Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Introducing the change buffer in MySQL Buffer pool
Introducing the change buffer in MySQL Buffer pool
- coldplay.xixiforward
- 2021-03-29 09:47:552064browse

4 change buffer
4.1 Basic concepts
change buffer is a special data structure that caches changes to secondary index pages when those pages are not in the buffer pool. Buffer changes that may be caused by INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations (DML) will be merged later when the page is loaded into the buffer pool by other read operations. 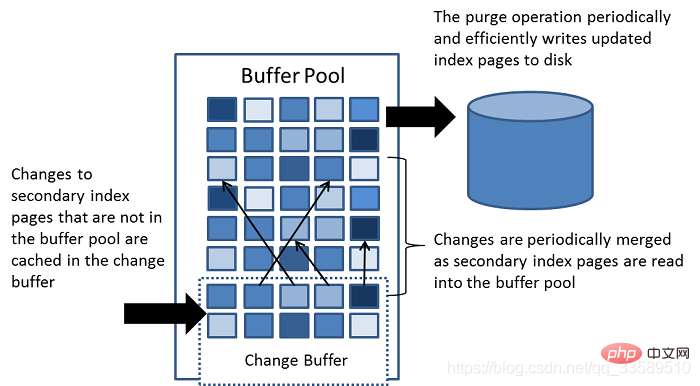
Related free learning recommendations: mysql video tutorial
As can be seen in the picture above, the change buffer is used The memory in the buffer pool cannot grow infinitely. The change buffer size can be dynamically set through the parameter innodb_change_buffer_max_size.
For example, if set to 50: the size of the change buffer can only occupy up to 50% of the buffer pool.
When a data page needs to be updated:
- The page is in memory, directly update the
- page is not in memory, without affecting data consistency, InooDB These update operations will be cached in the change buffer without the need to read the page from the disk.
When the next query accesses the data page, the data page will be read into the memory, and then the change buffer will be executed with this page related operations. In this way, the correctness of the data logic can be ensured.
change buffer is actually persistent data, that is, it is not only copied in memory, but also written to disk.
4.2 merge
The process of applying the operations in the change buffer to the original data page to obtain the latest results.
4.2.1 Trigger timing
- Access the data page
- System background thread merges regularly
- The database is closed normally (shutdown) process
If the update operation can be recorded in the change buffer first to reduce disk reading, the statement execution speed will be significantly improved. And reading data into memory requires occupying the buffer pool, so it can also reduce memory usage and improve memory utilization.
4.3 When to use change buffer
- For a unique index, update operations must first determine whether the operation violates the uniqueness constraint:
For example, To insert (4,400) records, you must first determine whether k=4 records are already stored in the table, and you must read the data page into the memory to determine. If everything has been read into the memory, updating the memory directly will be very fast, and there is no need to use the change buffer.
Therefore, the update of unique index cannot use change buffer, only ordinary index can use .
4.4 Applicable Scenarios
Can all scenarios of ordinary indexing be accelerated by using change buffer?
Note that merge is the time when the data is actually updated, and the change buffer mainly caches the recorded change actions. Therefore, before a data page is merged, the more changes the change buffer record has (that is, the more times the data page needs to be updated), the greater the benefit.
- Write more and read less business. The probability of the page being accessed immediately after writing is small. The use of change buffer has the best effect. Commonly used are billing and log systems.
- Query immediately after writing, the new record will be first recorded in the change buffer, but then the data page will be accessed immediately, and the merge will be triggered soon. In this case, the number of random access IO will not be reduced, but will increase the change buffer maintenance cost. , change buffer has side effects.
More related free learning recommendations: mysql tutorial(Video)
The above is the detailed content of Introducing the change buffer in MySQL Buffer pool. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

