Python solves advanced mathematics problems, and my mother no longer has to worry about my learning

Use Python to solve limits and derivatives in advanced mathematics , partial derivatives, definite integrals, indefinite integrals, double integrals and other problems
Sympy is a Python scientific computing library, which aims to become a fully functional computer algebra system. SymPy includes functions from basic symbolic arithmetic to calculus, algebra, discrete mathematics and quantum physics. It can display the results in LaTeX.
Sympy official website
Article directory
- Python solves advanced mathematics problems, my mother no longer has to worry about my study
- 1. Practical skills
- 1.1 Symbolic function
- 1.2 Expansion expression expand
- 1.3 Taylor expansion formula series
- 1.4 Sign expansion
- 2. Find the limit limit
- 3. Find the derivative diff
- 3.1 Unary function
- 3.2 Multivariate function
- 4. Integral integrate
- 4.1 Definite integral
- 4.2 Indefinite integral
- 4.3 Double integral
- 5. Solve the system of equations solve
- 6. Calculate the summation
(Free Learning recommendation: python video tutorial)

Watch Looking at this picture, do you feel like you can't breathe? Python is here to help you solve it.
from sympy import *import sympy
Enter the "x= symbols("x")" command to define a symbol
x = Symbol("x")y = Symbol("y")
1. Practical tips
1.1 Symbol function
sympy provides a lot of mathematical symbols, summarized as follows
- Imaginary unit
sympy.I
- Natural logarithm
sympy.E
- Infinity
sympy.oo
- Pi
sympy.pi
- Find the nth square root
sympy.root(8,3)
- Get the logarithm
sympy.log(1024,2)
- Find the factorial
sympy.factorial(4)
- Trigonometric function
sympy.sin(sympy.pi)sympy.tan(sympy.pi/4)sympy.cos(sympy.pi/2)
1.2 Expand expression expand
f = (1+x)**3expand(f)
x 3 + 3 x 2 + 3 x + 1 \displaystyle x^{3} + 3 x^{2} + 3 x + 1 x3+3x2+3x+1
1.3 泰勒展开公式series
ln(1+x).series(x,0,4)
x − x 2 2 + x 3 3 + O ( x 4 ) \displaystyle x - \frac{x^{2}}{2} + \frac{x^{3}}{3} + O\left(x^{4}\right) x−2x2 3x3 O(x4)
sin(x).series(x,0,8)
x − x 3 6 + x 5 120 − x 7 5040 + O ( x 8 ) \displaystyle x - \frac{x^{3}}{6} + \frac{x^{5}}{120} - \frac{x^{7}}{5040} + O\left(x^{8}\right) x−6x3 120x5−5040x7 O(x8)
cos(x).series(x,0,9)
1 − x 2 2 + x 4 24 − x 6 720 + x 8 40320 + O ( x 9 ) \displaystyle 1 - \frac{x^{2}}{2} + \frac{x^{4}}{24} - \frac{x^{6}}{720} + \frac{x^{8}}{40320} + O\left(x^{9}\right) 1−2x2 24x4−720x6 40320x8 O(x9)
(1/(1+x)).series(x,0,5)
1 − x + x 2 − x 3 + x 4 + O ( x 5 ) \displaystyle 1 - x + x^{2} - x^{3} + x^{4} + O\left(x^{5}\right) 1−x x2−x3 x4 O(x5)
tan(x).series(x,0,4)
x + x 3 3 + O ( x 4 ) \displaystyle x + \frac{x^{3}}{3} + O\left(x^{4}\right) x+3x3+O(x4)
(1/(1-x)).series(x,0,4)
1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + O ( x 4 ) \displaystyle 1 + x + x^{2} + x^{3} + O\left(x^{4}\right) 1+x+x2+x3+O(x4)
(1/(1+x)).series(x,0,4)
1 − x + x 2 − x 3 + O ( x 4 ) \displaystyle 1 - x + x^{2} - x^{3} + O\left(x^{4}\right) 1−x+x2−x3+O(x4)
1.4 符号展开
a = Symbol("a")b = Symbol("b")#simplify( )普通的化简simplify((x**3 + x**2 - x - 1)/(x**2 + 2*x + 1))#trigsimp( )三角化简trigsimp(sin(x)/cos(x))#powsimp( )指数化简powsimp(x**a*x**b)
x a + b \displaystyle x^{a + b} xa+b
2. 求极限limit
limit(sin(x)/x,x,0)
1 \displaystyle 1 1
f2=(1+x)**(1/x)
f2
( x + 1 ) 1 x \displaystyle \left(x + 1\right)^{\frac{1}{x}} (x+1)x1
重要极限
f1=sin(x)/x f2=(1+x)**(1/x)f3=(1+1/x)**x lim1=limit(f1,x,0)lim2=limit(f2,x,0)lim3=limit(f3,x,oo)print(lim1,lim2,lim3)
1 E E
dir可以表示极限的趋近方向
f4 = (1+exp(1/x))f4
e 1 x + 1 \displaystyle e^{\frac{1}{x}} + 1 ex1+1
lim4 = limit(f4,x,0,dir="-")lim4
1 \displaystyle 1 1
lim5 = limit(f4,x,0,dir="+")lim5
∞ \displaystyle \infty ∞
3. 求导diff
diff(函数,自变量,求导次数)
3.1 一元函数
求导问题
diff(sin(2*x),x)
2 cos ( 2 x ) \displaystyle 2 \cos{\left(2 x \right)} 2cos(2x)
diff(ln(x),x)
1 x \displaystyle \frac{1}{x} x1
3.2 多元函数
求偏导问题
diff(sin(x*y),x,y)
− x y sin ( x y ) + cos ( x y ) \displaystyle - x y \sin{\left(x y \right)} + \cos{\left(x y \right)} −xysin(xy)+cos(xy)
4. 积分integrate
4.1 定积分
- 函数的定积分: integrate(函数,(变量,下限,上限))
- 函数的不定积分: integrate(函数,变量)
f = x**2 + 1integrate(f,(x,-1.1))
− 1.54366666666667 \displaystyle -1.54366666666667 −1.54366666666667
