Home >Technology peripherals >AI >'Science' announces the top ten breakthroughs of the year, AIGC and AI for science win
'Science' announces the top ten breakthroughs of the year, AIGC and AI for science win
- 王林forward
- 2023-04-14 09:01:051559browse
Just now, "Science" selected the top ten scientific breakthroughs of 2022.
The two popular research directions that have won a place for artificial intelligence this year are AI-generated content (AIGC) and AI-accelerated scientific discovery.

Artistic creation and scientific discovery were once considered two areas that were difficult for artificial intelligence to enter, because they require human intelligence and creativity. But now, AI is already doing a great job in both directions.
The most researched in the field of AIGC in 2022 is undoubtedly the text-to-image generation model. Such models use machine learning to analyze text and image pairings online, finding patterns that create new images based on new text.
Starting from the 2021 OpenAI demonstration of DALL·E generating an "avocado-shaped chair", the text-to-image generation model has entered a new stage.

In April 2022, OpenAI released an upgraded version of the model DALL·E 2. DALL·E 2 is built on CLIP and uses a process called diffusion to generate images from "noise".
DALL·E 2 can produce realistic pictures efficiently. A variety of diffusion models have been released this year, and companies such as Meta and Google have also released diffusion models that can generate videos.
The picture below is "Space Opera" generated by the text-to-image generation model Midjourney. The 39-year-old game designer Jason Allen won the award held in Colorado, USA for this AI-generated painting. Art Fair Digital Art Category Champion.
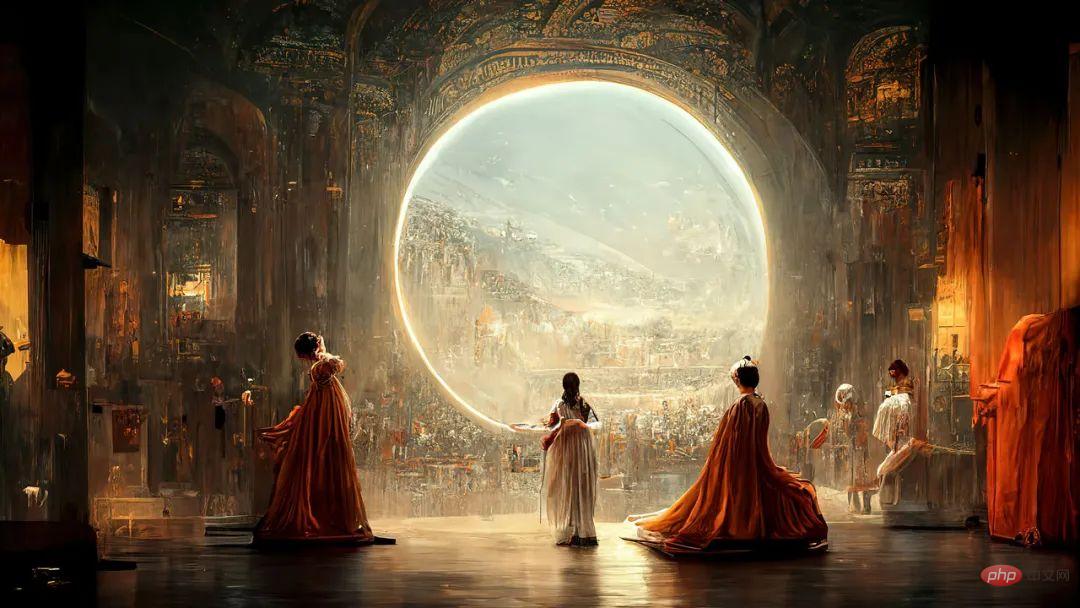

The development of the AIGC model in 2022 has triggered people’s attention and ethical thinking about the art of AI creation.
On the other hand, AI models in science, mathematics, and programming also continued their progress in 2021. Science's top 10 breakthroughs of the year in 2021 include AlphaFold, an AI model that predicts protein structures. Building on this work, researchers have now used artificial intelligence to design entirely new proteins that could be used in vaccines, building materials or nanomachines.
In a paper published in Science in September this year, researchers such as David Baker, professor of biochemistry at the University of Washington School of Medicine, proposed that AI can design proteins from scratch through two ideas. One technique, called "fantasy," starts with random sequences and then mutates them into sequences that other AI tools are confident will fold into stable proteins.
They designed a new algorithm "ProteinMPNN" for generating amino acid sequences, which can start computing within 1 second, which is more than 200 times faster than the previous top software. times.
At the same time, DeepMind released a tool called AlphaTensor. It discovers shortcuts that human mathematicians have ignored for decades, allowing the design of more efficient algorithms for matrix multiplication blocks. Matrix multiplication is a core component of many computing tasks, including computer graphics, digital communications, neural network training, and scientific computing, and the algorithms discovered by AlphaTensor can significantly improve computing efficiency in these fields.

According to DeepMind, AlphaTensor is built on AlphaZero. This work demonstrates AlphaZero's transition from being used for gaming to being used for the first time to solve difficult mathematical problems.
Although AlphaTensor was initially focused on the specific problem of matrix multiplication, DeepMind said it hopes to inspire more people to use AI to guide algorithm discovery for other basic computing tasks. Moreover, DeepMind’s research also shows that AlphaZero’s powerful algorithm goes far beyond the realm of traditional games and can help solve open problems in the field of mathematics.
DeepMind also launched AlphaCode, a system that can be programmed to solve numerical problems, such as counting how many binary strings of a given length do not have consecutive zeros. AlphaCode uses a model trained on previous programs and their descriptions to generate a number of candidate programs and then picks the most promising ones.
Last week, AlphaCode’s research was officially published in Science.

AlphaCode’s performance is average compared to human programmers. DeepMind researchers put AlphaCode to the test in the Codeforces challenge, a programming competition platform. AlphaCode was tested against 10 challenges solved by 5,000 users on the Codeforces website. The overall ranking was in the top 54.3%, beating 46% of the contestants.
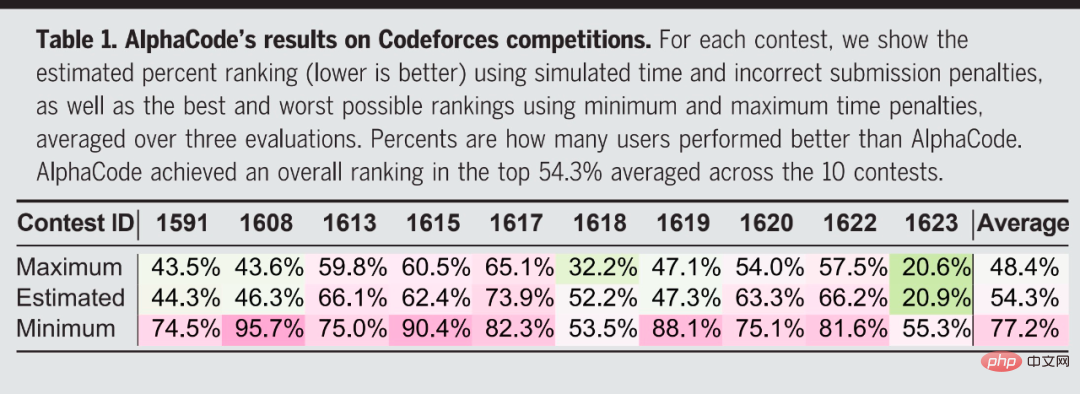
Although it failed to win the competition, this result represents a substantial leap in the ability of artificial intelligence to solve problems and proves that deep learning models are needed potential in critical thinking tasks.
DeepMind noted that AlphaCode’s current skill set is currently only applicable to competitive programming fields, but its capabilities open new doors to create future tools that make programming accessible. Easier and one day fully automated.
In addition to the debate over whether these feats count as true creativity, they also raise practical and ethical dilemmas. Some observers worry that these artificially crafted programmers and artists could infringe copyrights, perpetuate stereotypes, spread misinformation or eliminate jobs. But there is no doubt that humans will use these tools to expand their creativity, just as they did with looms, cameras, and other once disturbing inventions.
The above is the detailed content of 'Science' announces the top ten breakthroughs of the year, AIGC and AI for science win. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Technology trends to watch in 2023
- How Artificial Intelligence is Bringing New Everyday Work to Data Center Teams
- Can artificial intelligence or automation solve the problem of low energy efficiency in buildings?
- OpenAI co-founder interviewed by Huang Renxun: GPT-4's reasoning capabilities have not yet reached expectations
- Microsoft's Bing surpasses Google in search traffic thanks to OpenAI technology

