Explain Redis publish and subscribe demonstration, transaction demonstration, and persistence
- coldplay.xixiforward
- 2021-02-23 09:54:222171browse

Recommended (free): redis tutorial
Article Directory
- 1. Introduction to Redis publish and subscribe
- 2. Redis publish and subscribe demonstration
- 3. Transactions in Redis
- 4. Transfer function -Redis transaction demonstration
- 5. Upgraded version of transfer function-watch
- 6. Transaction error handling
- Business logic error
- Syntax error
- 7. Redis persistence
-
- RDB persistence
- AOF persistence
1. Introduction to Redis publish and subscribe
Redis publish and subscribe (pub/sub) is a message communication mode: sender (pub) Send a message and the subscriber (sub) receives the message. Redis clients can subscribe to any number of channels.
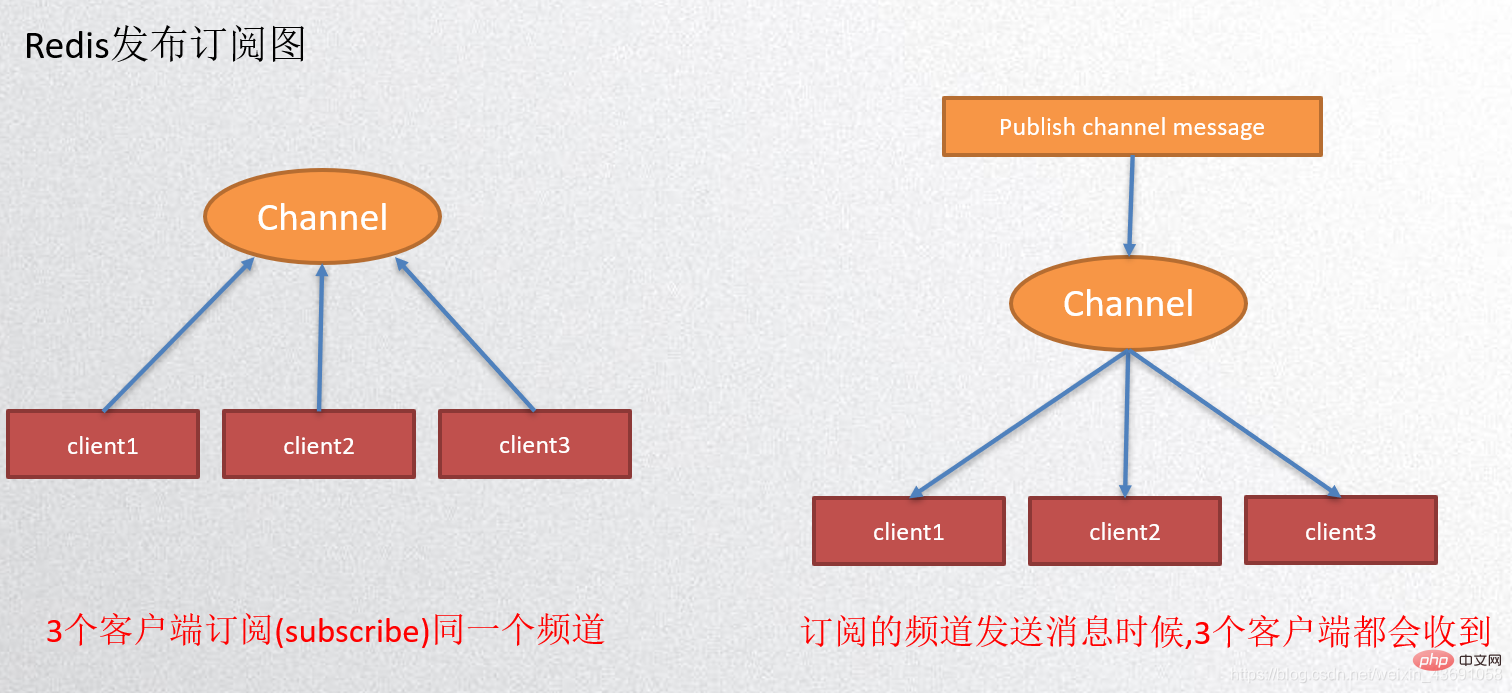
Application scenarios:
- ①
Build a real-time messaging system, such as ordinary instant chat , group chat and other functions. - ②In a blog website, there are n number of fans who have subscribed to you. When you publish a new article, you can
push messagesto the fans. - ③
WeChat public account mode.
2. Redis publish and subscribe demonstration
Publish and subscribe syntax
Subscription channel:
subscribe channel1 [channel2 ...] Subscribe to the information of one or more given channels##psubscribe pattern1 [pattern2 .. .]
Subscribe to one or more channels that match a given pattern.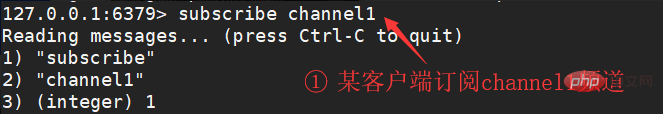 Publish channel:
Publish channel: publish channel message
Send the message to the specified channel.
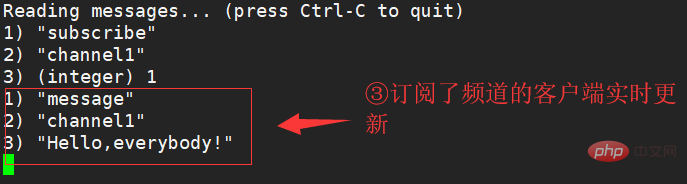 Unsubscribe channel:
Unsubscribe channel: unsubscribe channel1 [channel2 ...]
Refers to unsubscribe given channel.punsubscribe pattern1 [pattern2 ...]
Unsubscribe from all channels of the given pattern.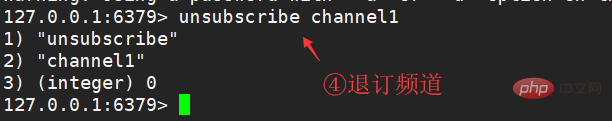
3. Transactions in Redis
Redis transactions can execute multiple commands at one time, (sequentially string Lineized execution, no other commands will be inserted during execution, and no blocking is allowed)Transaction application scenarios:
- Product Flash Sale
- Transfer
Two features:
- Redis will transfer all command sequences in a transaction ization, and then execute them in order (if any command fails to execute, the remaining commands will still be executed)
- will not be inserted by other commands during execution, and no extra races are allowed.
Start the transaction, command the queue, and execute the transaction.
Transaction related commands:
multi Mark the beginning of a transaction block.
exec Execute all commands within the transaction block.
discard Cancel the transaction and abandon the execution of all commands within the transaction block.
watch key Monitor one (or more) keys. If this (or these) keys are changed by other commands before the transaction is executed, the transaction will be interrupted.
unwatch Cancel the monitoring of all keys by the watch command.
4. Transfer function - Redis transaction demonstration
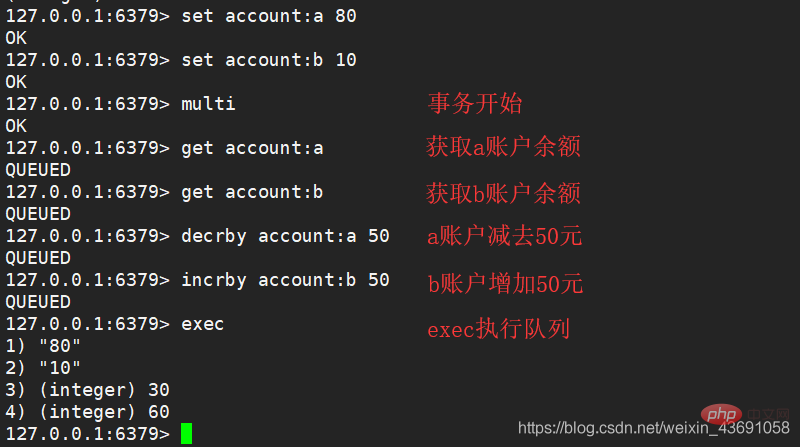
Requirements: Transfer function, A transfers 50 yuan to account B.This example starts a transaction withBefore the transfer, A had 80 yuan and B had 10 yuan.
- After the transfer, A has 30 yuan and B has 60 yuan.
multi, then queues multiple commands into the transaction, and finally triggers the transaction with the exec command .
- Start by entering the Multi command. The entered commands will enter the command queue one by one, but will not be executed.
- Until Exec is entered, Redis will execute the commands in the previous command queue in sequence.
-
 Before executing exec, if you find that there is a problem with the added command, you can use the
Before executing exec, if you find that there is a problem with the added command, you can use the
discardcommand to abandon the queue operation, similar to the rollback operation in MySQL.
5. Upgraded version of transfer function-watch
Requirements: An account operates within a transaction. Before submitting the transaction, another A process operates on the account.
The transfer above is unsafe. If there are other commands operating on account a or b during execution, phantom reads may occur; the solution is to add a watch command to monitor the account. Once other commands operate on account a or b during transaction execution, the program will directly report an error and roll back.
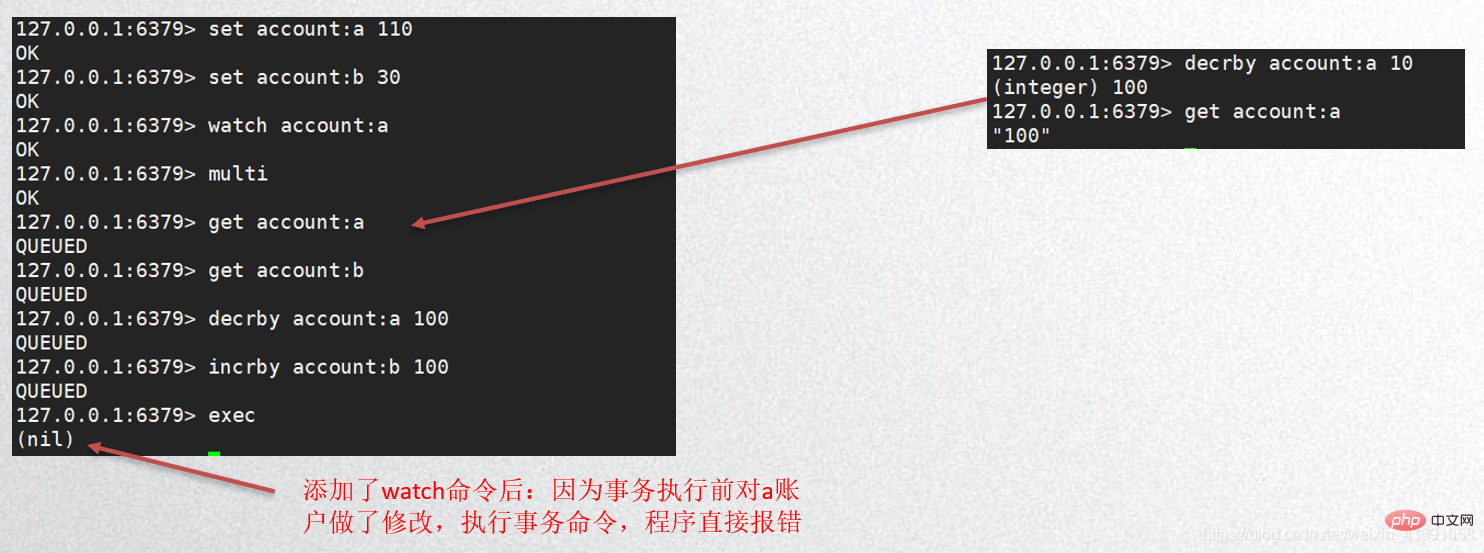
After executing the watch command, if the exec or discard command is executed first, there is no need to execute it again Use unwatch to cancel the monitoring of the key, because the exec or discard command will automatically cancel the monitoring.
6. Transaction error handling
Business logic error
Business logic error occurs: only error reporting The command will not be executed, but other commands will be executed and will not be rolled back. 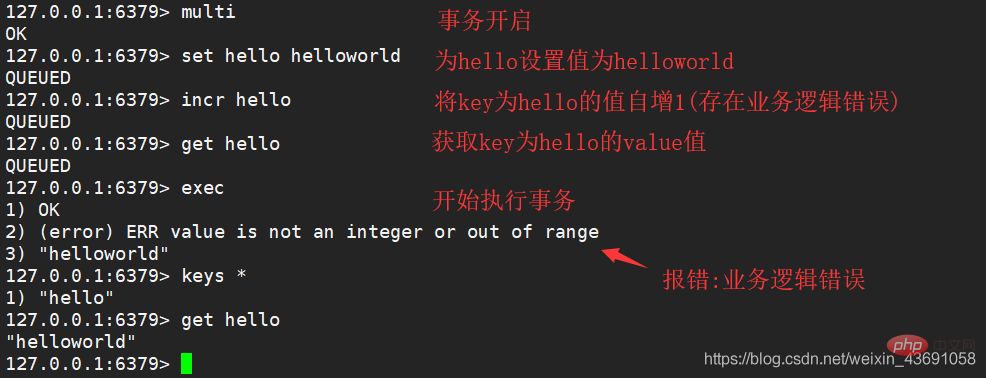
Syntax error
A syntax error occurred: all queues will be canceled during execution. 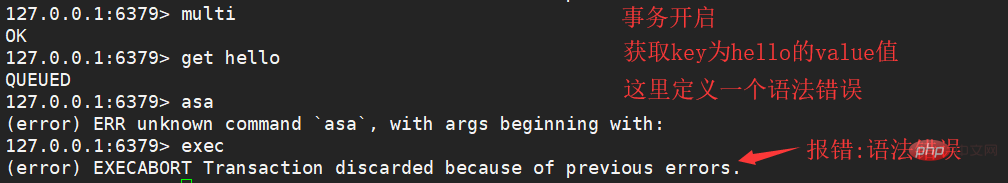
7. Redis persistence
Data is stored in memory: efficient, but memory data will be lost when power is turned off.
Data is stored in the hard disk: the read and write speed is slower than that of the memory, but the data will not be lost when the power is turned off.
RDB persistence
RDB is the default persistence mechanism of redis. RDB is equivalent to taking a snapshot, which saves a state of data. (Dozens of gigabytes of data can be saved as snapshots of several KB)
Snapshots are the default persistence method. This method is to write the data in the memory into a binary file in the form of a snapshot. The default file name is dump.rdb (existing in the redis.conf file).
Advantages:
- Snapshot saves data very quickly and restores data very quickly
- Suitable for disaster backup
Disadvantages:
- Small memory machines are not suitable for use. If the RDB mechanism meets the requirements, it will take snapshots and occupy memory.
AOF persistence
Since the snapshot method is done once at a certain interval, if redis unexpectedly goes down, the last snapshot will be lost. all modifications. If the application requires that no modifications can be lost, the AOF (Append-Only File) persistence method can be used.
appendonly yes command can enable AOF persistence.
There are three ways as follows (the default is: fsync once per second)
-
appendfsync alwaysWrite to the disk immediately after receiving the write command, which is the slowest, but Guaranteeing complete persistence -
appendfsync everysecWriting to disk once every second, making a good compromise between performance and persistence -
appendfsync nodedleg in , but the persistence is not guaranteed
Advantages:
AOF has better persistence than the snapshot method. Because when using AOF persistence mode: redis will append every received write command to the file through the write function (the default is appendonly.aof). When redis restarts, the contents of the entire database will be rebuilt in memory by re-executing the write commands saved in the file.
Disadvantages:
The AOF method also brings another problem. The persistent file will become larger and larger, occupying the hard disk. For example, if we call the incr test command 100 times, all 100 commands must be saved in the file. In fact, 99 of them are redundant.
The above is the detailed content of Explain Redis publish and subscribe demonstration, transaction demonstration, and persistence. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

