Home >Web Front-end >Front-end Q&A >An in-depth analysis of JavaScript built-in objects (summary sharing)
An in-depth analysis of JavaScript built-in objects (summary sharing)
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-01-04 17:54:591620browse
This article brings you knowledge about built-in objects in JavaScript. The biggest advantage of built-in objects is that they can help us develop quickly. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

1. Built-in objects
- Objects in JavaScript are divided into three types: Custom objects, Built-in objects , Browser objects.
- The first two objects are the basic content of JS and belong to ECMAScript; the third browser object is unique to our JS.
- Built-in objects refers to some objects that come with the JS language. These objects are for developers to use and provide some commonly used or the most basic and necessary functions (properties and methods) .
- The biggest advantage of built-in objects is that they help us develop quickly.
- JavaScript provides multiple built-in objects:
Math, Date, Array, String, etc..
2. Built-in object: Math object
2.1 Math overview
The Math object is not a constructor, it Properties and methods with mathematical constants and functions. Math-related operations (finding absolute values, rounding, maximum values, etc.) can use members in Math.
Math.PI // 圆周率 Math.floor() // 向下取整 Math.ceil() // 向上取整 Math.round() // 四舍五入版 就近取整 注意 -3.5 结果是 -3 Math.abs() // 绝对值 Math.max()/Math.min() // 求最大和最小值
Note: The above method must have brackets .
Case: Encapsulate your own mathematical objects
Use objects to encapsulate your own mathematical objects, which contain PI, maximum and minimum values.
<script>
// 利用对象封装自己的数学对象 里面有 PI 最大值和最小值
var myMath = {
PI: 3.141592653,
max: function () {
var max = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] > max) {
max = arguments[i];
}
}
return max;
},
min: function () {
var min = arguments[0];
for (var i = 1; i < arguments.length; i++) {
if (arguments[i] < min) {
min = arguments[i];
}
}
return min;
}
}
console.log(myMath.PI);
console.log(myMath.max(1, 9, 20, 3, 21, 54, 211, 567, 80));
console.log(myMath.min(1, 0, 90, -10, 82));</script>
2.2 Random number method random()
random() method can randomly return a decimal number, and its value range is [0, 1), left closed, right open 0
If you want to get a random integer between two numbers, including these two numbers, the method is as follows:
// 得到一个两数之间的随机整数,包括两个数在内function getRandom(min, max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;}
3. Built-in object: date object
3.1 Date Overview
- The Date object is different from the Math object. It is a constructor, so we need to instantiate it before it can be used.
- Date instances are used to handle dates and times.
3.2 Use of Date() method
(1) To obtain the current time, it must be instantiated
var now = new Date();console.log(now);
(2) Parameters of Date() constructor
If there is time in the brackets, the time in the parameter will be returned. For example, the date format string is ‘2019-5-1’, which can be written as new Date(‘2019-5-1’) or new Date(‘2019/5/1’).
-
If Date() does not write parameters, it will return the current time. -
If parameters are written in Date(), the timeentered in the brackets will be returned.
3.3 Date formatting
We want the date in the format of 2019-8-8 8:8:8, what should we do?
We need to get the specified part of the date, so we have to get this format manually.
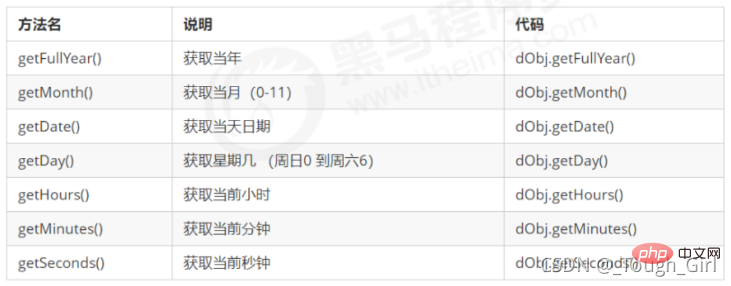
3.4 Get the total millisecond form of the date
The Date object is based on January 1, 1970 (Universal Time) The number of milliseconds since.
We often use total milliseconds to calculate time because it is more accurate.
<script>
// Date 对象是基于1970年1月1日(世界标准时间)起的毫秒数
// 获得Date 总的毫秒数(时间戳) 不是当前时间的毫秒数 而是距离1970年1月1日过了多少毫秒数
// 1.通过 valueOf() 或者 getTime()
var date = new Date();
console.log(date.valueOf()); // 就是我们现在时间 距离1970.1.1 总的毫秒数
console.log(date.getTime());
// 2.简单的写法(实际开发中最常用的写法)
var date1 = +new Date(); // +new Date() 返回的就是总的毫秒数
console.log(date1);
// 3.H5 新增的 获得总的毫秒数
console.log(Date.now());</script>
3.5 Case: Countdown effect
Case analysis:
(1) Core algorithm: Subtract the input time The current time is the remaining time, that is, the countdown, but you cannot subtract hours, minutes, and seconds. For example, subtracting 25 minutes from 05 minutes will result in a negative number.
(2) Use timestamp to do it. The total number of milliseconds in the user input time is subtracted from the total number of milliseconds in the current time, and the result is the number of milliseconds in the remaining time.
(3) Convert the total number of milliseconds of the remaining time into days, hours, minutes and seconds (timestamps are converted into hours, minutes and seconds)
The conversion formula is as follows:
-
d = parseInt(Total seconds / 60 / 60 / 24);// Calculate the number of days -
h = parseInt(Total seconds / 60/ 60 % 24)// Calculate hours -
m = parseInt(Total seconds / 60 % 60 );// Calculate fraction -
s = parseInt(Total seconds % 60);// Calculate the current seconds
function coutDown(time) {
var nowTime = +new Date(); // 返回的是当前时间总的毫秒数
var inputTime = +new Date(time); // 返回的是用户输入时间总的毫秒数
var times = (inputTime - nowTime) / 1000; // times是剩余时间总的秒数(毫秒变
var d = parseInt(times / 60 / 60 / 24); // 计算天数
d = d <h2>4. Built-in object: Array object</h2><h3><strong>4.1 Creation of array object</strong></h3><p>Two ways to create an array object</p>
- Literal method
- new Array()
// 创建数组的两种方式 // 1.利用数组字面量 var arr = [1, 2, 3]; console.log(arr[0]); // 1 // 2.利用new Array() var arr1 = new Array(); // 创建一个空的数组 console.log(arr1); // [] var arr2 = new Array(2); // 这个2表示, 数组的长度为2, 里面有2个空的数组元素 console.log(arr2); // [空 × 2] console.log(arr2[0], arr2[1]); // undefined undefined var arr3 = new Array(2, 3); // 等价于[2, 3] 这样写表示里面有2个数组元素,是2和3 console.log(arr3); // [2, 3] var arr4 = new Array(['a', 'b', 'c']); console.log(arr4); // [Array(3)] console.log(arr4[0]); // ["a", "b", "c"]
4.2 Check whether it is an array
-
instanceofoperator can determine whether an object belongs to a certain type. -
Array.isArray()Used to determine whether an object is an array. isArray() is a method provided in HTML5.
// 检测是否为数组
// (1)instanceof 运算符,可以判断一个对象是否属于某种类型
var arr = [];
console.log(arr instanceof Array); // true
var obj = {};
console.log(obj instanceof Array); // false
// (2)Array.isArray()用于判断一个对象是否为数组,isArray() 是 HTML5 中提供的方法
console.log(Array.isArray(arr)); // true
console.log(Array.isArray(obj)); // false
4.3 Commonly used methods for arrays
(1) Add and delete methods for array elements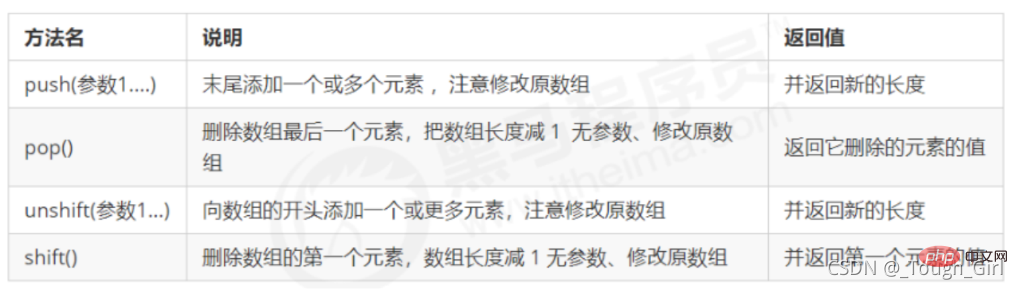
(2) Array sorting
| 方法名 | 说明 | 是否修改原数组 |
|---|---|---|
| reverse() | 颠倒数组中元素的顺序,无参数 | 该方法会改变原来的数组,返回新数组 |
| sort() | 对数组的元素进行排序 | 该方法会改变原来的数组,返回新数组 |
<script>
// 数组排序
// 1.翻转数组
// reverse() 颠倒数组中元素的顺序,无参数
// 该方法会改变原来的数组 返回新数组
var arr = ['pink', 'red', 'purple', 'blue'];
arr.reverse();
console.log(arr); // ["blue", "purple", "red", "pink"]
// 2.数组排序(冒泡排序)
// sort() 对数组的元素进行排序
// 该方法会改变原来的数组 返回新数组
var arr1 = [1, 14, 7, 9, 5, 77, 1];
arr1.sort(function (a, b) { // 固定写法
return a - b; // 升序的顺序排列
// return b - a; // 降序
});
console.log(arr1); // [1, 1, 5, 7, 9, 14, 77]</script>
(3)数组索引方法
| 方法名 | 说明 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|
| indexOf() | 数组中查找给定元素的第一个索引 | 如果存在返回索引号,如果不存在,则返回-1 |
| lastIndexOf() | 在数组中的最后一个索引 | 如果存在返回索引号,如果不存在,则返回-1 |
// 返回数组元素索引方法
// indexOf(数组元素) 作用就是返回该数组元素的索引号 从前面开始查找
// 数组中查找给定元素的第一个索引,如果存在返回索引号,如果不存在,则返回-1
var arr = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'pink', 'blue'];
console.log(arr.indexOf('blue')); // 2
// lastIndexOf(数组元素) 从后面开始查找,如果存在返回索引号,如果不存在,则返回-1
console.log(arr.lastIndexOf('blue')); // 4
(4)数组转换为字符串
| 方法名 | 说明 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|
| toString() | 把数组转换成字符串,逗号分隔每一项 | 返回一个字符串 |
| join(‘分隔符’) | 方法用于把数组中的所有元素转换为一个字符串,不写分隔符,默认逗号分隔 | 返回一个字符串 |
// 数组转换为字符串
// 1.toString() 将数组转换成字符串,逗号分隔每一项,返回一个字符串
var arr = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(arr.toString()); // "1,2,3"
// 2.join(分隔符)
var arr1 = ['green', 'blue', 'pink'];
console.log(arr1.join()); // "green,blue,pink"
console.log(arr1.join('-')); // "green-blue-pink"
console.log(arr1.join('&')); // "green&blue&pink"
(5)其他一些方法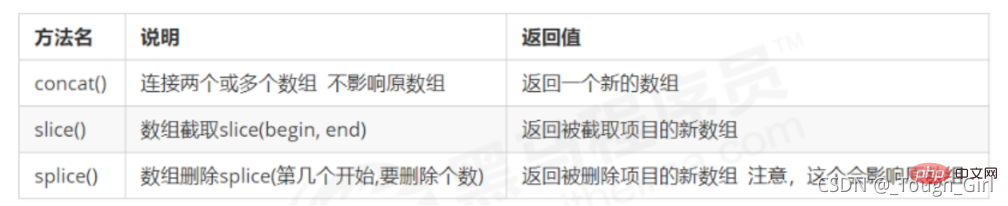
// 1.concat() 连接两个或多个数组,不影响原数组 最后返回一个新数组 var arr1 = [1, 2, 3]; var arr2 = ['red', 'pink', 'blue']; console.log(arr1.concat(arr2)); // [1, 2, 3, "red", "pink", "blue"] // 2.slice(begin, end) 数组截取 返回被截取项目的新数组 var arr3 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 'red', 'yellow', 'blue']; console.log(arr2.slice(0, 1)); // ["red"] console.log(arr3.slice(2, 7)); // [3, 4, 5, "red", "yellow"] // 3.splice(第几个开始,要删除个数) 数组删除 返回被删除项目的新数组,注意,这个会影响原数组 console.log(arr3.splice(2, 5)); // [3, 4, 5, "red", "yellow"]
4.4 案例:数组去重
有一个数组[‘c’, ‘a’, ‘z’, ‘a’, ‘x’, ‘a’, ‘x’, ‘c’, ‘b’],要求去除数组中重复的元素。
- 目标:把旧数组里面不重复的元素选取出来放到新数组中,重复的元素只保留一个,放到新数组中去重。
- 核心算法:我们遍历旧数组,然后拿着旧数组元素去查询新数组,如果该元素在新数组里面没有出现过,我们就添加,否则不添加。
- 我们怎么知道该元素没有存在? 利用
新数组.indexOf(数组元素)如果返回-1,就说明新数组里面没有改元素
// 封装一个去重的函数 unique 独一无二的
function unique(arr) {
var newArr = [];
for (var i = 0; i <h2>5、内置对象:字符串对象</h2><h3><strong>5.1 基本包装类型</strong></h3><p>为了方便操作基本数据类型,JavaScript 还提供了三个特殊的引用类型:String、Number和 Boolean。</p><p><strong>基本包装类型就是把简单数据类型包装成为复杂数据类型</strong>,这样基本数据类型就有了属性和方法。</p><p>下面代码有什么问题?</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">var str = 'andy';console.log(str.length); // 4按道理基本数据类型是没有属性和方法的,而对象才有属性和方法,但上面代码却可以执行,这是因为 js 会把基本数据类型包装为复杂数据类型,其执行过程如下 :
// 1. 生成临时变量,把简单类型包装为复杂数据类型var temp = new String('andy');
// 2. 赋值给我们声明的字符变量str = temp;
// 3. 销毁临时变量temp = null;5.2 字符串的不可变
字符串的不可变指的是里面的值不可变,虽然看上去可以改变内容,但其实是地址变了,内存中新开辟了一个内存空间。
字符串的不可变的特点:重新给字符串赋值,会重新在内存中开辟空间。
var str = 'abc';str = 'hello';// 当重新给 str 赋值的时候,常量'abc'不会被修改,依然在内存中// 重新给字符串赋值,会重新在内存中开辟空间,这个特点就是字符串的不可变// 由于字符串的不可变,在大量拼接字符串的时候会有效率问题var str = '';for (var i = 0; i <h3>5.3 字符串对象常用的方法</h3><p><strong>字符串所有的方法,都不会修改字符串本身(字符串是不可变的),操作完成会返回一个新的字符串。</strong></p><p><strong>(1)根据字符返回位置</strong></p>
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| indexOf(‘要查找的字符’,开始的位置) | 返回指定内容在原字符串中的位置,如果找不到就返回 -1 ,开始的位置是 index 索引号 |
| lastIndexOf() | 从后往前找,只找第一个匹配的 |
// 根据字符返回位置
// 1.indexOf('要查找的字符', '开始的位置')
// 返回指定内容在元字符串中的位置,如果找不到就返回-1,开始的位置index的索引号
var str = '改革春风吹满地,春天来了';
console.log(str.indexOf('春')); // 2
console.log(str.indexOf('春', 3)); // 从索引号是 3 的位置开始往后查找 // 8
// 2.lastIndexOf() 从后往前找,只找第一个匹配的
console.log(str.lastIndexOf('春')); // 8
console.log(str.lastIndexOf('春', 7)); // 2
案例:返回字符位置
查找字符串"oabcoefoxyozzopp"中所有 o 出现的位置以及次数。
思路:
- 核心算法:先查找第一个o出现的位置。
- 然后,只要indexOf 返回的结果不是 - 1 就继续往后查找。
- 因为 indexOf 只能查找到第一个,所以后面的查找,利用第二个参数,当前索引加1,从而继续查找。
代码:
var str = 'oabcoefoxyozzopp';var index = str.indexOf('o');var num = 0;while (index !== -1) {
// console.log(index);
num++;
index = str.indexOf('o', index + 1);}console.log('o出现的次数为:' + num); // 5
(2)根据位置返回字符
| 方法名 | 说明 | 使用 |
|---|---|---|
| charAt(index) | 返回指定位置的字符(index 字符串的索引号) | str.charAt(0) |
| charCodeAt(index) | 获取指定位置处字符的ASCII码(inex 索引号) | str.charCodeAt(0) |
| str[index] | 获取指定位置处字符 | HTML5,IE8+支持,和 charAt()等效 |
// 根据位置返回字符(重点)
// 1.charAt(index) 根据索引号返回指定位置的字符
var str = 'andy';
console.log(str.charAt(3)); // "y"
// 遍历所有的字符
for (var i = 0; i <p><strong>案例:返回字符位置</strong></p><p>判断一个字符串 <code>'abcoefoxyozzopp'</code> 中出现次数最多的字符,并统计其次数。</p><p><strong>思路:</strong><br> ① 核心算法:利用 charAt()遍历这个字符串。</p><p>② 把每个字符都存储给对象, 如果对象没有该属性,就为1,如果存在了就 +1。</p><p>③ 遍历对象,得到最大值和该字符。</p><p>代码:</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">// 案例:返回字符位置// 有一个对象 来判断是否有该属性 对象['属性名']var o1 = {
age: 18}if (o1['age']) {
console.log('里面有该属性');} else {
console.log('里面没有该属性');}// 判断一个字符串 'abcoefoxyozzopp' 中出现次数最多的字符,并统计其次数。var str = 'abcoefoxyozzopp';var o = {}; // 声明一个对象for (var i = 0; i max) {
max = o[k];
ch = k;
}}console.log('出现次数最多字符的为:' + ch, '次数为:' + max);(3)字符串操作方法
// 字符串操作方法(重点) // 1.concat('字符串1', '字符串2',....) 连接两个或多个字符串,等效于+ var str = 'andy'; console.log(str.concat('red')); // "andyred" // 2.substr('截取的起始位置','截取几个字符') 截取字符串 var str1 = '改革春风吹满地'; console.log(str1.substr(2, 2)); // "春风" 第一个2 是索引号 第二个2 是取的字符串个数
(4)replace() 方法和 split() 方法
replace() 方法用于在字符串中用一些字符替换另一些字符。
其使用格式如下:
replace(被替换的字符串, 要替换为的字符串);
// 3.replace(被替换的字符串, 要替换为的字符串); 替换字符 它只会替换第一个字符
var str3 = 'andyandy';
console.log(str3.replace('a', 'b')); // "bndyandy"
// 有一个字符串 'abcoefoxyozzopp' 要求把里面所有的 'o' 替换为*
var str4 = 'abcoefoxyozzopp';
while (str4.indexOf('o') !== -1) {
str4 = str4.replace('o', '*');
}
console.log(str4); // "abc*ef*xy*zz*pp"split() 方法用于切分字符串,它可以将字符串切分为数组。在切分完毕之后,返回的是一个新数组。
// 4.split()方法用于切分字符串,它可以将字符串切分为数组。在切分完毕之后,返回的是一个新数组。
// split('分隔符') 把字符转换为数组 前面我们学过 join 把数组转换为字符串
var str5 = 'red, pink, blue';
console.log(str5.split(',')); // ["red", " pink", " blue"]
var str6 = 'red&pink&blue';
console.log(str6.split('&')); // ["red", " pink", " blue"]其他一些方法:
-
toUpperCase()// 转换大写 -
toLowerCase()// 转换小写
【相关推荐:javascript学习教程】
The above is the detailed content of An in-depth analysis of JavaScript built-in objects (summary sharing). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