integrate(exp(x),(x,-oo,0))
1 \displaystyle 1 1
4.2 不定积分
f = 1/(1+x*x)integrate(f,x)
atan ( x ) \displaystyle \operatorname{atan}{\left(x \right)} atan(x)
4.3 双重积分
f = (4/3)*x + 2*y integrate(f,(x,0,1),(y,-3,4))
11.6666666666667 \displaystyle 11.6666666666667 11.6666666666667
5. 求解方程组solve
#解方程组#定义变量f1=x+y-3f2=x-y+5solve([f1,f2],[x,y])
{x: -1, y: 4}
6. 计算求和式summation
计算求和式可以使用sympy.summation函数,其函数原型为sympy.summation(f, *symbols, **kwargs)
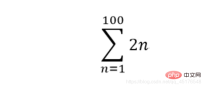
**
sympy.summation(2 * n,(n,1,100))
10100
到这里就结束了,如果对你有帮助,欢迎点赞关注评论,你的点赞对我很重要。在此也祝愿大家可以把数学学好
相关免费学习推荐:python教程(视频)
The above is the detailed content of Learn Python to solve advanced mathematics problems. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How do you slice a Python array?May 01, 2025 am 12:18 AM
How do you slice a Python array?May 01, 2025 am 12:18 AMThe basic syntax for Python list slicing is list[start:stop:step]. 1.start is the first element index included, 2.stop is the first element index excluded, and 3.step determines the step size between elements. Slices are not only used to extract data, but also to modify and invert lists.
 Under what circumstances might lists perform better than arrays?May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Under what circumstances might lists perform better than arrays?May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMListsoutperformarraysin:1)dynamicsizingandfrequentinsertions/deletions,2)storingheterogeneousdata,and3)memoryefficiencyforsparsedata,butmayhaveslightperformancecostsincertainoperations.
 How can you convert a Python array to a Python list?May 01, 2025 am 12:05 AM
How can you convert a Python array to a Python list?May 01, 2025 am 12:05 AMToconvertaPythonarraytoalist,usethelist()constructororageneratorexpression.1)Importthearraymoduleandcreateanarray.2)Uselist(arr)or[xforxinarr]toconvertittoalist,consideringperformanceandmemoryefficiencyforlargedatasets.
 What is the purpose of using arrays when lists exist in Python?May 01, 2025 am 12:04 AM
What is the purpose of using arrays when lists exist in Python?May 01, 2025 am 12:04 AMChoosearraysoverlistsinPythonforbetterperformanceandmemoryefficiencyinspecificscenarios.1)Largenumericaldatasets:Arraysreducememoryusage.2)Performance-criticaloperations:Arraysofferspeedboostsfortaskslikeappendingorsearching.3)Typesafety:Arraysenforc
 Explain how to iterate through the elements of a list and an array.May 01, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Explain how to iterate through the elements of a list and an array.May 01, 2025 am 12:01 AMIn Python, you can use for loops, enumerate and list comprehensions to traverse lists; in Java, you can use traditional for loops and enhanced for loops to traverse arrays. 1. Python list traversal methods include: for loop, enumerate and list comprehension. 2. Java array traversal methods include: traditional for loop and enhanced for loop.
 What is Python Switch Statement?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:08 PM
What is Python Switch Statement?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:08 PMThe article discusses Python's new "match" statement introduced in version 3.10, which serves as an equivalent to switch statements in other languages. It enhances code readability and offers performance benefits over traditional if-elif-el
 What are Exception Groups in Python?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:07 PM
What are Exception Groups in Python?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:07 PMException Groups in Python 3.11 allow handling multiple exceptions simultaneously, improving error management in concurrent scenarios and complex operations.
 What are Function Annotations in Python?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
What are Function Annotations in Python?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:06 PMFunction annotations in Python add metadata to functions for type checking, documentation, and IDE support. They enhance code readability, maintenance, and are crucial in API development, data science, and library creation.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools






