 Web Front-end
Web Front-end Vue.js
Vue.js Vue practice: using custom instructions to achieve the effect of mouse dragging elements
Vue practice: using custom instructions to achieve the effect of mouse dragging elementsVue practice: using custom instructions to achieve the effect of mouse dragging elements
This article shares a Vue practice, introducing the use of Vue's custom instructions to achieve the effect of mouse dragging elements and solving the problem of mobile terminal adaptation.

Core Properties
-
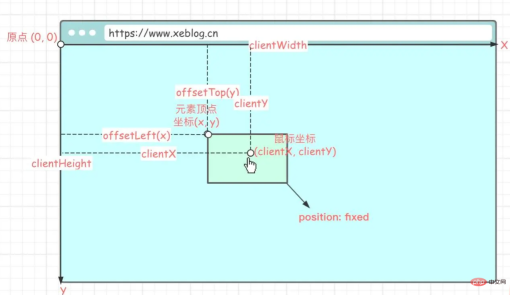
Element.clientWidth: Element can View width. -
Element.clientHeight: The visual height of the element. -
MouseEvent.clientX: The horizontal coordinate of the mouse relative to the upper left vertex of the browser. -
MouseEvent.clientY: The vertical coordinate of the mouse relative to the upper left vertex of the browser. -
Touch.clientX: The horizontal coordinate of the touch point relative to the upper left vertex of the browser (mobile property). -
Touch.clientY: The vertical coordinate of the touch point relative to the upper left vertex of the browser (mobile property). -
HTMLElement.offsetLeft: The offset distance of the upper left corner of the current element relative to the left side of the parent node (HTMLElement.offsetParent). When the element leaves the document flow (position: fixed), it is offset relative to the origin (the upper left vertex of the browser). [Related recommendations: vuejs video tutorial] -
HTMLElement.offsetTop: The upper left corner of the current element is relative to the parent node (HTMLElement. offsetParent). When the element leaves the document flow (position: fixed), it is offset relative to the origin (the upper left vertex of the browser). -
Element.style.top: Readable and writable, the value isoffsetTop. -
Element.style.left: Readable and writable, the value isoffsetLeft.
Implementation ideas
The element to be slid must be set
position: fixed or absolute
Element sliding depends on the movement of the mouse. The moving position of the mouse determines the sliding position of the element. The position of the element is determined by adjusting the coordinates of the upper left vertex, so we need to know the position of the element after it slides. The coordinates of the upper left vertex so that the element can be moved to the specified position (the position where the mouse is hovering).
First, calculate the position of the mouse relative to the element before moving the element (x, y):
// 鼠标当前的位置减去元素当前的位置 (x, y) = (e.clientX - el.offsetLeft, e.clientY - el.offsetTop)
The relative position of the mouse to the element refers to the position relative to the upper left vertex of the element Location.
e refers to the mouse event, el refers to the sliding element.
Knowing the relative position of the mouse and subsequent mouse movements, as long as you know the coordinates of the mouse after the movement, you can easily calculate the coordinates of the upper left vertex of the element.
Calculate the coordinates of the upper left vertex of the element after movement(x', y'):
// 鼠标当前的位置减去滑动前的相对位置 (x‘, y’) = (e.clientX - x, e.clientY - y)
(x', y') is to The final coordinates of the move, and then adjust the position of the element
el.style.left = x' + 'px' el.style.top = y' + 'px'
Code
<template>
<div>
<!-- 省略... -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
isDrag: false
},
methods: {
click() {
if (this.isDrag) {
return
}
// 省略...
}
},
directives: {
drag(el, binding, vnode) {
/**
* 获取客户端可见内容的高度
*
* @returns {number}
*/
const getClientHeight = () => {
return window.innerHeight || Math.min(document.documentElement.clientHeight, document.body.clientHeight)
}
/**
* 获取客户端可见内容的宽度
*
* @returns {number}
*/
const getClientWidth = () => {
return window.innerWidth || Math.min(document.documentElement.clientWidth, document.body.clientWidth)
}
/**
* startX = null:获取鼠标相对于元素(左上顶点)的x轴坐标(移动前坐标)
* startX != null:获取移动后的左上顶点x轴坐标
*
* e.clientX:鼠标相对客户端(客户端左上顶点)的x轴坐标
* el.offsetLeft:元素顶点(左上顶点)相对客户端(客户端左上顶点)的x轴坐标(元素必须脱离文档流,position: fixed or absolute)
* el.clientWidth:元素宽度
*
* @param el
* @param e
* @param startX
* @returns {number}
*/
const getX = (el, e, startX) => {
if (startX === null) {
// 返回鼠标相对于元素(左上顶点)的x轴坐标
return e.clientX - el.offsetLeft
}
// 客户端可视宽度
const clientWidth = getClientWidth()
// 元素自身宽度
const elWidth = el.clientWidth
// 移动到x轴位置
let x = e.clientX - startX
// 水平方向边界处理
if (x <= 0) {
// x轴最小为0
x = 0
} else if (x + elWidth > clientWidth) {
// x是左上顶点的坐标,是否触碰到右边边界(超出可视宽度)要通过右顶点判断,所以需要加上元素自身宽度
x = clientWidth - elWidth
}
return x
}
/**
* startY = null:获取鼠标相对于元素(左上顶点)的y轴坐标(移动前坐标)
* startY != null:获取移动后的左上顶点y轴坐标
*
* e.clientY:鼠标相对客户端(客户端左上顶点)的y轴坐标
* el.offsetTop:元素顶点(左上顶点)相对客户端(客户端左上顶点)的y轴坐标(元素必须脱离文档流,position: fixed or absolute)
* el.clientHeight:元素高度
*
* @param el
* @param e
* @param startY
* @returns {number}
*/
const getY = (el, e, startY) => {
if (startY === null) {
// 返回鼠标相对于元素(左上顶点)的y轴坐标
return e.clientY - el.offsetTop
}
// 客户端可视高度
const clientHeight = getClientHeight()
// 元素自身高度
const elHeight = el.clientHeight
// 移动到y轴位置
let y = e.clientY - startY
// 垂直方向边界处理
if (y <= 0) {
// y轴最小为0
y = 0
} else if (y + elHeight > clientHeight) {
// 同理,判断是否超出可视高度要加上自身高度
y = clientHeight - elHeight
}
return y
}
/**
* 监听鼠标按下事件(PC端拖动)
*
* @param e
*/
el.onmousedown = (e) => {
vnode.context.isDrag = false
// 获取当前位置信息 (startX,startY)
const startX = getX(el, e, null)
const startY = getY(el, e, null)
/**
* 监听鼠标移动事件
*
* @param e
*/
document.onmousemove = (e) => {
// 标记正在移动,解决元素移动后点击事件被触发的问题
vnode.context.isDrag = true
// 更新元素位置(移动元素)
el.style.left = getX(el, e, startX) + 'px'
el.style.top = getY(el, e, startY) + 'px'
}
/**
* 监听鼠标松开事件
*/
document.onmouseup = () => {
// 移除鼠标相关事件,防止元素无法脱离鼠标
document.onmousemove = document.onmouseup = null
}
}
/**
* 监听手指按下事件(移动端拖动)
* @param e
*/
el.ontouchstart = (e) => {
// 获取被触摸的元素
const touch = e.targetTouches[0]
// 获取当前位置信息 (startX,startY)
const startX = getX(el, touch, null)
const startY = getY(el, touch, null)
/**
* 监听手指移动事件
* @param e
*/
document.ontouchmove = (e) => {
// 获取被触摸的元素
const touch = e.targetTouches[0]
// 更新元素位置(移动元素)
el.style.left = getX(el, touch, startX) + 'px'
el.style.top = getY(el, touch, startY) + 'px'
}
/**
* 监听手指移开事件
*/
document.ontouchend = () => {
// 移除touch相关事件,防止元素无法脱离手指
document.ontouchmove = document.ontouchend = null
}
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.ball-wrap {
position: fixed;
}
</style>
drag is our custom instruction, when you need to slide Just bind v-drag to the element.
Note
Custom directive this points to the problem
Cannot be used within custom directivesdirectives When accessing this, if you need to modify the value in data, you need to modify it through vnode.context.Field name = value.
The click event is triggered after sliding
Mouse event triggering sequence:
mouseover - mousedown - mouseup - click - mouseout
The premise of sliding is that the mouse must be pressed and then slid, so when we release the mouse after sliding, the click event will be triggered.
Solution: Define a flag variable to indicate whether it is sliding. When the click event is executed, this variable is used as a precondition. If it is sliding, it will not be executed .
// ...
data()
return {
isDrag: false
}
}
// ...
el.onmousedown = (e) => {
// ...
vnode.context.isDrag = false
document.onmousemove = (e) => {
// 标记正在移动,解决元素移动后点击事件被触发的问题
vnode.context.isDrag = true
// ...
