Home >Technology peripherals >AI >From Decision Tree to Transformer—Comparison of Sentiment Analysis Models for Restaurant Reviews
From Decision Tree to Transformer—Comparison of Sentiment Analysis Models for Restaurant Reviews
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-05-04 12:31:062007browse
Translator | Zhu Xianzhong
Reviewer| Sun Shujuan
##This articlewillshow various popularThe effectiveness of machine learning models and embedding techniques for sentiment analysis of Macedonian restaurant reviews,Explore and compare several classic machine learning models as well as including neural networks and ## Modern deep learning technology including #Transformers. Experiments show that using the latest OpenAI embedded fine-tuned Transformers models and deep learning models are far Better than other methods.

etcpopular languages;butis the development of less commonly used languages In terms of relatedresearch and applicationof machine learning modelsthere are much less. On the other hand, with the rise of e-commerce due to the COVID-19 epidemic, less common languages such as Macedonian have also generated a large amount of data through online reviews. This provides an opportunity to develop and train machine learning models for sentiment analysis of Macedonian restaurant reviews ; if successful, this could help businesses more Understand customer emotions well and improve related services. In this study, we address the challenges posed by this problem and explore and compare various sentiment analysis models, ranging from classic Random forests to modern deep learning techniques and Transformersetc.
First of all, we give an outline of the content of this article: However, for languages that use Cyrillic (Cyrillic), users on the Internet often The use of Latin scripts to express oneself, resulting in mixed data consisting of Latin and Cyrillic scripts, created an additional challenge. To address this challenge, I used a dataset of a local restaurant with approximately 500 reviews -- which contained both Latin and Cyrillic scripts. The dataset also includes a small set of English comments, which will help evaluate performance on hybrid data. Additionally, online text may contain symbols, such as emoticons, that need to be removed. Therefore, preprocessing is a crucial step before performing any text embedding.
##Machine Learning Model
Random Forest
Results and discussion
Language is a unique form of human communication Tools, computers cannot interpret language without appropriate processing technology. In order for machines to analyze and understand language, we need to represent complex semantic and lexical information in a computably processable way. A popular way to achieve this is to use vector representation. In recent years, in addition to language-specific representation models, multilingual models have emerged. These models can capture the semantic context of text across a wide range of languages.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
#把数据集加载进一个dataframe
df = pd.read_csv('/content/data.tsv', sep='t')
# 注意sentiment类别的分布情况
df['sentiment'].value_counts()
# -------
# 0 337
# 1 322
# Name: sentiment, dtype: int64Notice that the data set contains the
distribution of almost equal positive Negative class. To remove emojis I used Python library emoji which can easily remove emojis and other symbols.
!pip install emoji import emoji clt = [] for comm in df['comment'].to_numpy(): clt.append(emoji.replace_emoji(comm, replace="")) df['comment'] = clt df.head()For the Cyrillic and Latin questions, I converted all the text to one or the other so that the machine learning model could Tested on both to compare performance. I use "cyrtranslit" library to perform this task. It supports most Cyrillic alphabets like Macedonian, Bulgarian, Ukrainian, etc.
import cyrtranslit latin = [] cyrillic = [] for comm in df['comment'].to_numpy(): latin.append(cyrtranslit.to_latin(comm, "mk")) cyrillic.append(cyrtranslit.to_cyrillic(comm, "mk")) df['comment_cyrillic'] = cyrillic df['comment_latin'] = latin df.head()
Figure 1
: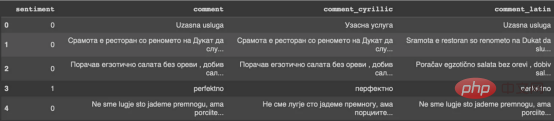 Conversion output
Conversion output
RESULTSFor the embedding models I use, removing punctuation, stop words, and other text cleaning is generally not necessary. These models are designed to process natural language text, including punctuation, and are often able to more accurately capture the meaning of a sentence when it remains intact. In this way, text preprocessing is completed.
矢量嵌入
目前,没有大规模的马其顿语言描述模型可用。然而,我们可以使用基于马其顿语文本训练的多语言模型。当前,有几种这样的模型可用,但对于这项任务,我发现LASER和多语言通用句子编码器是最合适的选择。
LASER
LASER(Language-Agnostic Sentence Representations)是一种生成高质量多语言句子嵌入的语言不可知方法。LASER模型基于两阶段过程。其中,第一阶段是对文本进行预处理,包括标记化、小写和应用句子。这部分是特定于语言的;第二阶段涉及使用多层双向LSTM将预处理的输入文本映射到固定长度的嵌入。
在一系列基准数据集上,LASER已经被证明优于其他流行的句子嵌入方法,如fastText和InferSent。此外,LASER模型是开源的,免费提供,使每个人都可以轻松访问。
使用LASER创建嵌入是一个简单的过程:
!pip install laserembeddings
!python -m laserembeddings download-models
from laserembeddings import Laser
#创建嵌入
laser = Laser()
embeddings_c = laser.embed_sentences(df['comment_cyrillic'].to_numpy(),lang='mk')
embeddings_l = laser.embed_sentences(df['comment_latin'].to_numpy(),lang='mk')
# 保存嵌入
np.save('/content/laser_multi_c.npy', embeddings_c)
np.save('/content/laser_multi_l.npy', embeddings_l)多语言通用句子编码器
多语言通用句子编码器(MUSE)是由Facebook开发的用于生成句子嵌入的预训练模型。MUSE旨在将多种语言的句子编码到一个公共空间中。
该模型基于深度神经网络,该网络使用“编码器-解码器”架构来学习句子与其在高维空间中的对应嵌入向量之间的映射。MUSE是在一个大规模的多语言语料库上训练的,其中包括维基百科的文本、新闻文章和网页。
!pip install tensorflow_text
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import numpy as np
import tensorflow_text
#加载MUSE模型
module_url = "https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder-multilingual-large/3"
embed = hub.load(module_url)
sentences = df['comment_cyrillic'].to_numpy()
muse_c = embed(sentences)
muse_c = np.array(muse_c)
sentences = df['comment_latin'].to_numpy()
muse_l = embed(sentences)
muse_l = np.array(muse_l)
np.save('/content/muse_c.npy', muse_c)
np.save('/content/muse_l.npy', muse_l)OpenAI Ada v2
2022年底,OpenAI宣布了他们全新的最先进嵌入模型text-embedding-ada-002(https://openai.com/blog/new-and-improved-embedding-model/)。由于此模型基于GPT-3构建,因此具有多语言处理能力。为了比较西里尔文和拉丁语评论的结果,我决定在两个数据集上运行了模型:
!pip install openai
import openai
openai.api_key = 'YOUR_KEY_HERE'
embeds_c = openai.Embedding.create(input = df['comment_cyrillic'].to_numpy().tolist(), model='text-embedding-ada-002')['data']
embeds_l = openai.Embedding.create(input = df['comment_latin'].to_numpy().tolist(), model='text-embedding-ada-002')['data']
full_arr_c = []
for e in embeds_c:
full_arr_c.append(e['embedding'])
full_arr_c = np.array(full_arr_c)
full_arr_l = []
for e in embeds_l:
full_arr_l.append(e['embedding'])
full_arr_l = np.array(full_arr_l)
np.save('/content/openai_ada_c.npy', full_arr_c)
np.save('/content/openai_ada_l.npy', full_arr_l)机器学习模型
本节将探讨用于预测马其顿餐厅评论中情绪的各种机器学习模型。从传统的机器学习模型到深度学习技术,我们将研究每个模型的优缺点,并比较它们在数据集上的性能。
在运行任何模型之前,应该先对数据进行分割,以便针对每种嵌入类型进行训练和测试。这可以通过sklearn库轻松完成。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(embeddings_c, df['sentiment'], test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
随机森林
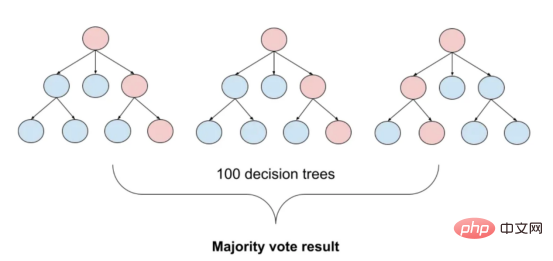
图2:随机森林分类的简化表示。构建100个决策树,并将结果作为每个决策树的结果之间的多数表决进行计算
随机森林是一种广泛使用的机器学习算法,它使用决策树集合对数据点进行分类。该算法通过在完整数据集的子集和特征的随机子集上训练每个决策树来工作。在推理过程中,每个决策树都会生成一个情绪预测,最终的结果是通过对所有树进行多数投票获得的。这种方法有助于防止过度拟合,并可导致更稳健和准确的预测结果。
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100) rfc.fit(X_train, y_train) print(classification_report(y_test,rfc.predict(X_test))) print(confusion_matrix(y_test,rfc.predict(X_test)))
XGBoost
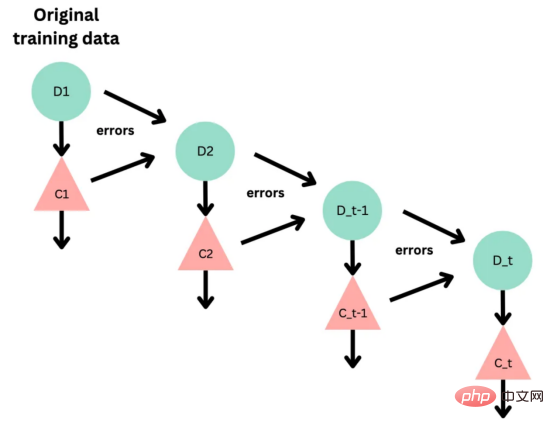
图3:基于boosting算法的顺序过程。每个下一个决策树都基于上一个决策的残差(误差)进行训练
XGBoost(极限梯度增强)是一种强大的集成方法,主要用于表格数据。与随机森林算法模型一样,XGBoost也使用决策树对数据点进行分类,但方法不同。XGBoost不是一次训练所有树,而是以顺序的方式训练每棵树,从上一棵树所犯的错误中学习。这个过程被称为“增强”,这意味着将弱模型结合起来,形成一个更强的模型。虽然XGBoost主要使用表格数据产生了很好的结果,但使用向量嵌入测试该模型也会很有趣。
from xgboost import XGBClassifier from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix rfc = XGBClassifier(max_depth=15) rfc.fit(X_train, y_train) print(classification_report(y_test,rfc.predict(X_test))) print(confusion_matrix(y_test,rfc.predict(X_test)))
支持向量机
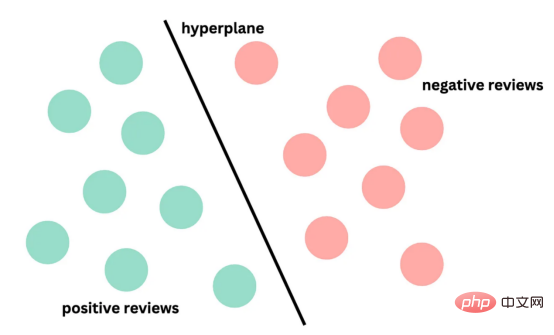
图4:支持向量分类的简化表示。在具有1024个输入特征的这种情绪分析的情况下,超平面将是1023维
支持向量机(SVM)是一种用于分类和回归任务的流行且强大的机器学习算法。它的工作原理是找到将数据分成不同类的最佳超平面,同时最大化类之间的边界。SVM对高维数据特别有用,可以使用核函数处理非线性边界。
from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix rfc = SVC() rfc.fit(X_train, y_train) print(classification_report(y_test,rfc.predict(X_test))) print(confusion_matrix(y_test,rfc.predict(X_test)))
深度学习
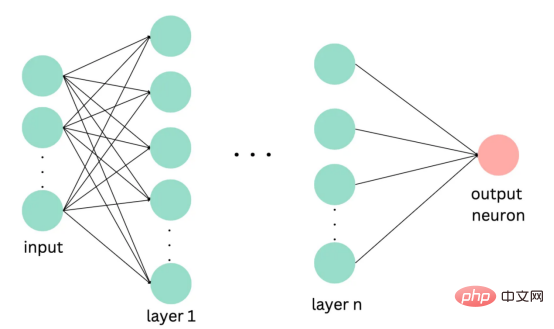
图5:此问题中使用的神经网络的简化表示
深度学习是一种先进的机器学习方法,它利用由多层和神经元组成的人工神经网络。深度学习网络在文本和图像数据方面表现出色。使用Keras库实现这些网络是一个很简单的过程。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(256, activatinotallow='relu', input_shape=(1024,)))
model.add(keras.layers.Dropout(0.2))
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(128, activatinotallow='relu'))
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(1, activatinotallow='sigmoid'))
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=11, validation_data=(X_test, y_test))
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
print('Test accuracy:', test_acc)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test,y_pred.round()))
print(confusion_matrix(y_test,y_pred.round()))在此,使用了具有两个隐藏层和校正线性单元(ReLU)激活函数的神经网络。输出层包含一个具有S形激活函数的神经元,使网络能够对积极或消极情绪进行二元预测。二元交叉熵损失函数与S形激活配对以训练模型。此外,Dropout被用于帮助防止过度拟合和改进模型的泛化。我用各种不同的超参数进行了测试,发现这种配置最适合这个问题。
通过以下函数,我们可以可视化模型的训练。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_accuracy(history):
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'])
plt.title('Model Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Validation'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()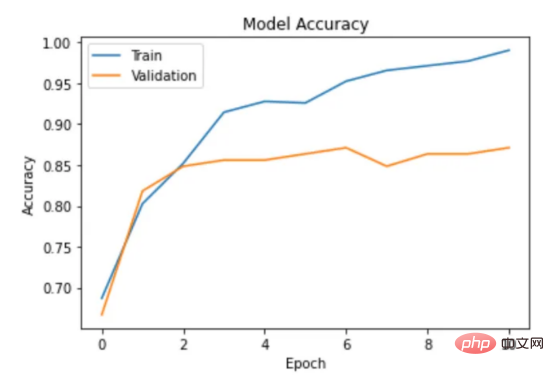
图6:示例训练输出
Transformers
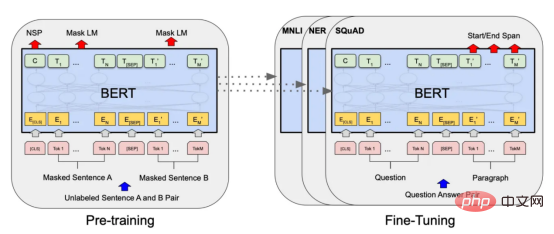
图7:BERT大型语言模型的预训练和微调过程。(BERT原始论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805v2.pdf)
微调Transformers是自然语言处理中的一种流行技术,涉及调整预先训练的变换器模型以适应特定任务。Transformers,如BERT、GPT-2和RoBERTa,在大量文本数据上进行了预训练,能够学习语言中的复杂模式和关系。然而,为了在特定任务(如情绪分析或文本分类)上表现良好,需要根据任务特定数据对这些模型进行微调。
对于这些类型的模型,不需要我们之前创建的向量表示,因为它们直接处理标记(直接从文本中提取)。在马其顿语的情绪分析任务中,我使用了bert-base-multilingual-uncased,这是BERT模型的多语言版本。
HuggingFace使微调Transformers成为一项非常简单的任务。首先,需要将数据加载到Transformers数据集中。然后将文本标记化,最后训练模型。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
# 创建由数据集加载的训练和测试集的csv文件
df.rename(columns={"sentiment": "label"}, inplace=True)
train, test = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2)
pd.DataFrame(train).to_csv('train.csv',index=False)
pd.DataFrame(test).to_csv('test.csv',index=False)
#加载数据集
dataset = load_dataset("csv", data_files={"train": "train.csv", "test": "test.csv"})
# 标记文本
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-multilingual-uncased')
encoded_dataset = dataset.map(lambda t: tokenizer(t['comment_cyrillic'], truncatinotallow=True), batched=True,load_from_cache_file=False)
# 加载预训练的模型
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('bert-base-multilingual-uncased',num_labels =2)
#微调模型
arg = TrainingArguments(
"mbert-sentiment-mk",
learning_rate=5e-5,
num_train_epochs=5,
per_device_eval_batch_size=8,
per_device_train_batch_size=8,
seed=42,
push_to_hub=True
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=arg,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
train_dataset=encoded_dataset['train'],
eval_dataset=encoded_dataset['test']
)
trainer.train()
# 取得预测结果
predictions = trainer.predict(encoded_dataset["test"])
preds = np.argmax(predictions.predictions, axis=-1)
# 评估
print(classification_report(predictions.label_ids,preds))
print(confusion_matrix(predictions.label_ids,preds))因此,我们成功地调整了BERT进行情绪分析。
实验结果与讨论
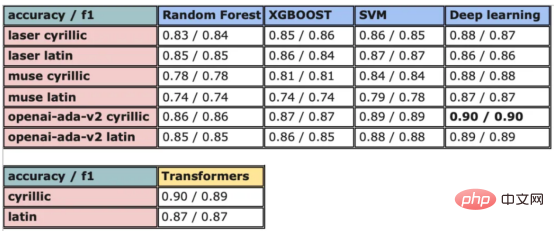
图8:所有模型的结果大对比
实验证明,马其顿餐厅评论的情绪分析结果是很有希望的,从上图中可见,其中有几个模型获得了很高的准确性和F1分数。实验表明,深度学习模型和变换器的性能优于传统的机器学习模型,如随机森林和支持向量机,尽管相差不大。使用新OpenAI嵌入的Transformers和深度神经网络成功打破了0.9精度的障碍。
OpenAI嵌入模型textembedding-ada-002成功地极大提高了从经典ML模型获得的结果,尤其是在支持向量机上。本研究中的最佳结果是在深度学习模型上嵌入西里尔文文本。
一般来说,拉丁语文本的表现比西里尔语文本差。尽管我最初假设这些模型的性能会更好,但考虑到拉丁语中类似单词在其他斯拉夫语言中的流行,以及嵌入模型是基于这些数据训练的事实,这些发现并不支持这一假设。
Future Work
In future work, it would be very valuable to collect more data to further train and test the model, especially if the review topics and sources are more diverse in the case of. Additionally, trying to incorporate more features such as metadata (e.g., age, gender, location of the reviewer) or temporal information (e.g., review time) into the model may improve its accuracy. Finally, it would be interesting to extend the analysis to other less commonly used languages and compare the performance of the model with the model trained in the Macedonian review. Conclusion
This article demonstrates various popularmachine learning models and effectiveness of embedding techniques for sentiment analysis of Macedonian restaurant reviews. Several classic machine learning models, such as random forests and SVMs, are explored and compared, as well as modern deep learning techniques including neural networks and Transformers. The results show that fine-tuned Transformers models and deep learning models using the latest OpenAI embeddings outperform other methods, with verification accuracy as high as 90%. Translator Introduction
Zhu Xianzhong, 51CTO community editor, 51CTO expert blogger, lecturer, computer teacher at a university in Weifang, freelance programming A veteran of the world. Original title:
From Decision Trees to Transformers: Comparing Sentiment Analysis Models for Macedonian Restaurant Reviews , Author: Danilo Najkov
The above is the detailed content of From Decision Tree to Transformer—Comparison of Sentiment Analysis Models for Restaurant Reviews. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Technology trends to watch in 2023
- How Artificial Intelligence is Bringing New Everyday Work to Data Center Teams
- Can artificial intelligence or automation solve the problem of low energy efficiency in buildings?
- OpenAI co-founder interviewed by Huang Renxun: GPT-4's reasoning capabilities have not yet reached expectations
- Microsoft's Bing surpasses Google in search traffic thanks to OpenAI technology

