Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Example analysis of MySQL sub-database and sub-table
Example analysis of MySQL sub-database and sub-table
- PHPzforward
- 2023-06-03 18:34:301257browse
1. Why do we need to divide databases into tables? As the server traffic is getting larger and larger, and it is facing more and more requests, we have separated database reading and writing, using multiple slave database copies (Slave) to be responsible for reading, and using the master database (Master) to be responsible for writing, master and slave. Synchronous data updates are achieved through master-slave replication to keep data consistent. The slave database can be expanded horizontally, so more read requests are not a problem
But when the user level increases and there are more and more write requests, how to ensure that the database load is sufficient? Adding a Master cannot solve the problem, because the data needs to be consistent, and the write operation requires synchronization between the two masters, which is equivalent to duplication, and the architecture design is more complicated
At this time, you need to use sub-database partitioning Table (sharding), store the library and table on different MySQL Servers, each server can balance the number of write requests
2. Problems caused by too large library tables
A single database is too large: The single database has limited processing capacity, insufficient disk space on the server, and encounters IO bottlenecks. The single database needs to be divided into more and smaller databases
-
Single table is too large: CURD efficiency is very low,
The amount of data is too large, causing the index file to be too large, and disk IO takes time to load the index, resulting in query timeout. Therefore, only using indexes is not enough. You need to split a single table into multiple tables with smaller data sets . The table splitting algorithms provided by MyCat are all in rule.xml, which can be split according to different table splitting algorithms, such as splitting based on time, consistent hashing, directly using the primary key to modulo the number of split tables, etc. -
Split strategy
A single database is too large, first consider whether there are too many tables or too much data:
If If there is too much data due to too many tables, use vertical splitting, that is, split it into different libraries according to the business
If the amount of data in a single table is too large, use horizontal splitting Splitting, that is, splitting the table data into multiple tables according to certain rules (table splitting algorithm defined in rule. First consider vertical splitting, and then consider horizontal splitting
- 3. Vertical splittingSub-database, sub-table and read-write separation can be performed together
server.xml
<user name="root"> <property name="password">123456</property> <property name="schemas">USERDB1,USERDB2</property> </user>is configured with two logical libraries USERDB1 and USERDB2 schema.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE mycat:schema SYSTEM "schema.dtd"> <mycat:schema xmlns:mycat="http://io.mycat/"> <!-- 逻辑数据库 --> <schema name="USERDB1" checkSQLschema="false" sqlMaxLimit="100" dataNode="dn1" /> <!-- 两个逻辑库对应两个不同的数据节点 --> <schema name="USERDB2" checkSQLschema="false" sqlMaxLimit="100"dataNode="dn2" /> <!-- 存储节点 --> <dataNode name="dn1" dataHost="node1" database="mytest1" /> <!-- 两个数据节点对应两个不同的物理机器 --> <dataNode name="dn2" dataHost="node2" database="mytest2" /> <!-- USERDB1对应mytest1,USERDB2对应mytest2 --> <!-- 数据库主机 --> <dataHost name="node1" maxCon="1000" minCon="10" balance="0" writeType="0" dbType="mysql" dbDriver="native"> <heartbeat>select user()</heartbeat> <writeHost host="192.168.131.129" url="192.168.131.129:3306" user="root" password="123456" /> </dataHost> <dataHost name="node2" maxCon="1000" minCon="10" balance="0"writeType="0" dbType="mysql" dbDriver="native"> <heartbeat>select user()</heartbeat> <writeHost host="192.168.0.6" url="192.168.0.6:3306" user="root" password="123456" /> </dataHost> </mycat:schema>Corresponding to two different data nodes, the two data nodes correspond to two different physical machines
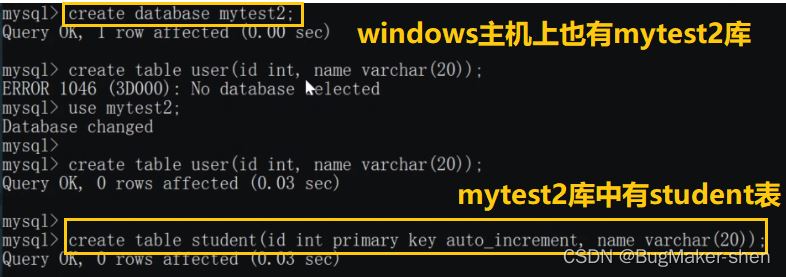
mytest1 and mytest2 are divided into different libraries on different machines, each containing a part The tables, which were originally integrated into one machine, are now split vertically.
The client needs to connect to different logical libraries. Different logical libraries are used according to business operations.Then two writing libraries are configured and two machines are used to store the libraries. It's evenly divided, sharing the pressure of the original single machine. Database sharding is accompanied by table sharding, and the table is split from a business perspective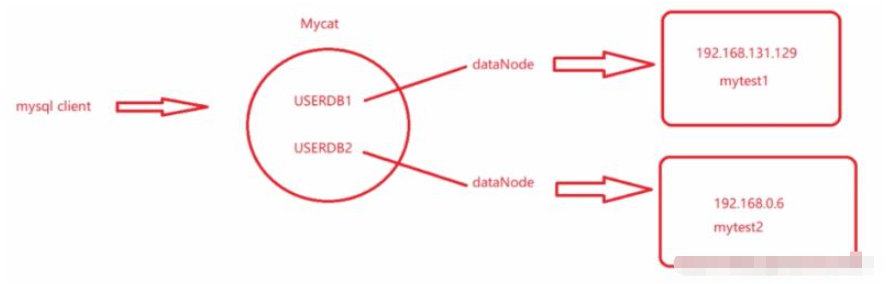
Vertical table sharding is based on column fields. It is generally used for large tables with hundreds of columns to avoid "cross-page" problems caused by large amounts of data during queries.
Generally, there are many fields in the table, and those that are not commonly used, have large data, and are long (such as text type fields) are split into extended tables. Fields with higher access frequency are placed in a separate table
Sub-database Table sharding can be performed at the same time as master-slave replication, but it is not based on master-slave replication; read-write separation is based on master-slave replication
server.xml<user name="root"> <property name="password">123456</property> <property name="schemas">USERDB</property> </user>schema.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE mycat:schema SYSTEM "schema.dtd"> <mycat:schema xmlns:mycat="http://io.mycat/"> <!-- 逻辑数据库 --> <schema name="USERDB" checkSQLschema="false" sqlMaxLimit="100"> <table name="user" dataNode="dn1" /> <!-- 这里的user和student都是实际存在的物理表名 --> <table name="student" primaryKey="id" autoIncrement="true" dataNode="dn1,dn2" rule="mod-long"/> </schema> <!-- 存储节点 --> <dataNode name="dn1" dataHost="node1" database="mytest1" /> <dataNode name="dn2" dataHost="node2" database="mytest2" /> <!-- 数据库主机 --> <dataHost name="node1" maxCon="1000" minCon="10" balance="0" writeType="0" dbType="mysql" dbDriver="native"> <heartbeat>select user()</heartbeat> <writeHost host="192.168.131.129" url="192.168.131.129:3306" user="root" password="123456" /> </dataHost> <dataHost name="node2" maxCon="1000" minCon="10" balance="0" writeType="0" dbType="mysql" dbDriver="native"> <heartbeat>select user()</heartbeat> <writeHost host="192.168.0.6" url="192.168.0.6:3306" user="root" password="123456" /> </dataHost> </mycat:schema>
user represents an ordinary table, which is placed directly on the data node dn1 and placed on a machine. This table does not need to be split
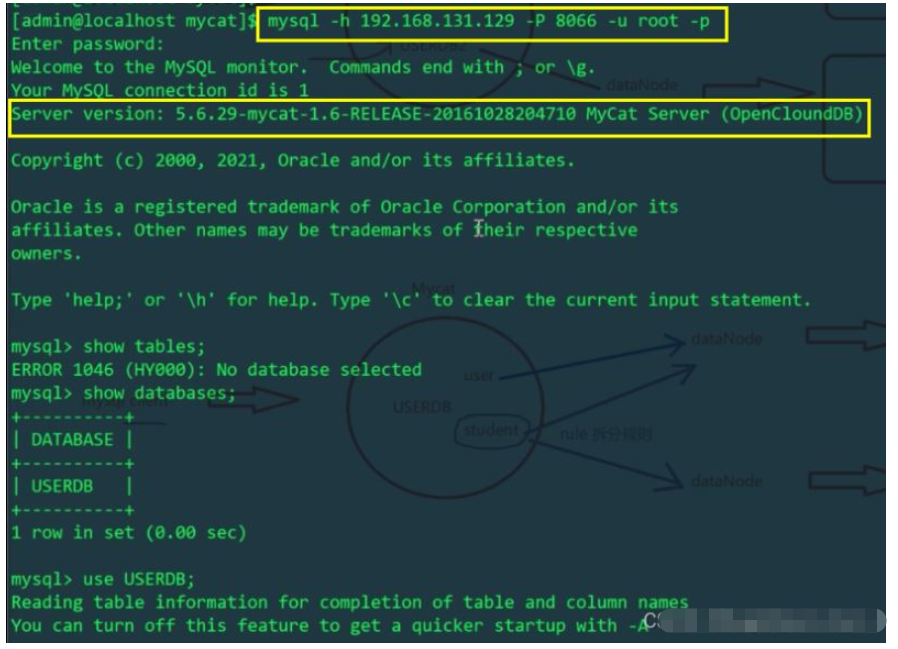
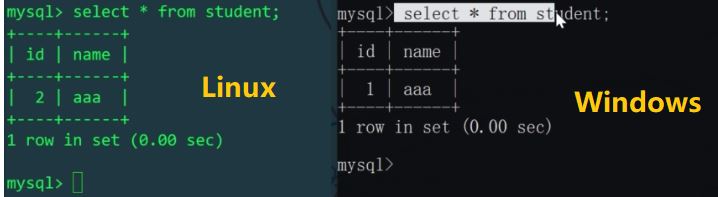
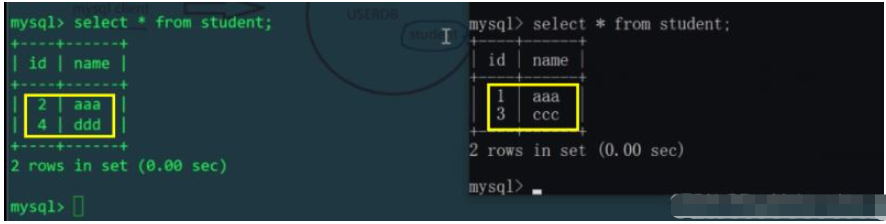
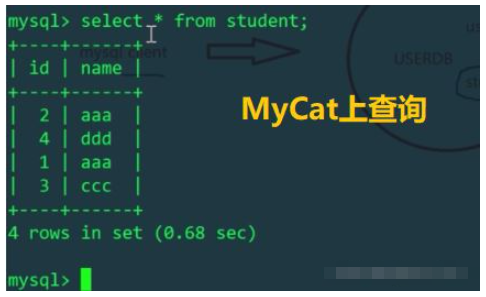
student table The primaryKey is the id, split according to the id, and placed on dn1 and dn2. In the end, this table will be divided into two machines. They are physically separated, but logically they are still one. Which table should be added to? In 2 How to query and merge these operations on each machine is completed by mycat
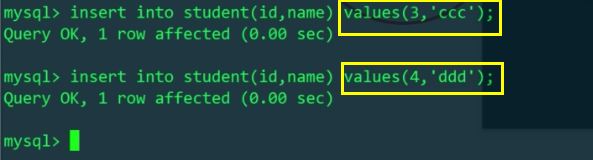
The splitting rule is to take the modulo (mod - long), and each insertion uses the number of machines existing on the id modulo (2)
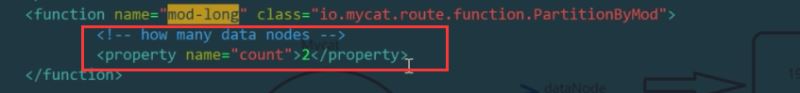
In addition, you need to configure the following splitting algorithm in rule.xml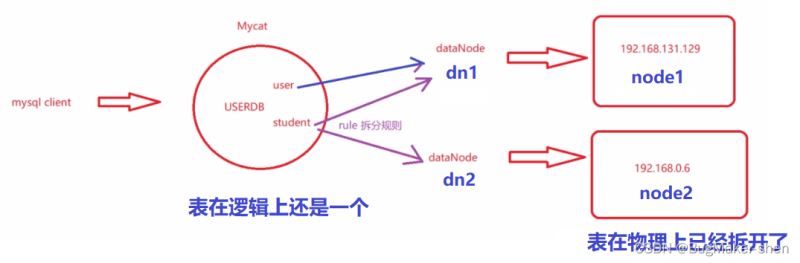
Find the algorithm mod-long. Because we map the logical table student to two hosts separately, the number of modified data nodes is 2
2. Test level Sub-table
Linux host
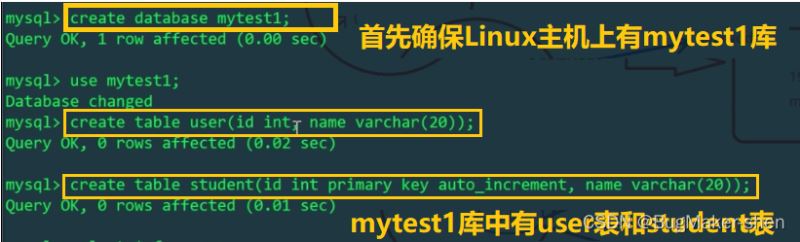

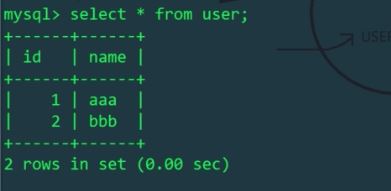


id% machine number to determine which physical table to insert into). Let’s check the student tables of Linux and Windows hosts respectively:
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of MySQL sub-database and sub-table. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

