Home >Common Problem >what is gsm network
what is gsm network
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2022-09-30 12:10:4930682browse
gsm network is a 2G network. GSM network refers to the Global System for Mobile Communications, also known as "Global Communication". It is a mobile communication technology standard originated in Europe. It is the second generation mobile communication technology and the first in the world to integrate digital modulation, network layer structure and business operations. A network of specified cellular systems. The GSM network is a network that adopts hierarchical control. A GSM network is divided into three network subsystems (NSS, BSS and MS, NMS).

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
gsm network is a 2G network.
GSM network introduction
GSM network is the abbreviation of Global System for Mobile Communications, Chinese is the Global System for Mobile Communications, commonly known as " "Global Communication" is a digital mobile communication standard formulated by ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute). It is the second generation of mobile communication technology. Its air interface uses time division multiple access technology. The GSM network is the world's first cellular system network that specifies digital modulation, network layer structure and services.
Since it was put into commercial use in the mid-1990s, it has been adopted by more than 100 countries around the world. The ubiquity of the GSM standard has made it commonplace for users to roam internationally following roaming agreements between mobile phone operators. The biggest difference between GSM and its previous standards is that its signaling and voice channels are digital, so GSM is considered a second-generation (2G) mobile phone system.

System composition
The GSM system mainly consists of mobile station (MS), mobile network subsystem (NSS), base station subsystem (BSS) and operation and maintenance center (OMC). ) composed of four parts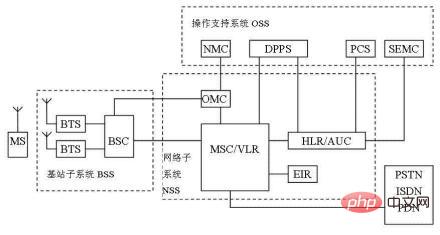
- Mobile station (MS) MS is a device used by users in the public GSM mobile communication network, and is also Users have direct access to equipment in the entire GSM system. The types of mobile stations include not only handheld stations, but also vehicle-mounted stations and portable stations. With the development trend of GSM standard digital handheld stations becoming further small, lightweight and adding functions, the users of handheld stations will account for a large part of the total users [4] .
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS)The Base Station Subsystem (BSS) is the basic component of the GSM system that is most directly related to the wireless cellular aspect. It is directly connected to the mobile station through the wireless interface and is responsible for wireless transmission and reception and wireless resource management. On the other hand, the base station subsystem is connected to the mobile service switching center (MSC) in the network subsystem (NSS) to realize communication connections between mobile users or between mobile users and fixed network users, and transmit system signals and user information, etc. . Of course, to operate, maintain and manage the BSS part, it is also necessary to establish a communication connection between the BSS and the operation support subsystem (OSS).
- Mobile Network Subsystem (NSS)
NSS consists of Mobile Services Switching Center (MSC), Home Location Register (HLR), Visited Location Register (VLR), Authentication Center (AUC), Equipment Identification Register (EIR), Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC-S) and Composed of Short Message Service Center (SC). MSC is a functional entity that controls and exchanges traffic for MSs located in its coverage area. It is also an interface entity between the mobile communication network and other communication networks. It is responsible for call control, mobility management and wireless resource management within the entire MSC area. VLR is a dynamic database that stores information about users and call processing entering its coverage area. In order to process the incoming and outgoing calls of the MS located in this coverage area, the MSC needs to retrieve information from the VLR. Usually the VLR and the MSC are co-located in the same physical entity. HLR is a database used for mobile user management. Each mobile user should be registered in its home location register. HLR mainly stores two types of information, one is the user's business information, and the other is the user's location information.
-
Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC)
The Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC), also known as OSS or M2000, needs to complete many tasks, including mobile user management, mobile device management, and Network operations and maintenance. [4] Mobile subscriber management includes user data management and call billing. Mobile device management requires interaction between some or all basic devices. Network operation and maintenance promotes calls by mediating between operators and all devices.
The difference between 2G and 3G
##3G is the abbreviation of 3rd Generation in English, which refers to the third generation of mobile communication technology . Compared with the first generation of analog mobile phones (1G) and the second generation of digital mobile phones (2G) such as GSM and CDMA, the third generation of mobile phones generally refers to a new generation of mobile communication systems that combine wireless communications with multimedia communications such as the Internet. . It can handle a variety of media forms such as images, music, and video streams, and provides a variety of information services including web browsing, teleconferencing, and e-commerce. In order to provide this service, the wireless network must be able to support different data transmission speeds, which means that it can support at least 2Mbps (megabits per second) and 384kbps (kilobits per second) in indoor, outdoor and driving environments respectively. And a transmission speed of 144kbps (kilobits per second). 2G (second generation) represents the second generation of mobile communication technology. Represented by GSM. Taking digital voice transmission technology as the core.Expand knowledge: mobile communications
Mobile communications (mobile communications) Communication between mobile users and fixed point users or between mobile users Way. Mobile communication is a modern technology for wireless communication. This technology is one of the important achievements of the development of electronic computers and mobile Internet. Mobile communication technology has developed through the first, second, third and fourth generation technologies. At present, it has entered the era of fifth generation development (5G mobile communication technology), which are also several types of technologies that are currently changing the world. One of the main technologies. Modern mobile communication technology can be mainly divided into several frequency bands: low frequency, medium frequency, high frequency, very high frequency and ultra high frequency. Among these frequency bands, technicians can use mobile station technology and base station technology. , mobile switching technology, connects terminal equipment within the mobile communication network to meet people's mobile communication needs. From analog mobile communication systems, digital cellular communication systems, mobile multimedia communication systems to current high-speed mobile communication systems, the speed of mobile communication technology continues to increase, delays and bit errors are reduced, and the stability and reliability of the technology continue to improve. Improvement provides a variety of flexible communication methods for people's production and life. In the past half century, the development of mobile communications has had a profound impact on people’s lives, production, work, entertainment and even politics, economy and culture. The drones imagined 30 years ago , smart home, online video, online shopping, etc. have all been realized. Mobile communication technology has gone through five development stages: analog transmission, digital voice transmission, Internet communication, personal communication, and new generation wireless mobile communication. For more related knowledge, please visit theFAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of what is gsm network. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

