In CSS, the baseline "base line" is not the lower edge of Chinese characters, but the lower edge of English letters. The baseline is always consistent with the tallest element in the row, and the baseline changes with the tallest element in the row.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, CSS3&&HTML5 version, Dell G3 computer.
1. Basic concepts
1. Baseline, bottom line, top line, middle line

Note: Baseline (base line) is not The lower edge of the Chinese character text is the lower edge of the English letter "x".
2. Content area
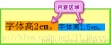
The content area refers to the area wrapped by the bottom line and the top line (inline elements display:inline; can be displayed through the background-color attribute out), you may not necessarily see it in practice, but it does exist. The size of the content area changes based on the value of font-size and the number of words.
3. Line spacing and line height
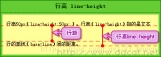
Line-height: includes the content area and the blank area that is symmetrically expanded based on the content area. We call this row height. Generally speaking, it can also be considered as the distance between the baselines of adjacent text lines.
Line spacing: refers to the distance between the baseline of the previous text line and the top line of the next text line between adjacent texts. Of course, I prefer to think of it as (upper text line height - content area height)/2 (lower text line height - content area height)/2.
4. Inline box
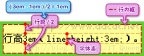
The inline box is a concept in the browser rendering model. It cannot be displayed, but it does exist. Its height It is the height specified by the row height.
5. Line box

Line box (line box) is a similar concept to the inner box of the same line. The line box refers to a virtual rectangle of the current line. Box is also a concept in browser rendering mode. The height of the line box is equal to the largest value of the inline box among all elements in this line (the inline box with the largest line height value is used as the benchmark, and other inline boxes are aligned to the benchmark using their own alignment methods, and the height of the line box is finally calculated)
2. Vertical-align: Set the vertical alignment of the element.
Line-height is the vertical centering (line-height) of a single line of pure text. If the line contains pictures and text, after the browser renders them, readers can find that the text and pictures are not centered along the center line in the vertical direction. , but aligned along the baseline. This is because the default vertical alignment of elements is baseline alignment (vertical-align: baseline).

CSS syntax: vertical-align
Syntax:
baseline | sub | super | top | text-top | middle | bottom | text-bottom |
Description:
Set the vertical alignment of the element content.
Parameters:
baseline: Baseline alignment;
sub: Subscript display;
super: Superscript display; : Top alignment;
∼ posit text-top: Top alignment of text;
∼ posit middle: Middle alignment; // Not well-studied properties
∼ bottom: Bottom alignment;
## text -bottom: The bottom alignment of the text;## # Percentage and length: CSS2, can be negative.
Initial value: baseline
Inheritance: Not inherited element nodes to correctly handle the vertical-align attribute). Also, this property cannot be inherited.
Detailed explanation of attribute values
In the above section, we introduced the baseline, top line, middle line and bottom line of the text, as well as the content area, inline box and line box. In this section, the vertical Alignment is closely related to these concepts.
1. Baseline alignment (vertical-align: baseline) Baseline alignment (vertical-align: baseline) makes the baseline of the element the same as the base element (take Baseline alignment with the highest row height as the baseline

3. Text top alignment (vertical-align: text-top)
Text top alignment (vertical-align: text-top) is to frame the element inline The top is aligned with the top line of the text line

4. Vertical-align : bottom
Vertical-align : bottom ) is the opposite of top alignment (vertical-align : top)

5. Text bottom alignment (vertical-align : text-bottom)

6. Vertical-align: middle
Middle alignment (vertical-align: middle) is usually used on pictures to align the vertical center line of the picture with the line of text. Centerline alignment. (There are some deviations in the processing of words. The specific basis has not been researched yet. Students who have done research can contact me~~)

The definition of the midline is: the midline is located at the baseline. Above, the distance from the baseline is half the height of the lowercase letter Align a quarter of an em above the baseline as the midline.
7. Superscript and subscript
Superscript (vertical-align:super) raises the baseline of the element relative to the baseline of the base element, and subscript (vertical-align:sub) Lowering the baseline of the element and moving it by a certain amount are not specified in the CSS specification and are determined by the browser.

Superscript and subscript will not change the size of the element text.
8. Length values and percentages
Similar to superscripts and subscripts, length values and percentage values can make the baseline of an element higher (positive value) or lower (negative value) relative to the baseline of the base element. ).
The moving size of superscripts and subscripts is determined by the browser, and setting the length value or percentage can accurately control the range of text movement up and down.
Percentage is related to line-height. For example, the following code is displayed as shown in the figure below.

My test under @FireFox
Test code:
<style type="text/css">
p {
vertical-align:baseline;
font-size:20px;
line-height:60px;
background-color:yellow;
}
span {
background-color: red;
}
u {
background-color: blue;
}
del {
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
//HTML代码
<p>
<span>Ajax测试</span>
<u>Ajax测试</u>
<del>Ajax测试</del>
Ajax测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试
</p>Default:

Other instructions:
1. The offsetWidth of SPAN, U, and DEL tags = SUM (character * font-size * correction coefficient) (here, the correction coefficient for Chinese is 1, and the correction coefficient for numbers is 1 0.6, English character correction coefficients vary greatly, for example, ijl is very small, wmk, etc. are relatively large, and the correction coefficients for uppercase English are also not uniform).
2. The offsetHeight of SPAN, U, and DEL tags.
Corollary: The background rendering area of the inline element, that is, the size of the content area, is directly affected by font-size.
For
block-level elements, the calculated height of the block-level element is calculated by adding up the height of the included line boxes, so the height here is 60px;
3. Change span.style .lineHeight is set to 15px (changed from 10px to 60px) —-> Found no change
Inference: The size of the content area is not affected by line-height, which is used to handle the gap between the baselines of adjacent text lines distance.
4. Set span.style.lineHeight to 70px (from 61px to 80px) —->The height of the line box begins to adjust with the setting
Corollary 1: The height of the line box is within the line The highest inline box height, adjusted through line-height.
The calculated height value of p element is span.style.lineHeight value, which is not controlled by p.style.lineHeight.
Corollary 2: The calculated height value of
without setting the height attribute is the accumulated value of the line box height.

d) Top and bottom are inline box alignments. Top refers to the alignment of the top of the element's inline box with the top of the base inline box;
# d) Top and text-bottom will also affect the final line box. Height means that the top of the inline box of the element is aligned with the top of the content area of the base element (when line-height=content area height, it is aligned with the top of the base content area. When line-height is less than the height of the content area, the text will continue to rise. The phenomenon of shifting, when line-height is set to 0px, the vertical middle of the content area is exactly aligned with the top of the reference content area.)
The above is the detailed content of what is css baseline. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The Lost CSS Tricks of Cohost.orgApr 25, 2025 am 09:51 AM
The Lost CSS Tricks of Cohost.orgApr 25, 2025 am 09:51 AMIn this post, Blackle Mori shows you a few of the hacks found while trying to push the limits of Cohost’s HTML support. Use these if you dare, lest you too get labelled a CSS criminal.
 Next Level CSS Styling for CursorsApr 23, 2025 am 11:04 AM
Next Level CSS Styling for CursorsApr 23, 2025 am 11:04 AMCustom cursors with CSS are great, but we can take things to the next level with JavaScript. Using JavaScript, we can transition between cursor states, place dynamic text within the cursor, apply complex animations, and apply filters.
 Worlds Collide: Keyframe Collision Detection Using Style QueriesApr 23, 2025 am 10:42 AM
Worlds Collide: Keyframe Collision Detection Using Style QueriesApr 23, 2025 am 10:42 AMInteractive CSS animations with elements ricocheting off each other seem more plausible in 2025. While it’s unnecessary to implement Pong in CSS, the increasing flexibility and power of CSS reinforce Lee's suspicion that one day it will be a
 Using CSS backdrop-filter for UI EffectsApr 23, 2025 am 10:20 AM
Using CSS backdrop-filter for UI EffectsApr 23, 2025 am 10:20 AMTips and tricks on utilizing the CSS backdrop-filter property to style user interfaces. You’ll learn how to layer backdrop filters among multiple elements, and integrate them with other CSS graphical effects to create elaborate designs.
 SMIL on?Apr 23, 2025 am 09:57 AM
SMIL on?Apr 23, 2025 am 09:57 AMWell, it turns out that SVG's built-in animation features were never deprecated as planned. Sure, CSS and JavaScript are more than capable of carrying the load, but it's good to know that SMIL is not dead in the water as previously
 'Pretty' is in the eye of the beholderApr 23, 2025 am 09:40 AM
'Pretty' is in the eye of the beholderApr 23, 2025 am 09:40 AMYay, let's jump for text-wrap: pretty landing in Safari Technology Preview! But beware that it's different from how it works in Chromium browsers.
 CSS-Tricks Chronicles XLIIIApr 23, 2025 am 09:35 AM
CSS-Tricks Chronicles XLIIIApr 23, 2025 am 09:35 AMThis CSS-Tricks update highlights significant progress in the Almanac, recent podcast appearances, a new CSS counters guide, and the addition of several new authors contributing valuable content.
 Tailwind's @apply Feature is Better Than it SoundsApr 23, 2025 am 09:23 AM
Tailwind's @apply Feature is Better Than it SoundsApr 23, 2025 am 09:23 AMMost of the time, people showcase Tailwind's @apply feature with one of Tailwind's single-property utilities (which changes a single CSS declaration). When showcased this way, @apply doesn't sound promising at all. So obvio


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!