}
}
// ...
methods: {
click() {
if (this.isDrag) {
return
}
// ...
}
}
Mobile side sliding problem
The default event will be triggered when the mobile side slides, causing the sliding to freeze.
Add @touchmove.prevent on the element to trigger sliding to prevent the default event from occurring.
Source code
https://github.com/anlingyi/xeblog-vue/blob/master/src/components/xe-pokeball/index. vue
(Learning video sharing: web front-end development, Basic programming video)
The above is the detailed content of Vue practice: using custom instructions to achieve the effect of mouse dragging elements. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The Frontend Landscape: How Netflix Approached its ChoicesApr 15, 2025 am 12:13 AM
The Frontend Landscape: How Netflix Approached its ChoicesApr 15, 2025 am 12:13 AMNetflix's choice in front-end technology mainly focuses on three aspects: performance optimization, scalability and user experience. 1. Performance optimization: Netflix chose React as the main framework and developed tools such as SpeedCurve and Boomerang to monitor and optimize the user experience. 2. Scalability: They adopt a micro front-end architecture, splitting applications into independent modules, improving development efficiency and system scalability. 3. User experience: Netflix uses the Material-UI component library to continuously optimize the interface through A/B testing and user feedback to ensure consistency and aesthetics.
 React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AMNetflixusesacustomframeworkcalled"Gibbon"builtonReact,notReactorVuedirectly.1)TeamExperience:Choosebasedonfamiliarity.2)ProjectComplexity:Vueforsimplerprojects,Reactforcomplexones.3)CustomizationNeeds:Reactoffersmoreflexibility.4)Ecosystema
 The Choice of Frameworks: What Drives Netflix's Decisions?Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The Choice of Frameworks: What Drives Netflix's Decisions?Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AMNetflix mainly considers performance, scalability, development efficiency, ecosystem, technical debt and maintenance costs in framework selection. 1. Performance and scalability: Java and SpringBoot are selected to efficiently process massive data and high concurrent requests. 2. Development efficiency and ecosystem: Use React to improve front-end development efficiency and utilize its rich ecosystem. 3. Technical debt and maintenance costs: Choose Node.js to build microservices to reduce maintenance costs and technical debt.
 React, Vue, and the Future of Netflix's FrontendApr 12, 2025 am 12:12 AM
React, Vue, and the Future of Netflix's FrontendApr 12, 2025 am 12:12 AMNetflix mainly uses React as the front-end framework, supplemented by Vue for specific functions. 1) React's componentization and virtual DOM improve the performance and development efficiency of Netflix applications. 2) Vue is used in Netflix's internal tools and small projects, and its flexibility and ease of use are key.
 Vue.js in the Frontend: Real-World Applications and ExamplesApr 11, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Vue.js in the Frontend: Real-World Applications and ExamplesApr 11, 2025 am 12:12 AMVue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework suitable for building complex user interfaces. 1) Its core concepts include responsive data, componentization and virtual DOM. 2) In practical applications, it can be demonstrated by building Todo applications and integrating VueRouter. 3) When debugging, it is recommended to use VueDevtools and console.log. 4) Performance optimization can be achieved through v-if/v-show, list rendering optimization, asynchronous loading of components, etc.
 Vue.js and React: Understanding the Key DifferencesApr 10, 2025 am 09:26 AM
Vue.js and React: Understanding the Key DifferencesApr 10, 2025 am 09:26 AMVue.js is suitable for small to medium-sized projects, while React is more suitable for large and complex applications. 1. Vue.js' responsive system automatically updates the DOM through dependency tracking, making it easy to manage data changes. 2.React adopts a one-way data flow, and data flows from the parent component to the child component, providing a clear data flow and an easy-to-debug structure.
 Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific ConsiderationsApr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Vue.js vs. React: Project-Specific ConsiderationsApr 09, 2025 am 12:01 AMVue.js is suitable for small and medium-sized projects and fast iterations, while React is suitable for large and complex applications. 1) Vue.js is easy to use and is suitable for situations where the team is insufficient or the project scale is small. 2) React has a richer ecosystem and is suitable for projects with high performance and complex functional needs.
 How to jump a tag to vueApr 08, 2025 am 09:24 AM
How to jump a tag to vueApr 08, 2025 am 09:24 AMThe methods to implement the jump of a tag in Vue include: using the a tag in the HTML template to specify the href attribute. Use the router-link component of Vue routing. Use this.$router.push() method in JavaScript. Parameters can be passed through the query parameter and routes are configured in the router options for dynamic jumps.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment





