 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Machine learning is unlocking the mysteries of the universe in surprising ways
Machine learning is unlocking the mysteries of the universe in surprising waysMachine learning is unlocking the mysteries of the universe in surprising ways

Space travel, exploration and observation often involve a series of the most complex and dangerous scientific and technological operations in human history. In these areas, artificial intelligence (AI) has proven itself to be a powerful assistant.

That’s why astronauts, scientists, and others whose mission is to explore and document the ultimate frontier are turning to machine learning (ML) to help deal with the challenges they face. Extraordinary challenge.
From guiding rockets through space to studying the surfaces of distant planets, to measuring the size of the universe and calculating the motion trajectories of celestial bodies, AI has many interesting and exciting application scenarios in space.
Space Voyage
During the take-off and landing process of a spacecraft, AI can automate engine operations and manage the actual deployment of functions such as landing gear, thereby optimizing the distribution and use of fuel.
SpaceX used the AI pilot system to achieve autonomous operation of its Falcon 9 spacecraft, and successfully docked with the International Space Station (ISS) in accordance with the cargo delivery contract signed with NASA. The system is able to calculate a rocket's trajectory through space, taking into account fuel use, atmospheric disturbances and liquid "sloshing" inside the engine.
CIMON 2 is a robot designed by Airbus, which is equivalent to a mobile Amazon Alexa virtual assistant next to astronauts. Built using the IBM Watson AI system, it uses an internal fan to propel itself forward and can act as a hands-free information database, computer and camera. It can even assess the mood and state of mind of astronauts by analyzing stress levels in their voices.
Mission planners at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory use AI to model and evaluate various mission parameters to understand the potential outcomes of different options and courses of action. These experiments can provide guidance information for future spacecraft design and engineering operations. The data collected can also be used for forward planning of a number of hypothetical future missions, including landings on Venus and Europa, the icy moon orbiting Jupiter.
SpaceX also uses AI algorithms to ensure that its Starlink satellites do not collide with other orbiting or transition vehicles in space. Their autonomous navigation system can detect nearby hazards in real time and adjust the satellite's speed and orbit to take evasive action.
The UK Space Agency has also developed autonomous systems that allow its spacecraft and satellites to avoid space debris through autonomous actions. By 2025, the British Space Agency plans to launch an autonomous spacecraft on this basis with the mission of capturing and cleaning up space debris. If not proactively controlled, space debris is likely to pose a threat to future spaceflight.
Planet Exploration
Mars rovers are robots designed to explore the surface of Mars. We can analyze and learn from the data they send back to Earth. Thanks to machine learning algorithms, these robots can navigate autonomously on the Martian surface, avoiding deep pits and steep walls that could damage or immobilize their hardware. The Spirit rover previously sent to Mars was stuck on the spot when its wheels got stuck in soft soil. NASA finally decided to give up rescue and contact in 2011. With the help of machine learning technology, NASA has successfully avoided the unexpected loss of another rover.
In recent years, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory has used image recognition tools to study images taken by ground robots such as Mars rovers and classify terrain features. They even discovered a crater on the surface of Mars only four meters in diameter.
The Perseverance rover is equipped with a computer vision system called AEGIS that can detect and classify different rock types found on the surface of Mars, allowing us to learn more about the geological composition of the red planet.
You can even participate in training the AI algorithm used by the Mars rover at home. The AI4Mars project invites users to download tools to improve the autonomous navigation system on the Curiosity rover by marking terrain features on their personal computers.
While most surface exploration so far has been accomplished with wheeled robots, the European Space Agency is experimenting with the use of "hopping" robots. These robots can use their legs to move forward and jump. AI algorithms will coordinate the movement and balance of the robot's limbs to explore previously inaccessible locations on the moon, such as the Aristarchus Plateau on the moon, which was formed by a huge crater.
People have begun to use AI to detect the lunar surface and determine the best landing sites for future manned missions. This also helps astronauts fully understand the environment in which they will land in the future, and they do not have to face huge risks like the first generation of lunar lander such as Armstrong.
Charting the Universe
Astronomers are using AI to identify patterns in star clusters in distant nebulae, combined with other classified features detected in deep space to map the universe.
Take NASA's Kepler telescope as an example. It can determine the possible location of a planet by analyzing the attenuation of light radiation emitted by a star.
AI is also used to predict the activity of stars and galaxies, helping us understand the potential locations of cosmic events such as supernova explosions.
By analyzing the timing of the gravitational waves produced when these mysterious objects collide with neutron stars, researchers have detected the existence of dozens of black holes.
AI technology is also used to overlook the earth and the entire universe. The Autonomous Sciencecraft Experiment project, which began operation in 2004, is connected to the Earth Prediction 1 satellite, allowing it to automatically classify images captured by cameras, and then determine which images are more worthy of spending precious bandwidth transmission Return to Earth.
The SETI@Home project at the University of California, Berkeley, uses AI algorithms to process large amounts of data generated by radio telescopes, hoping to search for signs of extraterrestrial intelligence in space. Although the project has stopped sending new data to volunteers for inspection, there is still a large amount of data that has not been analyzed and retrieved, so the exciting truth may lie in this material!
AI was also used to create the most accurate image of a black hole to date. Roger Penrose, Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Ghez won the 2020 Nobel Prize for creating realistic images of the supermassive black hole at the center of the M87 galaxy.
The application scope of AI goes far beyond this. Researchers now hope to go beyond the event horizon and use AI technology to reveal what is going on inside a black hole. The work will also involve quantum computing and is expected to help physicists solve one of the most central problems in the field - unifying Einstein's general theory of relativity with the Standard Model of particle physics.
People even hope that AI can help measure the universe and better grasp its size and shape. Using an AI supercomputer to study astronomical data from Japan, we have successfully created a simulated star map that matches the known existence of the universe. This means we can predict the characteristics of the universe and move beyond the current boundaries of exploration that are hampered by the speed of light limit (i.e., the observable universe).
The above is the detailed content of Machine learning is unlocking the mysteries of the universe in surprising ways. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AM
Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis article explores the growing concern of "AI agency decay"—the gradual decline in our ability to think and decide independently. This is especially crucial for business leaders navigating the increasingly automated world while retainin
 How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AM
How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AMEver wondered how AI agents like Siri and Alexa work? These intelligent systems are becoming more important in our daily lives. This article introduces the ReAct pattern, a method that enhances AI agents by combining reasoning an
 Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM"I think AI tools are changing the learning opportunities for college students. We believe in developing students in core courses, but more and more people also want to get a perspective of computational and statistical thinking," said University of Chicago President Paul Alivisatos in an interview with Deloitte Nitin Mittal at the Davos Forum in January. He believes that people will have to become creators and co-creators of AI, which means that learning and other aspects need to adapt to some major changes. Digital intelligence and critical thinking Professor Alexa Joubin of George Washington University described artificial intelligence as a “heuristic tool” in the humanities and explores how it changes
 Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AM
Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AMLangChain is a powerful toolkit for building sophisticated AI applications. Its agent architecture is particularly noteworthy, allowing developers to create intelligent systems capable of independent reasoning, decision-making, and action. This expl
 What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AM
What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AMRadial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs): A Comprehensive Guide Radial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs) are a powerful type of neural network architecture that leverages radial basis functions for activation. Their unique structure make
 The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AMBrain-computer interfaces (BCIs) directly link the brain to external devices, translating brain impulses into actions without physical movement. This technology utilizes implanted sensors to capture brain signals, converting them into digital comman
 Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis "Leading with Data" episode features Ines Montani, co-founder and CEO of Explosion AI, and co-developer of spaCy and Prodigy. Ines offers expert insights into the evolution of these tools, Explosion's unique business model, and the tr
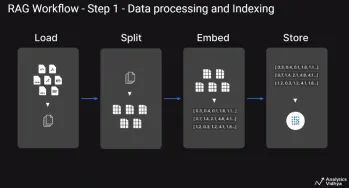 A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AMThis article explores Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems and how AI agents can enhance their capabilities. Traditional RAG systems, while useful for leveraging custom enterprise data, suffer from limitations such as a lack of real-time dat


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool





