Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >MySQL transaction instance analysis
MySQL transaction instance analysis
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-27 10:44:101040browse
MySQL transaction is mainly used to process data with large operations and high complexity. For example, in the personnel management system, if you delete a person, you need to delete not only the basic information of the person, but also the information related to the person, such as mailbox, articles, etc. In this way, these database operation statements constitute a transaction .

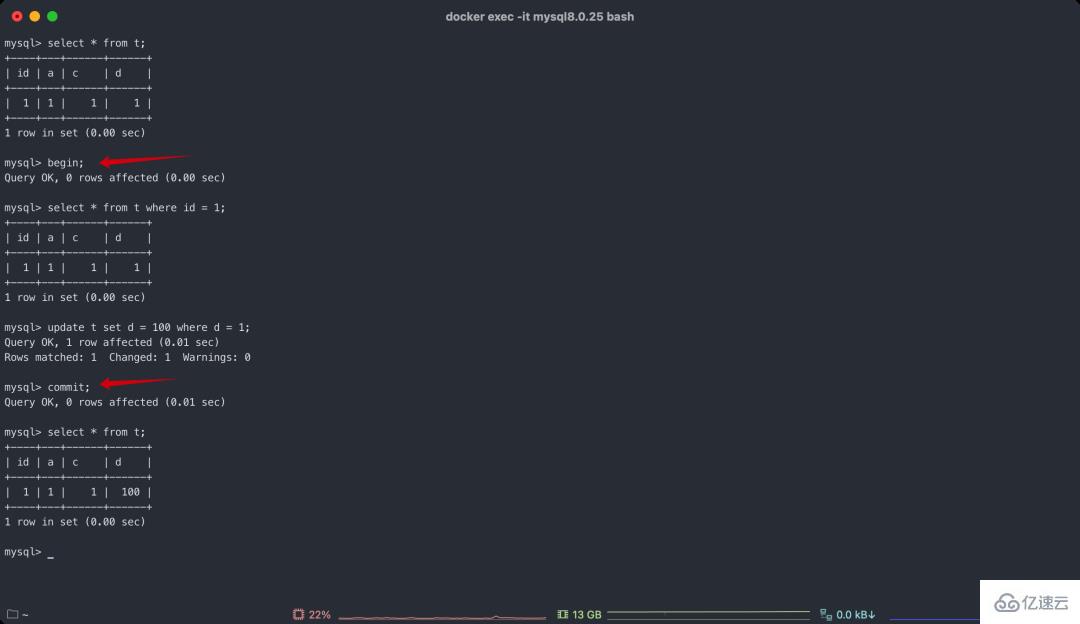
Method 1
START TRANSACTION or BEGIN starts a new transaction COMMIT commits the current transaction ROLLBACK rolls back the current transaction
This is well known to everyone A way to start a transaction, start transaction and begin are the same.
Method 2
SET autocommit = 0;
By default, autocommit = 1, which automatically commits transactions. Autocommit is session level, that is, if the current connection changes autocommit, it will have no impact on other connections. After setting autocommit, all SQLs connected this time are in the form of transactions, such as each commit.
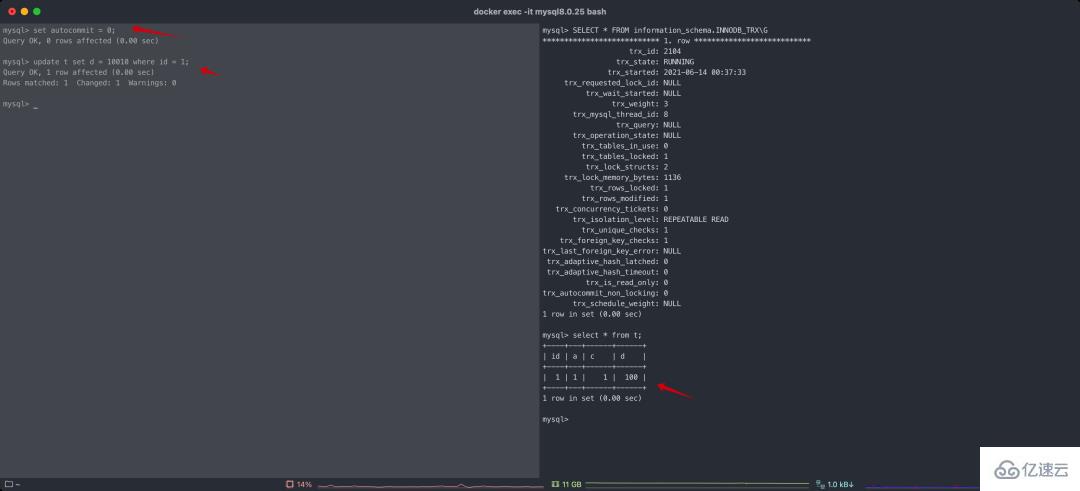
As can be seen from the screenshot, there is a transaction being executed. Because set autocommit = 0; is set, the subsequent update operation changes the result, and other sessions will not check it. to (RR level).
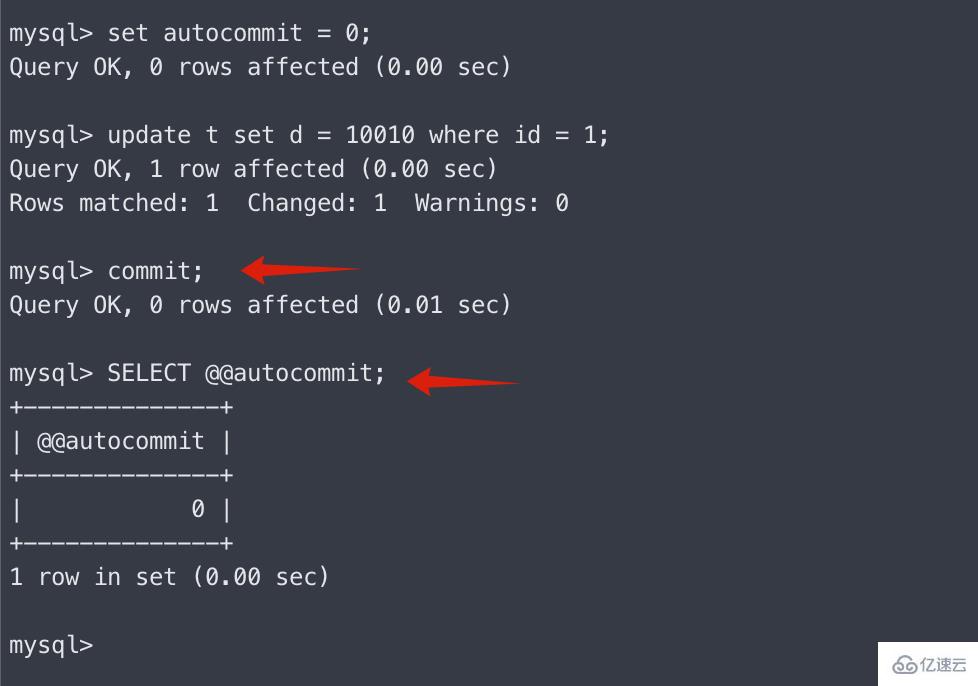
At this time, you need to manually execute the commit yourself.
Note that autocommit has not been changed. At this time, the autocommit value is still 0, which means that subsequent SQL statements of this session need to be manually committed.
The above is the detailed content of MySQL transaction instance analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

