 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI For robots to learn coffee latte art, we have to start with fluid mechanics! CMU&MIT launches fluid simulation platform
For robots to learn coffee latte art, we have to start with fluid mechanics! CMU&MIT launches fluid simulation platformFor robots to learn coffee latte art, we have to start with fluid mechanics! CMU&MIT launches fluid simulation platform
Robots can also do the work of baristas!
For example, let it stir the milk foam and coffee evenly. The effect is like this:

Then make it more difficult, make a latte, and then stir it It is easy to make a pattern with a stick:

These are based on a study that has been accepted as Spotlight by ICLR 2023. They launched the proposed fluid Control the new benchmark FluidLab and the multi-material differentiable physics engine FluidEngine.
The research team members come from CMU, Dartmouth College, Columbia University, MIT, MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab, and the University of Massachusetts Amherst.

With the support of FluidLab, it will be easy for robots to handle fluid work in more complex scenarios in the future.
What are the "hidden skills" of FluidLab? Let’s have fun together~
"Fluid Mechanics" Advanced Player
FluidLab relies on FluidEngine as the engine support. As the name says, the main simulation object is fluid, different materials, and various types. It can fully grasp the details of sports.
Let’s try simulating various scenes of making coffee. The movement trajectories of coffee and milk foam are also very realistic.

Of course, simulating ice cream is also a matter of sprinkling water.

Or simulate the movement trajectory of water flow under different conditions.

If you still can’t see the strength of FluidLab, then go straight to the difficulty level.
For example, let’s start with a comparison simulation and let the platform simulate the collision of different materials with the container when they fall. From left to right they are: hard materials, elastic materials and plastics.

Or the trajectories of different non-viscous liquids and viscous liquids when they fall.

#More difficult and simulate the state when gas and liquid meet.

Easily done!
At this time, some friends may wonder: Does the simulation in so many states conform to physics or fluid mechanics?
You can rest assured that the research team directly disclosed the verification video. When it comes to some specific physical phenomena, FluidEngine can accurately simulate it.
Common physical phenomena such as Karman vortex and dam failure can be accurately simulated.

Buoyancy, incompressibility and volume stability of liquids can also be easily reflected in the simulation.

Come to the advanced level, use the Magnus effect to verify: translation, slow counterclockwise rotation of translation, fast counterclockwise rotation of translation, and fast clockwise rotation of translation. All accurate.

Add 100 million points more difficulty and try conservation of momentum and Rayleigh-Taylor instability.
......
How did the research team achieve such a simulation that is so close to the real world?
Different states have different algorithms
First of all, in terms of programming language, FluidEngine chose Python and Taichi. Taichi is a recently proposed domain-specific programming language for GPU accelerated simulation.
This provides a user-friendly set of APIs for building simulation environments. At a higher level, it also follows the standard OpenAI Gym API and is compatible with standard reinforcement learning and optimization algorithms. .
The reason why it is possible to achieve realistic virtual simulation effects can perhaps be gleaned from the process of creating an environment with FluidEngine.
The environment it creates consists of five parts:
- A robot agent equipped with a user-defined end effector (an external robot)
- From the external network Objects imported from the grid and represented as signed distance fields (SDFs)
- Objects created using shape primitives or external meshes, used to represent particles
- For simulations on Eulerian meshes Gas fields for gas phenomena (including velocity fields and other advection fields such as smoke density and temperature)
- A set of user-defined geometric boundaries to support sparse calculations
where, During the simulation process, different calculation methods are used for materials in different states.
For solid and liquid materials, the simulation process uses the moving least squares material point method (MLS-MPM), which is a hybrid Lagrangian-Eulerian method that uses particles and meshes to simulate continuous body material.
For gases such as smoke or air, the advection-projection scheme is used in the simulation process to simulate them as incompressible fluids on a Cartesian grid.
In this way, realistic effects can be simulated for specific situations.
The paper, project address and code link are attached at the end of the article. Interested friends can click to view.
Project homepage: https://fluidlab2023.github.io/Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.02346 Code link: https://github.com/zhouxian/FluidLab
The above is the detailed content of For robots to learn coffee latte art, we have to start with fluid mechanics! CMU&MIT launches fluid simulation platform. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AM
Are You At Risk Of AI Agency Decay? Take The Test To Find OutApr 21, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis article explores the growing concern of "AI agency decay"—the gradual decline in our ability to think and decide independently. This is especially crucial for business leaders navigating the increasingly automated world while retainin
 How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AM
How to Build an AI Agent from Scratch? - Analytics VidhyaApr 21, 2025 am 11:30 AMEver wondered how AI agents like Siri and Alexa work? These intelligent systems are becoming more important in our daily lives. This article introduces the ReAct pattern, a method that enhances AI agents by combining reasoning an
 Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Revisiting The Humanities In The Age Of AIApr 21, 2025 am 11:28 AM"I think AI tools are changing the learning opportunities for college students. We believe in developing students in core courses, but more and more people also want to get a perspective of computational and statistical thinking," said University of Chicago President Paul Alivisatos in an interview with Deloitte Nitin Mittal at the Davos Forum in January. He believes that people will have to become creators and co-creators of AI, which means that learning and other aspects need to adapt to some major changes. Digital intelligence and critical thinking Professor Alexa Joubin of George Washington University described artificial intelligence as a “heuristic tool” in the humanities and explores how it changes
 Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AM
Understanding LangChain Agent FrameworkApr 21, 2025 am 11:25 AMLangChain is a powerful toolkit for building sophisticated AI applications. Its agent architecture is particularly noteworthy, allowing developers to create intelligent systems capable of independent reasoning, decision-making, and action. This expl
 What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AM
What are the Radial Basis Functions Neural Networks?Apr 21, 2025 am 11:13 AMRadial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs): A Comprehensive Guide Radial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNNs) are a powerful type of neural network architecture that leverages radial basis functions for activation. Their unique structure make
 The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
The Meshing Of Minds And Machines Has ArrivedApr 21, 2025 am 11:11 AMBrain-computer interfaces (BCIs) directly link the brain to external devices, translating brain impulses into actions without physical movement. This technology utilizes implanted sensors to capture brain signals, converting them into digital comman
 Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Insights on spaCy, Prodigy and Generative AI from Ines MontaniApr 21, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis "Leading with Data" episode features Ines Montani, co-founder and CEO of Explosion AI, and co-developer of spaCy and Prodigy. Ines offers expert insights into the evolution of these tools, Explosion's unique business model, and the tr
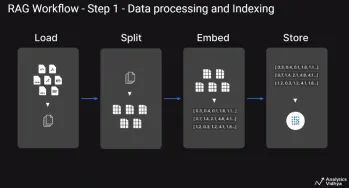 A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
A Guide to Building Agentic RAG Systems with LangGraphApr 21, 2025 am 11:00 AMThis article explores Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems and how AI agents can enhance their capabilities. Traditional RAG systems, while useful for leveraging custom enterprise data, suffer from limitations such as a lack of real-time dat


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software





