This article teaches you how to use ChatGPT to quickly write a report
This article will share the entire process of training ChatGPT (the latest GPT-4 model version) and generating reports, and discuss the common problems that exist in the use of ChatGPT, and how to use ChatGPT to maximize learning, work efficiency and other issues. .
The following is the entire process of generating an AI security report.
Infrastructure
Topic selection
High-quality topic selection can help academic researchers quickly determine the entry point of the report, guide readers to capture the main theme of the report, and make the entire report more comprehensive. Clear structure and logic. By introducing the background of the report or providing keywords and overview to ChatGPT, ChatGPT can generate topic selections in a few seconds for researchers' reference.
When we ask questions, we can ask ChatGPT to generate multiple topics at the same time. This not only helps academic researchers quickly select the titles that best meet their needs, but also guides researchers to think outside the box and broadens the scope of researchers. ideas.

Based on the actual situation, we need to guide ChatGPT to adjust and optimize the generated titles so that the topic selection of the final report is more in line with actual needs and more targeted.

It is worth mentioning that ChatGPT’s language capabilities are amazing, including “Little Red Book style” and “Zhihu style”. In order to improve the reading effect and dissemination of the report, we can set requirements on the wording and language style of the title.

If you need to further improve the title if the title style and wording do not deviate significantly from expectations, you can also directly issue an "optimize" command to ChatGPT. Similarly, when entering commands, the fastest and most effective way is to command ChatGPT to provide multiple answers at once to locate results more quickly and in a wider range.

Create an outline
After determining the topic, we can use ChatGPT to build a basic report outline, which greatly shortens the report The process of preliminary desktop investigation, data compilation and screening provides basic ideas for subsequent research.
Before this, we must first ensure that the overall context of the outline is basically consistent with our expectations, and there are no major digressions, deviations, etc., thereby saving the time and cost of later correction, adjustment, and optimization.
In order to achieve this result, we need to first let ChatGPT generate a report summary.

Obviously, the above answer came to an abrupt end. According to the official, the input and output limit of GPT-4 is 25,000 characters, which is approximately equivalent to 2,600 Chinese characters. Our test results show that Chinese character input and output content usually reaches the upper limit within 500-1000 characters.
Fortunately, answers interrupted due to character limit can continue to output results under guidance. When performing this operation, you need to pay attention to evaluate the position where the previously generated content is interrupted to roughly determine the proportion of missing content. If the interruption position is near the end, there will be a higher success rate for the model to continue answering.

The summary content is mainly to help us frame the overall position of the report and clarify the scope of the report outline. It also addresses possible improper wording, logic, and paragraph connection in the summary. We don’t need to pay too much attention to these issues at this stage.
Since this step is at the earliest stage of report creation, the specific content is usually quite different from the final generated report results, and the text content in the summary will not be directly used in the report. Therefore, we only need to check the focus and scope of the summary, and after additions, deletions, and modifications, the report outline can be generated.

It can be seen that the outline generated by ChatGPT has a basic structure and logic at first glance, but it still has the ability to process deep logical relationships. Very limited.
For example, the title of Chapter 6, "Promoting AI Security Awareness and Education", is part of the development recommendations, and is inclusive but not parallel to Chapter 7, "Conclusions and Recommendations". Another example is that the four subtitles under the "Governance and Supervision of AI Risks" section in Part 5 all focus on suggestions for AI risk governance, and the suggestions are short-lived and lack practicality, and do not cover AI supervision. Any content regarding current status and development.
Therefore, we need to conduct a detailed inspection of the structure, overall logic, and rationality of the views, and at the same time, add, delete, and adjust the content of the outline based on the report's own needs.
Breaking away from "intuitive thinking" is the core of this process. The most essential difference between the ChatGPT model and the structure of the human brain lies in the ability to process non-linear scenarios and judgment based on intuition. After recognizing this, we need to make the problem description as detailed, specific, and logically clear as possible. We can use the point-based description style to facilitate ChatGPT to understand the requirements more accurately.

The above generated results reflect both the capabilities and limitations of ChatGPT. On the one hand, ChatGPT accurately understood and responded to instructions such as "Integrating Chapter 6 into Chapter 7", "Adjusting the reporting framework of Chapter 5", and "The entry point of the introduction". On the other hand, ChatGPT's response content is relatively mechanical, and its cognitive level of common sense and intuitive knowledge is also very limited.
Taking the instruction “Integrate Chapter 6 into Chapter 7” as an example, ChatGPT mechanically appropriated the subtitles under the original Chapter 6 directly to Chapter 7 (points 5, 6, and 7). Obviously, points 5, 6, and 7 all belong to a part of "improving AI safety awareness and education" and cannot be directly paralleled with several other suggestions, resulting in an obvious imbalance in the outline structure. For another example, for the instructions for framework modification in Chapter 5, ChatGPT directly copied the input instructions intact.
We guide ChatGPT to optimize the above issues one by one. For example, we ask ChatGPT to merge the three titles of Chapter 6 into one point:

Once again , although ChatGPT correctly understood the content of the command, its execution operation was only to mechanically combine the content of titles 5, 6, and 7 into one long sentence. This form of title is almost impossible to come from the hands of human researchers. This is originated from human beings. Researchers can have a basic preset for the format of a report title (concise, clear focus, strong summary, etc.) with almost no need to think about it. This kind of common sense knowledge is what ChatGPT does not have.
At this point in the training, it is not difficult for us to draw a general conclusion: do not neglect to explain to ChatGPT those knowledge backgrounds that have become common sense and a priori knowledge in human thinking habits, and do not assume that ChatGPT can generate any instructions other than content, describing the output requirements as specifically as possible.
Based on the above experience summary, we tried to train ChatGPT again, optimized this part of the title, limited the length of the title of point 5 of Chapter 6, and listed the specific reference standards (with 1, 2, 3 , the length of the 4-point title is consistent), and finally achieved relatively satisfactory results.
Text Writing
Writing the text of the report is a task of peeling off layers and layers of cocoons. In summary, the training method and sequence need to follow the following basic principles: first confirm the direction of the major chapter, then confirm the direction of the small chapter, and finally optimize the content of the small chapter.
In order to shorten the time cost of later correction and rework as much as possible, we need to first ensure that the content generated in each chapter does not deviate significantly from expectations, and conduct the framework context of each chapter based on the ChatGPT answer content. Adjustment.
Taking the content of Chapter 3 as an example, we first ask ChatGPT to describe the content to be generated.

At first glance, there are no obvious problems with ChatGPT’s answer ideas, and they are quite organized. A careful reading of the generated results reveals a common flaw of ChatGPT: the content between points is separated from each other, or even overlaps.
For example, for the risks of deep learning, ChatGPT’s answers are “overfitting” and “adversarial sample attacks”. For the risks of natural language processing technology, ChatGPT’s answers include "The model leaked sensitive information".
These risks are common threats faced by different AI technologies. If a report is generated according to the above ideas, each description of risks in a specific AI technology field in this chapter will include a large number of commonality of AI technologies. Risks may result in confusion in report structure and overlapping content.
We have adjusted the framework of Chapter 3 in response to the above issues and asked ChatGPT to describe the commonalities and differences in network security risks in the three core AI technology fields.
After receiving the instruction, ChatGPT successfully differentiated between "common risks" and "unique risks".

#After all the preliminary preparations are done, you can proceed to the most core and most time-consuming link - writing the main content of the report.

It is not difficult to see that the output result at this stage is more like an outline, and subsequent steps involve the screening and confirmation of subtitles, as well as the extension and adjustment of specific content.
The most time-saving way to quickly expand content is to directly ask ChatGPT to supplement the generated content. You can use keywords such as "expand", "extend", and "specific explanation" and limit the length of the expansion.

The above are the roughest report generation steps. The subsequent work will focus on the most lengthy and trivial results correction, content adjustment and optimization links. Pay attention to verify first. The basic principles of information authenticity and accuracy, and then improving the structure and content.
Humbly admit mistakes and never change after repeated admonishment
The construction of the above infrastructure does not seem complicated. If you think that everything will be fine if you enter simple instructions, you can rest easy and leave the important task of report writing to ChatGPT. , which is totally wrong.
In fact, in the process of generating specific content of ChatGPT, there are endless problems that may arise. The most typical example is the widely criticized direct fraud such as "seriously talking nonsense" and "fabricating documents".
This problem is particularly obvious when we write Chapter 5 "Governance and Supervision of AI Risks", which is based on strict legal and policy documents. We encountered various types of errors during the training process: writing non-existent policy document names, writing false policy-promulgating agencies, writing wrong policy promulgation years, promulgating non-existent government actions, etc.
For example, during the training process on some U.S. policy content, ChatGPT made an obvious mistake in its initial 4-point answer: fabricating the untrue government behavior of the U.S. government establishing an AI policy office.

We made suggestions for improving the generated results, including asking about the establishment agency of the false information that "the US government established an AI policy office".
Regrettably, ChatGPT not only failed to recognize the error in the answer result, but instead made the mistake and continued to fabricate and generate content based on the question.

#For another example, the following answers can be said to be a large collection of AI-generated error content. Just 4 questions included 3 major errors. The most ridiculous error was undoubtedly the direct reference to "NISTIR 8272: Impact Analysis Tool for Interdependent Network Supply Chain Risks", a comprehensive analysis of network supply chain risks. Documents related to AI security were replaced, and the document numbered NISTIR 8272 was given the non-existent name "NISTIR 8272: Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework."
The only correct answer among the four points is to admit the error caused by the content generated in the previous question. It can be seen that although ChatGPT has a good attitude towards admitting mistakes, it adheres to the implementation principle of never correcting after repeated admonitions. The accuracy of ChatGPT's output results for serious government actions, policies and systems, documents and other content is very low. Users need to carefully review and proofread the generated content.

The picture below is another representative error example. The picture on the left is a summary of the AI safety regulatory policies issued by the European Union generated by ChatGPT. Obviously, the picture on the left The content mainly revolves around "AI" rather than "AI security".
We issue "revise and focus" instructions on the above issues, as shown on the right. Obviously, ChatGPT’s revised answer did not reorganize the EU government’s documents focusing on “AI security” as envisaged.
On the contrary, ChatGPT copied all the document names and government actions involved in the original answer, and directly replaced the purport and goals of the document, including: changing the goal of the "European Strategy for Artificial Intelligence" from "strengthening AI" Research..." is replaced by "strengthening AI safety research...", and the purpose of the EU's establishment of ELLIS is replaced from "promoting AI research" to "promoting AI safety research", etc.
This exposes another fatal problem of ChatGPT: ChatGPT may directly tamper with information in order to make the generated results seem to meet the needs of the problem.

Limitations and Suggestions
Except for the above factual errors, during the content review and proofreading process, we need to focus on checking whether there are any gaps between paragraphs Crossover overlap. Take data poisoning in subsection 4.1 as an example. The basic concept of data poisoning is mentioned simultaneously in the introduction and section 4.1.1.

Following the above example, we make a bold guess about the operating rules of ChatGPT: that is, the answers generated by ChatGPT are spliced together by scattered small tasks. These tasks are relatively independent and lack logical connection.
If the introduction part of data poisoning is regarded as a small generation task, the output result of ChatGPT has met the basic standards of a qualified introduction: (explaining the concept of data poisoning-introducing the following content). Similarly, if part 4.1.1 is regarded as a small generation task, there will be no obvious errors in the output results.
When we clearly pointed out the overlapping content to ChatGPT, ChatGPT quickly understood the modification instructions and re-completed the answer, as shown below.
Obviously, ChatGPT has the ability to "identify overlapping content", but what it lacks is the awareness that "there should not be a lot of overlapping content between paragraphs". It can be seen that the grid-based correlation analysis ability of the human brain is the most difficult part for AI to imitate and replace.

Interestingly, when ChatGPT merged the content of 4.1.1 into the introduction, the rest of the numbers were not adjusted accordingly, and when we pointed out that ChatGPT existed When a problem arises, the model effectively detects the error and accurately completes the numbering modification.
This type of numbering error does not affect our actual use of ChatGPT, but it can be used as a good example to confirm our hypothesis about ChatGPT’s distributed task splicing mechanism.

We also tried to guide the model to enhance the connectivity of paragraphs, and received feedback results in the format of "After XXX, companies need to pay attention to XXX". Obviously, this mechanical mode of adding sequence cannot truly reflect the substantive connection between paragraphs.

At this point, we have formed a rough expectation of the limitations and upper limits of capabilities of ChatGPT. To put it simply, ChatGPT can quickly summarize phenomena, facts, opinions, etc. in large quantities, and it also has certain logical judgment capabilities.
However, because ChatGPT’s logical judgment mainly relies on linguistic statistics rather than cognitive ability, it often suffers from logical errors, structural confusion, and even inversion of cause and effect, and it is unable to truly explore the deep relationship between information. levels and original connections.
The human brain is responsible for conducting higher-level analysis and summary such as accuracy review, commonality summary, and trend summary on the basic information provided by ChatGPT.
After clarifying the division of roles between humans and ChatGPT, it is not difficult to find a way to maximize the use of ChatGPT to optimize report generation, optimize report content, and then empower work: use the human brain to construct a piece of information necessary to achieve the goal demand chain, and put aside intuition as much as possible to concretely describe the information needs on the chain.
Taking Report 4.1.1 as an example, when we required the report to provide a detailed explanation of the content of data poisoning, we framed the direction of information needs by asking for concrete descriptions such as the causes and asking ChatGPT to give examples.

Summary
Overall, ChatGPT has given us a satisfactory answer, although the training process faces many difficulties and uncertainties. Sex, ChatGPT’s ability to understand and execute instructions is surprising.
FreeBuf Consulting believes that ChatGPT can be used as a starting point for subject analysis and academic research, providing humans with the summary information needed to achieve their goals. Through the huge training database, academic researchers can quickly determine the entry point of the report, which greatly shortens the process of preliminary desktop investigation, data sorting and screening of the report, and provides reference ideas for subsequent research work.
However, ChatGPT’s limitations and upper limit of capabilities are also very obvious. Since the output content of ChatGPT is mainly based on the statistical distribution of contextual words rather than rigorous facts, the authenticity of the results generated by ChatGPT is often not guaranteed, and there are often even logical errors, structural confusion, and inversion of cause and effect.
In addition, due to the lack of non-linear correlation analysis capabilities, ChatGPT cannot truly mine the substantive connections between paragraphs, which leaves an insurmountable gap between it and the human brain. Higher-order analysis behaviors such as accuracy review, commonality induction, and trend summary still require human power to perform.
The above is the detailed content of This article teaches you how to use ChatGPT to quickly write a report. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Tesla's Robovan Was The Hidden Gem In 2024's Robotaxi TeaserApr 22, 2025 am 11:48 AMSince 2008, I've championed the shared-ride van—initially dubbed the "robotjitney," later the "vansit"—as the future of urban transportation. I foresee these vehicles as the 21st century's next-generation transit solution, surpas
 Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AM
Sam's Club Bets On AI To Eliminate Receipt Checks And Enhance RetailApr 22, 2025 am 11:29 AMRevolutionizing the Checkout Experience Sam's Club's innovative "Just Go" system builds on its existing AI-powered "Scan & Go" technology, allowing members to scan purchases via the Sam's Club app during their shopping trip.
 Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Nvidia's AI Omniverse Expands At GTC 2025Apr 22, 2025 am 11:28 AMNvidia's Enhanced Predictability and New Product Lineup at GTC 2025 Nvidia, a key player in AI infrastructure, is focusing on increased predictability for its clients. This involves consistent product delivery, meeting performance expectations, and
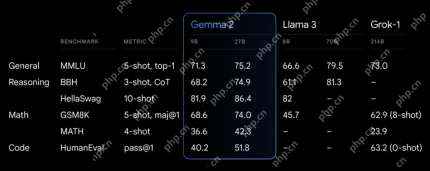 Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AM
Exploring the Capabilities of Google's Gemma 2 ModelsApr 22, 2025 am 11:26 AMGoogle's Gemma 2: A Powerful, Efficient Language Model Google's Gemma family of language models, celebrated for efficiency and performance, has expanded with the arrival of Gemma 2. This latest release comprises two models: a 27-billion parameter ver
 The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AM
The Next Wave of GenAI: Perspectives with Dr. Kirk Borne - Analytics VidhyaApr 22, 2025 am 11:21 AMThis Leading with Data episode features Dr. Kirk Borne, a leading data scientist, astrophysicist, and TEDx speaker. A renowned expert in big data, AI, and machine learning, Dr. Borne offers invaluable insights into the current state and future traje
 AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AM
AI For Runners And Athletes: We're Making Excellent ProgressApr 22, 2025 am 11:12 AMThere were some very insightful perspectives in this speech—background information about engineering that showed us why artificial intelligence is so good at supporting people’s physical exercise. I will outline a core idea from each contributor’s perspective to demonstrate three design aspects that are an important part of our exploration of the application of artificial intelligence in sports. Edge devices and raw personal data This idea about artificial intelligence actually contains two components—one related to where we place large language models and the other is related to the differences between our human language and the language that our vital signs “express” when measured in real time. Alexander Amini knows a lot about running and tennis, but he still
 Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Jamie Engstrom On Technology, Talent And Transformation At CaterpillarApr 22, 2025 am 11:10 AMCaterpillar's Chief Information Officer and Senior Vice President of IT, Jamie Engstrom, leads a global team of over 2,200 IT professionals across 28 countries. With 26 years at Caterpillar, including four and a half years in her current role, Engst
 New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AM
New Google Photos Update Makes Any Photo Pop With Ultra HDR QualityApr 22, 2025 am 11:09 AMGoogle Photos' New Ultra HDR Tool: A Quick Guide Enhance your photos with Google Photos' new Ultra HDR tool, transforming standard images into vibrant, high-dynamic-range masterpieces. Ideal for social media, this tool boosts the impact of any photo,


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools






