 Backend Development
Backend Development Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial How to use Jieba for word frequency statistics and keyword extraction in Python
How to use Jieba for word frequency statistics and keyword extraction in PythonHow to use Jieba for word frequency statistics and keyword extraction in Python
1 Word frequency statistics
1.1 Simple word frequency statistics
1. Import the jieba library and define the text
import jieba text = "Python是一种高级编程语言,广泛应用于人工智能、数据分析、Web开发等领域。"
2. Segment the text
words = jieba.cut(text)
This step will divide the text into several words and return a generator object words. You can use for to loop through all the words.
3. Count word frequency
word_count = {}
for word in words:
if len(word) > 1:
word_count[word] = word_count.get(word, 0) + 1This step traverses all words, counts the number of times each word appears, and saves it to a dictionaryword_count. When counting word frequencies, optimization can be performed by removing stop words. Here, words with a length less than 2 are simply filtered.
4. Result output
for word, count in word_count.items():
print(word, count)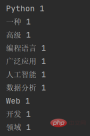
1.2 Add stop words
In order to count the word frequency more accurately, we can count the word frequency in the word frequency statistics Add stop words to remove some common but meaningless words. The specific steps are as follows:
Define the stop word list
import jieba # 停用词列表 stopwords = ['是', '一种', '等']
Segment the text and filter the stop words
text = "Python是一种高级编程语言,广泛应用于人工智能、数据分析、Web开发等领域。" words = jieba.cut(text) words_filtered = [word for word in words if word not in stopwords and len(word) > 1]
Count word frequencies and output the results
word_count = {}
for word in words_filtered:
word_count[word] = word_count.get(word, 0) + 1
for word, count in word_count.items():
print(word, count)After adding stop words, the output result is:
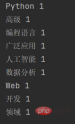
It can be seen that the disabled word kind of is not displayed.
2 Keyword Extraction
2.1 Keyword Extraction Principle
Different from word frequency statistics that simply count words, jieba’s principle of keyword extraction is based on TF-IDF ( Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) algorithm. The TF-IDF algorithm is a commonly used text feature extraction method that can measure the importance of a word in the text.
Specifically, the TF-IDF algorithm contains two parts:
Term Frequency: refers to the number of times a word appears in the text, usually using a Simple statistical value representation, such as word frequency, bigram word frequency, etc. Word frequency reflects the importance of a word in the text, but ignores the prevalence of the word in the entire corpus.
Inverse Document Frequency: refers to the reciprocal of the frequency of a word appearing in all documents, and is used to measure the prevalence of a word. The greater the inverse document frequency, the more common a word is and the lower the importance; the smaller the inverse document frequency is, the more unique the word is and the higher the importance.
The TF-IDF algorithm calculates the importance of each word in the text by comprehensively considering word frequency and inverse document frequency to extract keywords. In jieba, the specific implementation of keyword extraction includes the following steps:
Perform word segmentation on the text and obtain the word segmentation results.
Count the number of times each word appears in the text and calculate the word frequency.
Count the number of times each word appears in all documents and calculate the inverse document frequency.
Comprehensive consideration of word frequency and inverse document frequency, calculate the TF-IDF value of each word in the text.
Sort the TF-IDF values and select the words with the highest scores as keywords.
For example:
F (Term Frequency) refers to the frequency of a certain word appearing in a document. The calculation formula is as follows:
T F = (number of times a word appears in the document) / (total number of words in the document)
For example, in a document containing 100 words, a certain word appears 10 times , then the TF of the word is
10 / 100 = 0.1
IDF (Inverse Document Frequency) refers to the reciprocal of the number of documents in which a certain word appears in the document collection. The calculation formula is as follows:
I D F = log (total number of documents in the document collection/number of documents containing the word)
For example, in a document collection containing 1,000 documents, a certain word appears in 100 documents If so, the IDF of the word is log (1000 / 100) = 1.0
TFIDF is the result of multiplying TF and IDF. The calculation formula is as follows:
T F I D F = T F ∗ I D F
It should be noted that the TF-IDF algorithm only considers the occurrence of words in the text and ignores the correlation between words. Therefore, in some specific application scenarios, other text feature extraction methods need to be used, such as word vectors, topic models, etc.
2.2 Keyword extraction code
import jieba.analyse
# 待提取关键字的文本
text = "Python是一种高级编程语言,广泛应用于人工智能、数据分析、Web开发等领域。"
# 使用jieba提取关键字
keywords = jieba.analyse.extract_tags(text, topK=5, withWeight=True)
# 输出关键字和对应的权重
for keyword, weight in keywords:
print(keyword, weight)In this example, we first imported the jieba.analyse module, and then defined a text to be extracted for keywordstext. Next, we use the jieba.analyse.extract_tags() function to extract keywords, where the topK parameter indicates the number of keywords to be extracted, and the withWeight parameter indicates whether Returns the weight value of the keyword. Finally, we iterate through the keyword list and output each keyword and its corresponding weight value.
The output result of this function is:
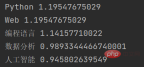
As you can see, jieba extracted several keywords in the input text based on the TF-IDF algorithm, and returned the weight value of each keyword.
The above is the detailed content of How to use Jieba for word frequency statistics and keyword extraction in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython is an interpreted language, but it also includes the compilation process. 1) Python code is first compiled into bytecode. 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by Python virtual machine. 3) This hybrid mechanism makes Python both flexible and efficient, but not as fast as a fully compiled language.
 Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseaforloopwheniteratingoverasequenceorforaspecificnumberoftimes;useawhileloopwhencontinuinguntilaconditionismet.Forloopsareidealforknownsequences,whilewhileloopssuitsituationswithundeterminediterations.
 Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMPythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyinglistsduringiteration,off-by-oneerrors,zero-indexingissues,andnestedloopinefficiencies.Toavoidthese:1)Use'i
 For loop and while loop in Python: What are the advantages of each?May 13, 2025 am 12:01 AM
For loop and while loop in Python: What are the advantages of each?May 13, 2025 am 12:01 AMForloopsareadvantageousforknowniterationsandsequences,offeringsimplicityandreadability;whileloopsareidealfordynamicconditionsandunknowniterations,providingcontrolovertermination.1)Forloopsareperfectforiteratingoverlists,tuples,orstrings,directlyacces
 Python: A Deep Dive into Compilation and InterpretationMay 12, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: A Deep Dive into Compilation and InterpretationMay 12, 2025 am 12:14 AMPythonusesahybridmodelofcompilationandinterpretation:1)ThePythoninterpretercompilessourcecodeintoplatform-independentbytecode.2)ThePythonVirtualMachine(PVM)thenexecutesthisbytecode,balancingeaseofusewithperformance.
 Is Python an interpreted or a compiled language, and why does it matter?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Is Python an interpreted or a compiled language, and why does it matter?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AMPythonisbothinterpretedandcompiled.1)It'scompiledtobytecodeforportabilityacrossplatforms.2)Thebytecodeistheninterpreted,allowingfordynamictypingandrapiddevelopment,thoughitmaybeslowerthanfullycompiledlanguages.
 For Loop vs While Loop in Python: Key Differences ExplainedMay 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM
For Loop vs While Loop in Python: Key Differences ExplainedMay 12, 2025 am 12:08 AMForloopsareidealwhenyouknowthenumberofiterationsinadvance,whilewhileloopsarebetterforsituationswhereyouneedtoloopuntilaconditionismet.Forloopsaremoreefficientandreadable,suitableforiteratingoversequences,whereaswhileloopsoffermorecontrolandareusefulf
 For and While loops: a practical guideMay 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
For and While loops: a practical guideMay 12, 2025 am 12:07 AMForloopsareusedwhenthenumberofiterationsisknowninadvance,whilewhileloopsareusedwhentheiterationsdependonacondition.1)Forloopsareidealforiteratingoversequenceslikelistsorarrays.2)Whileloopsaresuitableforscenarioswheretheloopcontinuesuntilaspecificcond


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool






