name | 0 | 0 | | performance_schema | replication_connection_status | 0 | 0 | | mysql | time_zone_leap_second | 0 | 0 | | mysql | columns_priv | 0 | 0 | | my | test03 | 0 | 0 | | bigdata | mylock | 0 | 0 |
加读锁——为mylock表加read锁(读阻塞写例子)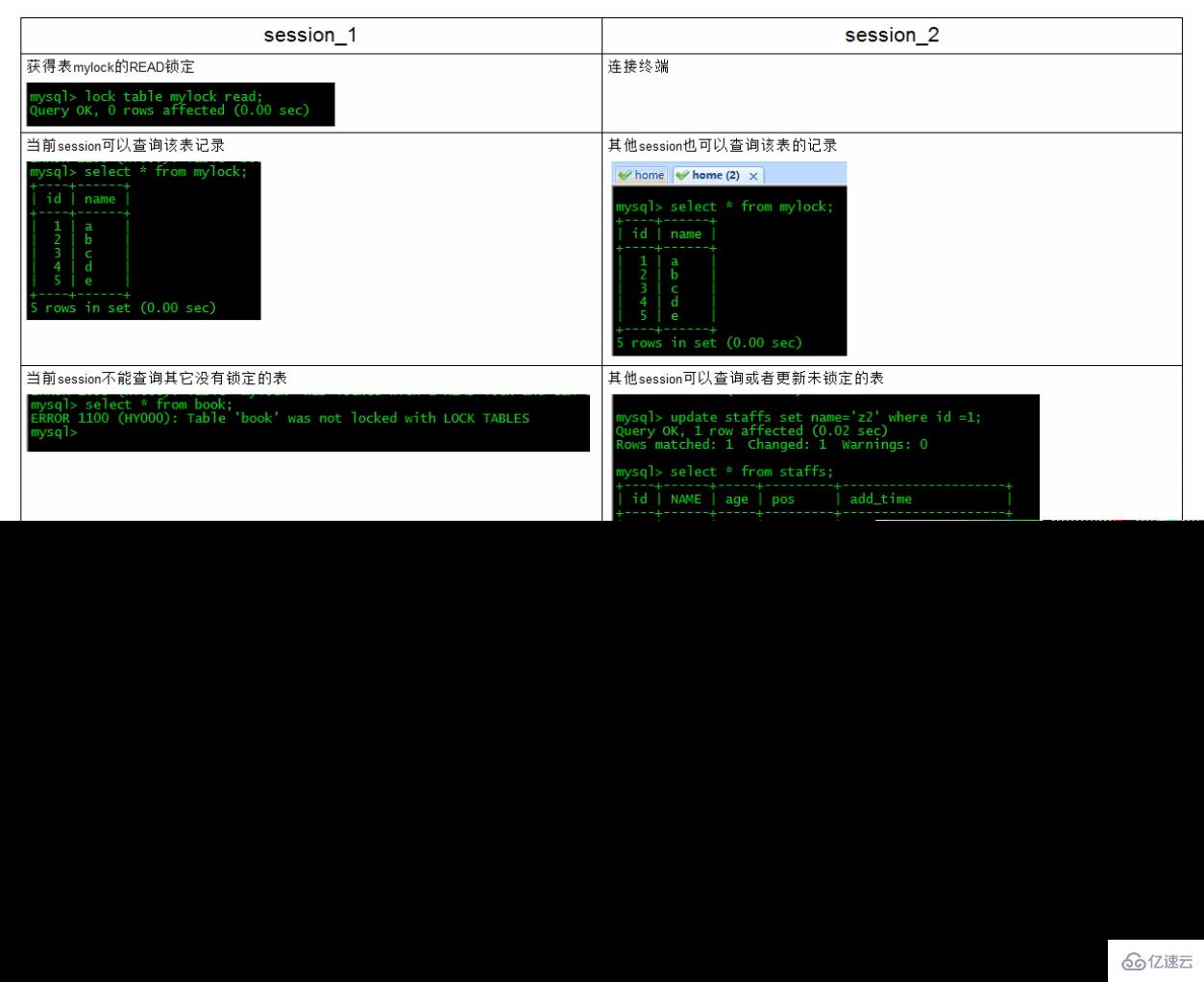
读锁案例讲解2
为mylock表加write锁(MylSAM存储引擎的写阻塞读例子)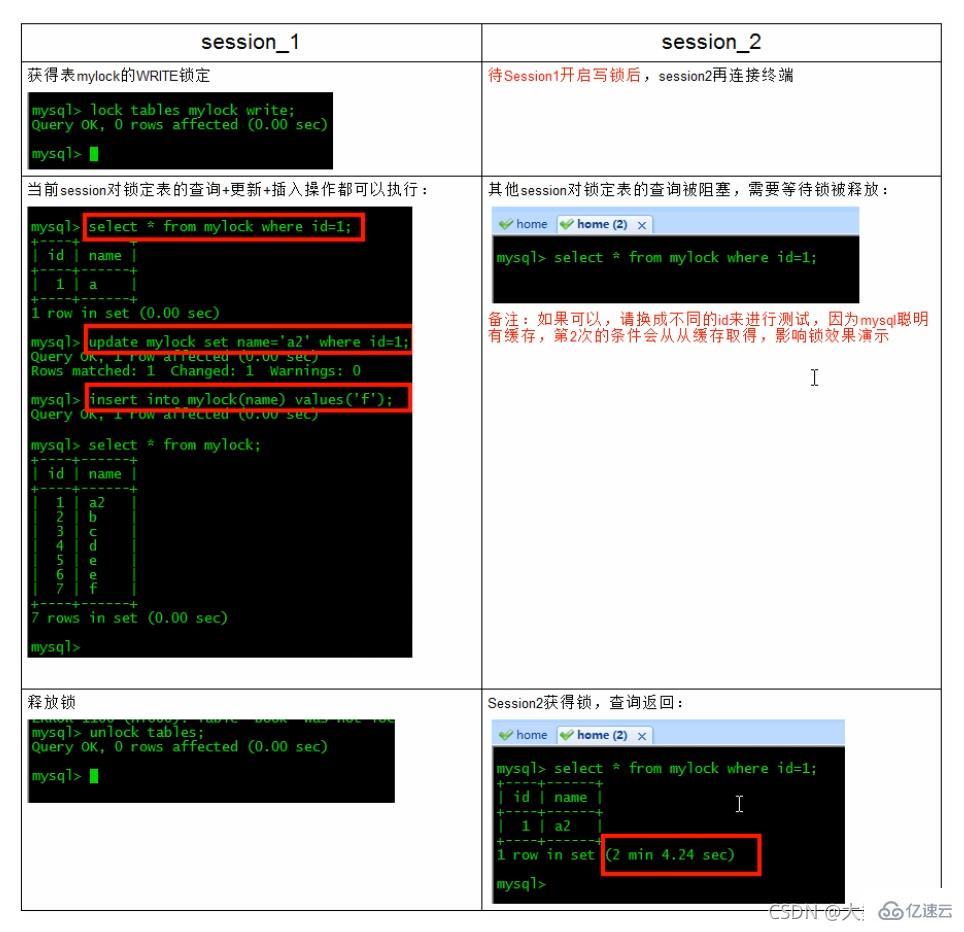
MyISAM在执行查询语句(SELECT)前,会自动给涉及的所有表加读锁,在执行增删改操作前,会自动给涉及的表加写锁。
MySQL的表级锁有两种模式:
表共享读锁(Table Read Lock)
表独占写锁(Table Write Lock)
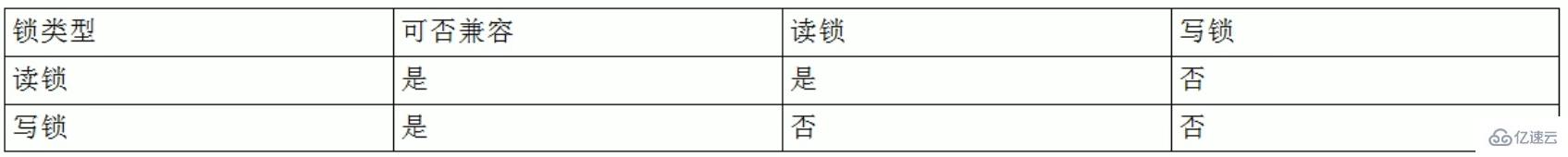
结合上表,所以对MyISAM表进行操作,会有以下情况:
对MyISAM表的读操作(加读锁),不会阻塞其他进程对同一表的读请求,但会阻塞对同一表的写请求。只有当读锁释放后,才会执行其它进程的写操作。
对MyISAM表的写操作〈加写锁),会阻塞其他进程对同一表的读和写操作,只有当写锁释放后,才会执行其它进程的读写操作。
重点!:简而言之,就是读锁会阻塞写,但是不会堵塞读。而写锁则会把读和写都堵塞
表锁总结
看看哪些表被加锁了:show open tables;
如何分析表锁定
可以通过检查table_locks_waited和table_locks_immediate状态变量来分析系统上的表锁定
mysql> show status like 'table_locks%'; +-----------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-----------------------+-------+ | Table_locks_immediate | 170 | | Table_locks_waited | 0 | +-----------------------+-------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
这里有两个状态变量记录MySQL内部表级锁定的情况,两个变量说明如下:
Table_locks_immediate:产生表级锁定的次数,表示可以立即获取锁的查询次数,每立即获取锁值加1 ;
Table_locks_waited(重点):出现表级锁定争用而发生等待的次数(不能立即获取锁的次数,每等待一次锁值加1),此值高则说明存在着较严重的表级锁争用情况;
MyISAM's read-write lock scheduling prioritizes write operations, which makes MyISAM unsuitable for table engines that mainly perform write operations. If a large number of updates are made, the write lock will block other threads, making it difficult for the query to obtain the lock and eventually causing permanent blocking
7.3 Row lock (write-biased)
biased towards the InnoDB storage engine , high overhead, slow locking; deadlocks will occur; the locking granularity is the smallest, the probability of lock conflicts is the lowest, and the concurrency is the highest.
The biggest differences between InnoDB and MyISAM are two points: one is that it supports transactions (TRANSACTION); the other is that it uses row-level locks
Because row locks support transactions, review Old knowledge:
Transaction and its ACID properties
Problems caused by concurrent transaction processing
Transaction Isolation Level
1) A transaction is a logical processing unit composed of a set of SQL statements. A transaction has the following 4 attributes, usually referred to as the ACID of the transaction. Attributes:
#A transaction is an atomic operation unit. Either all modifications to the data are performed or none are performed. This is atomicity.
Maintaining data consistency (Consistency) means that the data must remain consistent at the beginning and end of the transaction. This means that all relevant data rules must be applied to transaction modifications to maintain data integrity; at the end of the transaction, all internal data structures (such as B-tree indexes or doubly linked lists) must also be correct.
Isolation (lsolation): The database system provides a certain isolation mechanism to ensure that transactions are executed in an "independent" environment that is not affected by external concurrent operations. This means that intermediate states during a transaction are not visible to the outside world, and vice versa.
Durable: After a transaction is completed, its modifications to the data are permanent and can be maintained even if a system failure occurs.
2) Problems caused by concurrent transaction processing
-
Lost Update
The lost update problem occurs when two or more transactions select the same row and then update the row based on the originally selected value, because each transaction is unaware of the existence of the other transactions -
The last update overwrites updates made by other firms.For example, two programmers modify the same java file. Each programmer independently modifies his or her copy and saves the changes, overwriting the original document. The last editor to save a copy of his or her changes overwrites the changes made by the previous programmer.
This problem can be avoided if another programmer cannot access the same file until one programmer completes and commits the transaction.
-
Dirty Reads
A transaction is modifying a record. Before the transaction is completed and committed, the record The data is in an inconsistent state; at this time, another transaction also reads the same record. If it is not controlled, the second transaction reads these "dirty" data and performs further processing accordingly, which will cause Uncommitted data dependencies. This phenomenon is vividly called "dirty reading".
One sentence: Transaction A read the data that transaction B
has modified but has not yet submitted, and also performed operations based on this data. At this time, if transaction B is rolled back, the data read by A is invalid and does not meet the consistency requirements -
Non-Repeatable Reads
At some time after a transaction reads certain data, it reads the previously read data again, only to find that the data it read has changed, or that some records have been deleted. This kind of situation The phenomenon is called "non-repeatable reading".
One sentence:
Transaction A has read the modified datathat transaction B has submitted, which does not meet the isolation requirement. -
Phantom Reads
A transaction re-reads the previously retrieved data using the same query conditions, but other transactions are found New data that satisfies its query conditions is inserted. This phenomenon is called "phantom reading".
One sentence:
Transaction A has read the new data submitted by transaction B body, which does not meet the isolation requirementOne more sentence: phantom reading and dirty reading are somewhat similar . Dirty reading means that data has been modified in transaction B; phantom reading means that new data has been added in transaction B.
3) Transaction isolation level
"Dirty read", "Non-repeatable read" and "Phantom read" are actually database reads The consistency problem must be solved by the database providing a certain transaction isolation mechanism. 
The stricter the transaction isolation of the database, the smaller the concurrent side effects, but the greater the cost, because the transaction Isolation essentially means to "serialize" transactions to a certain extent, which is obviously contradictory to "concurrency". At the same time, different applications have different requirements for read consistency and transaction isolation. For example, many applications are not sensitive to "non-repeatable reads" and "phantom reads" and may be more concerned about the ability to access data concurrently.
常看当前数据库的事务隔离级别:show variables like 'tx_isolation';
mysql> show variables like 'tx_isolation'; +---------------+-----------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-----------------+ | tx_isolation | REPEATABLE-READ | +---------------+-----------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) # 默认情况下:MySQL避免了脏读和不可重复读
行锁案例讲解
建表:
CREATE TABLE test_innodb_lock (a INT(11),b VARCHAR(16))ENGINE=INNODB; INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(1,'b2'); INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(3,'3'); INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(4, '4000'); INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(5,'5000'); INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(6, '6000'); INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(7,'7000'); INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(8, '8000'); INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(9,'9000'); INSERT INTO test_innodb_lock VALUES(1,'b1'); CREATE INDEX test_innodb_a_ind ON test_innodb_lock(a); CREATE INDEX test_innodb_lock_b_ind ON test_innodb_lock(b); //查看 mysql> select * from test_innodb_lock; +------+------+ | a | b | +------+------+ | 1 | b2 | | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 4000 | | 5 | 5000 | | 6 | 6000 | | 7 | 7000 | | 8 | 8000 | | 9 | 9000 | | 1 | b1 | +------+------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show index from test_innodb_lock; +------------------+------------+------------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | +------------------+------------+------------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+ | test_innodb_lock | 1 | test_innodb_a_ind | 1 | a | A | 8 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | | test_innodb_lock | 1 | test_innodb_lock_b_ind | 1 | b | A | 9 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | +------------------+------------+------------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+
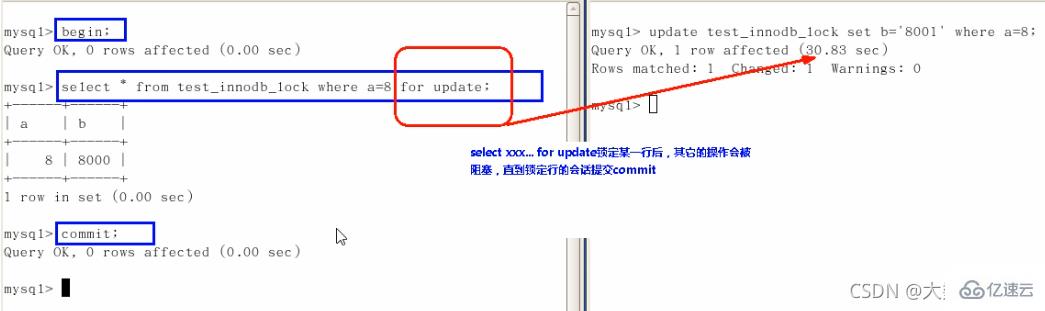
行锁定基本演示(两个客户端更新同一行记录)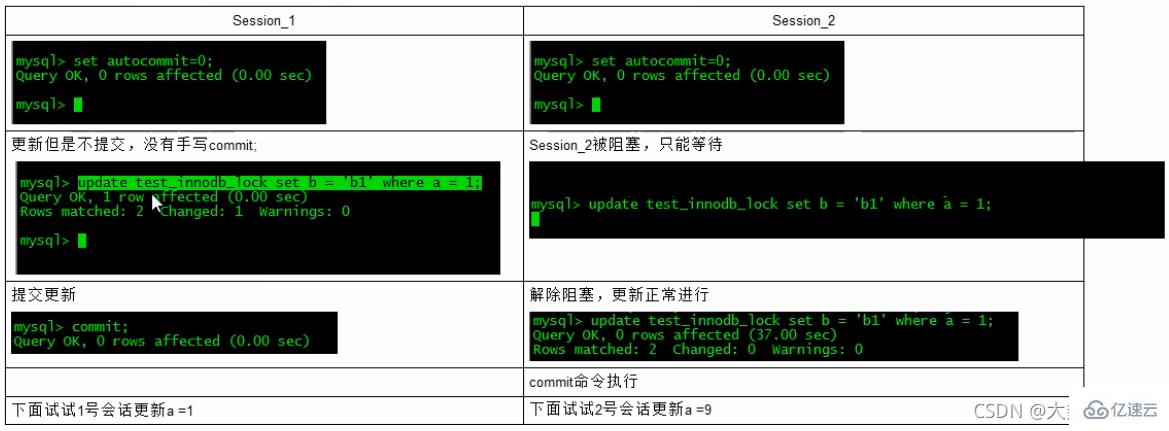
疑惑解答为什么两个都要commint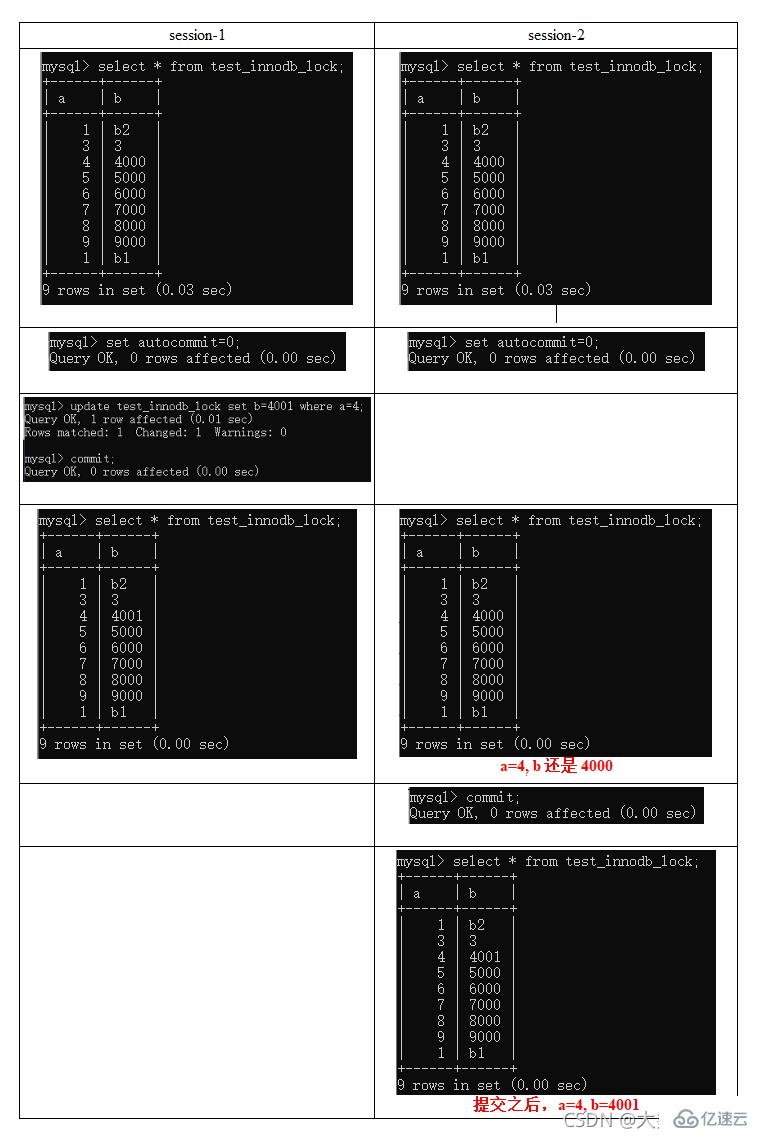
索引失效行锁变表锁
无索引行锁升级为表锁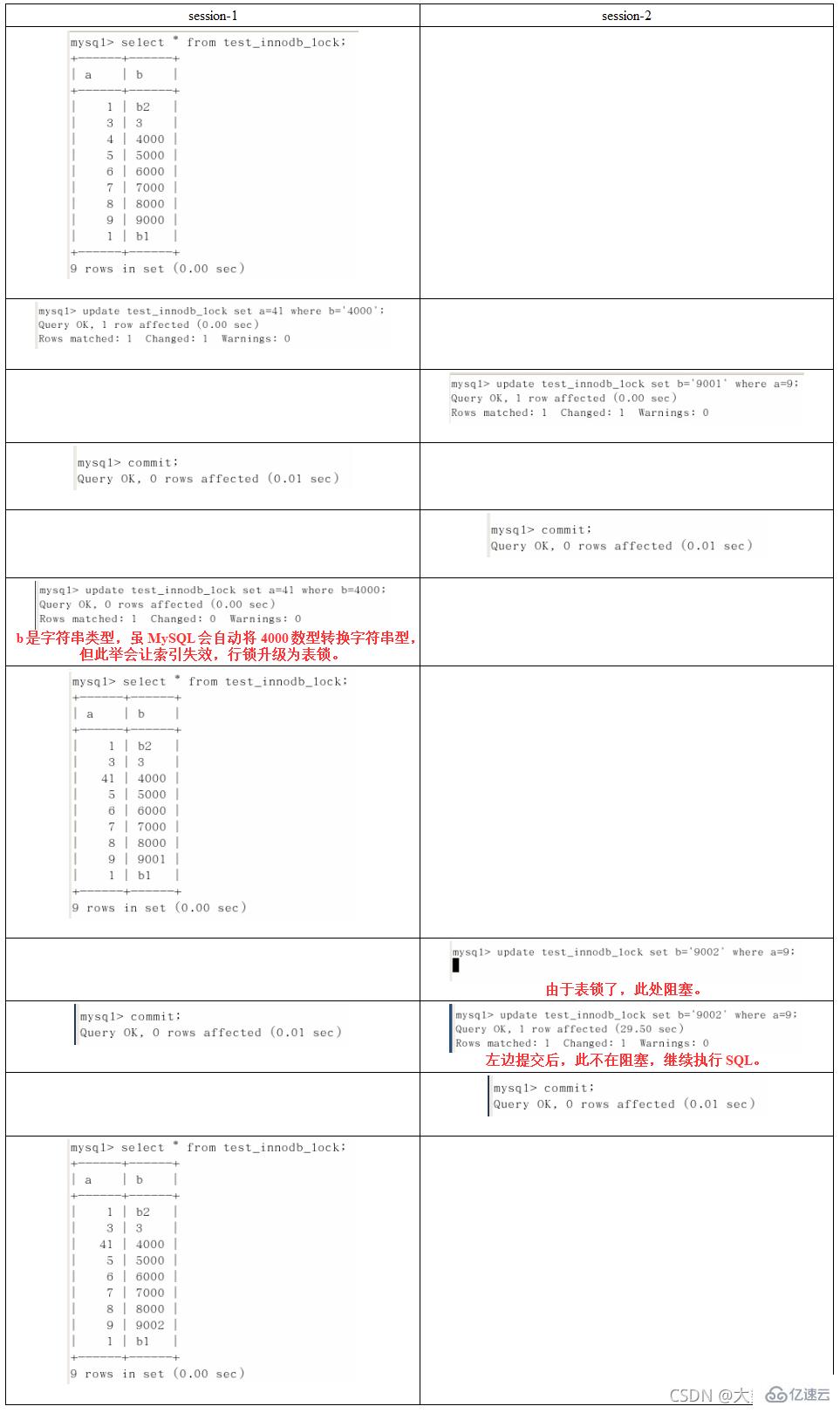
间隙锁

什么是间隙锁
当我们用范围条件而不是相等条件检索数据,并请求共享或排他锁时,InnoDB会给符合条件的已有数据记录的索引项加锁,对于键值在条件范围内但并不存在的记录,叫做“间隙(GAP)”。
InnoDB也会对这个“间隙”加锁,这种锁机制就是所谓的间隙锁(Next-Key锁)。
危害
如果在查询执行期间使用范围查找,它会锁定整个范围内的所有索引键值,即使这些键不存在。
间隙锁有一个比较致命的弱点,就是当锁定一个范围键值之后,即使某些不存在的键值也会被无辜的锁定,而造成在锁定的时候无法插入锁定键值范围内的任何数据。在某些场景下这可能会对性能造成很大的危害
面试题:如何锁定一行
begin(中间写自己的操作)commit
行锁总结
总结:
Innodb存储引擎由于实现了行级锁定,虽然在锁定机制的实现方面所带来的性能损耗可能比表级锁定会要更高一些,但是在整体并发处理能力方面要远远优于MyISAM的表级锁定的。当系统并发量较高的时候,Innodb的整体性能和MylISAM相比就会有比较明显的优势了。
但是,Innodb的行级锁定同样也有其脆弱的一面,当我们使用不当的时候,可能会让Innodb的整体性能表现不仅不能比MyISAM高,甚至可能会更差
如何分析行锁定?
通过检查lnnoDB_row_lock状态变量来分析系统上的行锁的争夺情况:show status like 'innodb_row_lock%';
mysql> show status like 'innodb_row_lock%'; +-------------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------------------+-------+ | Innodb_row_lock_current_waits | 0 | | Innodb_row_lock_time | 0 | | Innodb_row_lock_time_avg | 0 | | Innodb_row_lock_time_max | 0 | | Innodb_row_lock_waits | 0 | +-------------------------------+-------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
对各个状态量的说明如下:
Innodb_row_lock_current_waits:当前正在等待锁定的数量;
Innodb_row_lock_time:从系统启动到现在锁定总时间长度;
Innodb_row_lock_time_avg:每次等待所花平均时间;
Innodb_row_lock_time_max:从系统启动到现在等待最常的一次所花的时间;
Innodb_row_lock_waits:系统启动后到现在总共等待的次数;
对于这5个状态变量,比较重要的主要是:
lnnodb_row_lock_time(等待总时长)Innodb_row_lock_time_avg(等待平均时长)lnnodb_row_lock_waits(等待总次数)
尤其是当等待次数很高,而且每次等待时长也不小的时候,我们就需要分析(Show Profile)系统中为什么会有如此多的等待,然后根据分析结果着手指定优化计划。
优化建议
尽可能让所有数据检索都通过索引来完成,避免无索引行锁升级为表锁。
合理设计索引,尽量缩小锁的范围
尽可能较少检索条件,避免间隙锁
尽量控制事务大小,减少锁定资源量和时间长度
尽可能低级别事务隔离
页锁
在选择锁定方式时,需要考虑开销和加锁时间的平衡点,以避免死锁的出现;同时,锁定粒度介于表锁和行锁之间,通常并发度较为一般。(了解一下即可)
8 主从复制
8.1 复制的基本原理
slave会从master读取binlog来进行数据同步
原理图: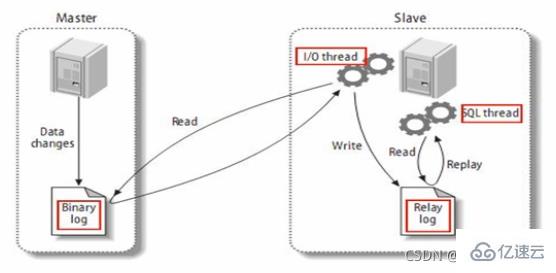
MySQL复制过程分成三步:
记录master的更改并存入二进制日志。二进制日志事件也称为binary log events
2、slave将master的binary log events拷贝到它的中继日志(relay log) ;
3、slave重做中继日志中的事件,将改变应用到自己的数据库中。MySQL复制是异步的且串行化的
8.2 复制的基本原则
每个slave只有一个master
每个slave只能有一个唯一的服务器ID
每个master可以有多个salve
复制的最大问题是延迟。
8.3 一主一从常见配置
一、mysql版本一致且后台以服务运行
二、主从都配置在[mysqld]结点下,都是小写
主机修改my.ini配置文件:
1、[必须]主服务器唯一ID:server-id=1
2、[必须]启用二进制日志
log-bin=自己本地的路径/mysqlbin
log-bin=D:/devSoft/MySQLServer5.5/data/mysqlbin
3、[可选]启用错误日志
log-err=自己本地的路径/mysqlerr
log-err=D:/devSoft/MySQLServer5.5/data/mysqlerr
4、[可选]根目录
basedir=“自己本地路径”
basedir=“D:/devSoft/MySQLServer5.5/”
5、[可选]临时目录
tmpdir=“自己本地路径”
tmpdir=“D:/devSoft/MySQLServer5.5/”
6、[可选]数据目录
datadir=“自己本地路径/Data/”
datadir=“D:/devSoft/MySQLServer5.5/Data/”
7、主机,读写都可以
read-only=O
8、[可选]设置不要复制的数据库
binlog-ignore-db=mysql
9、[可选]设置需要复制的数据库
binlog-do-db=需要复制的主数据库名字
从机修改my.cnf配置文件:
1、[必须]从服务器唯一ID:vim etc/my.cnf(进入修改配置文件)
...#server-id=1 //注释吊...server-id=1 //开启...
2、[可选]启用二进制日志
三、配置文件,请主机+从机都重启后台mysql服务
主机:手动重启
Linux从机命名:
service mysql stop
service mysql start
四、主机从机都关闭防火墙
windows手动关闭
关闭虚拟机linux防火墙: service iptables stop
五、在Windows主机上建立帐户并授权slave
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON . TO ‘zhangsan’@‘从机器数据库IP’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘123456’;
刷新:
flush privileges;查询master的状态
show master status;
记录下File和Position的值
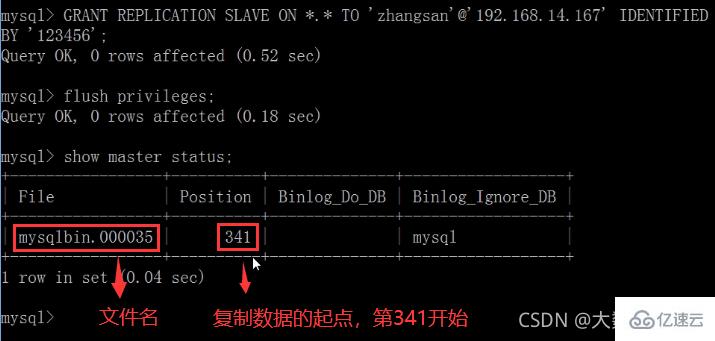
执行完此步骤后不要再操作主服务器MYSQL,防止主服务器状态值变化
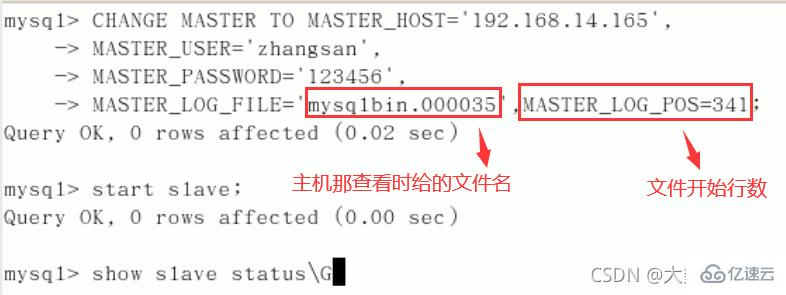
六、在Linux从机上配置需要复制的主机
CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST=’主机IP’,
MASTER_USER=‘zhangsan’,
MASTER_PASSWORD=’123456’,
MASTER_LOG_FILE='File名字’,
MASTER_LOG_POS=Position数字;启动从服务器复制功能:
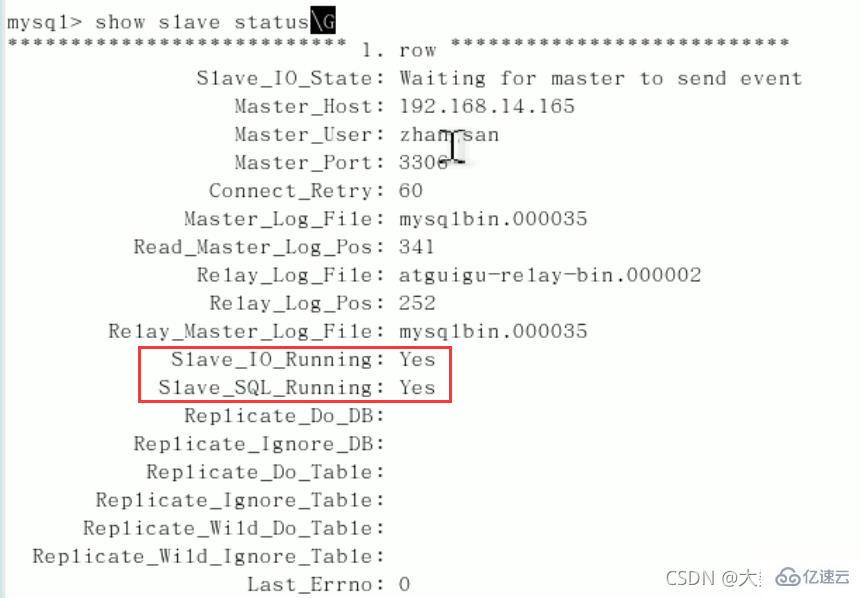
start slave;show slave status\G(下面两个参数都是Yes,则说明主从配置成功!)
Slave_IO_Running:Yes
Slave_SQL_Running:Yes
七、主机新建库、新建表、insert记录,从机复制
Host operation

Slave (automatic synchronization)

8. How to stop the slave service replication function: stop slave;
If there is a piece of data that is not needed temporarily?
Slave machine: 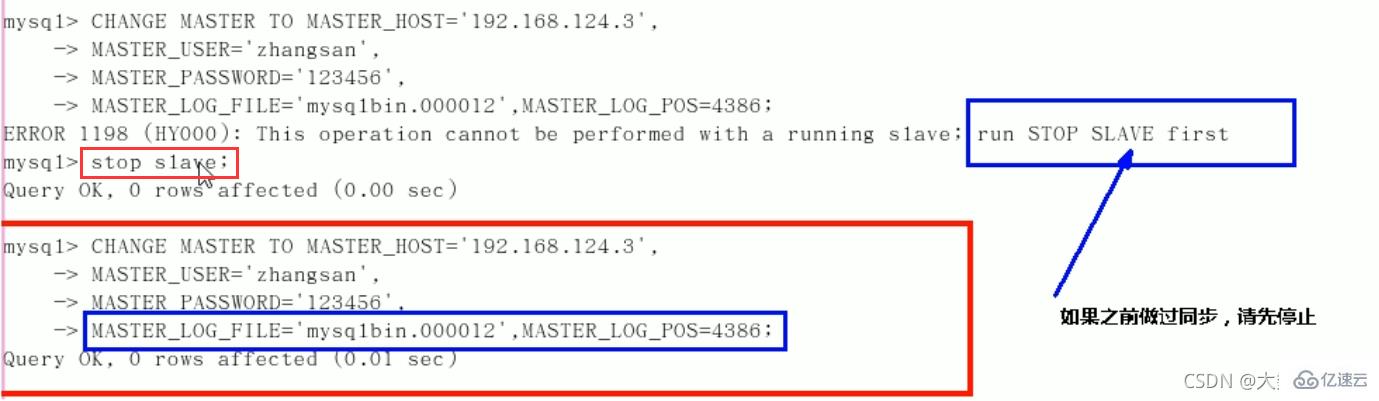
Host (need to recheck the scale): 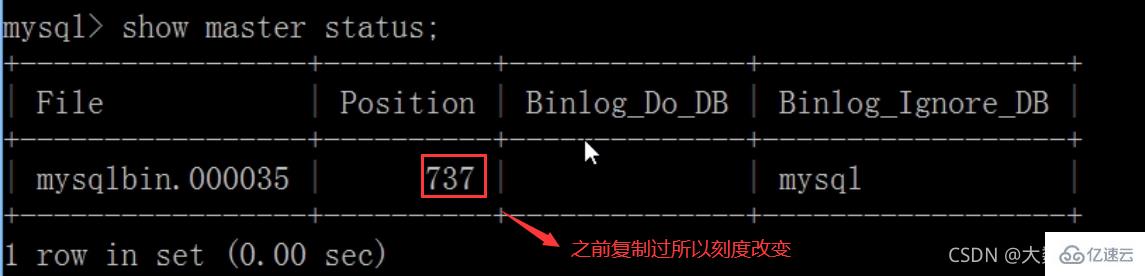
The above is the detailed content of What is the knowledge about MySQL's SQL optimization, index optimization, lock mechanism, and master-slave replication?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!











 中间列不能断:
中间列不能断: