Summary of Redis common data type operation instructions
- coldplay.xixiforward
- 2021-02-19 09:45:081930browse

Recommended (free): redis tutorial
Redis commands are used to perform operations on the redis service . To execute commands on the redis service a redis
client is required. You can use theredis-clicommand to start the Redis client. The complete startup command isredis-cli -h host -p port -a password.
There are five commonly used data types in Redis: string, hash, list, set and zset(sorted set ordered set). Before learning these types, you need to learn the management of common command keys. These types are introduced in detail below: For more detailed API, please refer to here
Common commands Key management
Key application scenarios:
- Limited time promotion information.
- Data cache of the website (for some data that needs to be updated regularly, such as score rankings)
- Mobile verification code
- Limit the frequency of website visitor access (for example, maximum access in 1 minute 10 times)
Key naming suggestions:
The key name is case-sensitive; the key should not be too long, try not to exceed 1024 bytes, too long will reduce the search efficiency; in a It is best to use a unified naming pattern for keys in the project, such asuser:id:password
##keys pattern Return all keys that satisfy the given pattern, you can Fuzzy matching, such as keys abc* represents the key starting with abc
exists key Determines whether a key exists, returns 1 if it exists, and returns 0 if it does not exist
expire key second Set the activity time of a key (seconds)
pexpire key milliseconds Set the activity time of a key (milliseconds)
del key Delete a key key
ttl key Returns the remaining time of a key. If the key does not exist, it returns -2; if the key exists but the remaining survival time is not set, it returns -1
persist key Cancel Expiration time
select dbindex over 16 by default, index starts from 0
move key, dbindex ure in you in dbindex Move key in the current database to dbindex database
Randomkey Randomly return a Key # Keyrename Key, Key2 名 DBSIZE Back to the number of KEY in the current database info View database informationconfig get * Store the received request in real time and return the relevant configurationtype(key) Return value type
flushdb wanted will be required> Delete all keys in all databases 1. String String
String is the most basic type of redis, and a key can store up to 523MB. The String type is binary safe. This means that redis' String can contain any data. Such as pictures or serialized objects.
String application scenarios:
String is usually used to save a single string or JSON string data.
- Because String is binary safe, the content of the image file can be stored as a string.
- Counter (regular key-value cache application, number of fans, number of Weibo, votes, etc.)
- INCR and other instructions themselves have the characteristics of atomic operations, so they are completely You can use Redis's NCR, INCRBY, DECR, DECRBY and other instructions to achieve the effect of atomic counting. If, in a certain scenario, three clients read the value of minum (the value is 2) at the same time, and then add 1 to it at the same time, then the final value of bynum must be 5. Many websites use this feature of reds to achieve business statistical counting needs.
Assignment syntax
set key value Assign value to key. Multiple settings will overwrite the old value and ignore the typesetnx key value If the key already exists, it will not be set and 0 will be returned, otherwise it will be set and 1 will be returned. It is one of the solutions to distributed locks. setex key time value Assign value to key and set expiration time. After expiration, both key and value will be cleared. setrange key start end Set the value within the specified interval, the subscript starts from 0, and replaces the string. Value syntax
get key Get the value of the specified key. If the key does not exist, nil is returned. getrange key start end Get the substring of the value of the specified key, including start and end subscriptgetbit key offset For the string value stored in key, get the bit (binary) of the specified offsetgetset key value Set a new value for key value, and returns the old value at the same time. If the key does not exist, it returns nilsubstr(key, start, end) Returns the substring of the value of the string named key
Delete value syntaxdel key Same as Key
Batch writemset k1 v1 k2 v2...kn vn Set multiple values
Read in batches
mget k1 k2... kn
Auto-increment and self-decrementincr key The value of key corresponds to 1incrby key integer The value of key corresponds to integerdecr key mondleigh
Append value to the end of the specified key
Set multiple keys and values at the same time, only when the key does not exist before ValidString lengthstrlen key
2. Double key-value pair Hash
The Hash type is a mapping table of field and value of String type. Hash is particularly suitable for storing objects. It takes up less disk space than String and can be regarded as a map container with key and value. Each hash in Redis can store (2^32)-1 key-value pairs.
Application scenarios of Hash:
is usually used to store a user information object data. Redis' Hash actually uses the internally stored value as a HashMap.
Assignment syntax
- hset key field value
- Set the field and value for the specified key
Set the field and value for the specified key. If the key already exists, it will not take effect. hmset key f1 v1 f2 v2 ... fn vn
Set multiple field-value (field value pairs) to the key of the hash table at the same time.Value syntax
hget key field Get the value based on the field
Get all value values based on multiple fieldshgetall key
Get all fields and values in the Hash tablehkeys key Get all fields in the Hash tablehvals key Get the values corresponding to all fields in the Hash tablehexists key field Check whether the specified field exists in the Hash table Keyhlen key Get the number of fields in the Hash table Delete syntax
hdel key field1 field2 ... fieldn Delete one or more Fields of Hash table
Same as Key
increase and subtraction syntax##hincrby key field integer
It is Hash The value corresponding to the field in the table Key is increased by integerhincrbyfloat key field increment
3. Double-ended linked list List
The List type is a collection of linked list structures. Its main functions include push, pop, and obtaining elements. In more detail, the List type is a double-ended linked list structure. The head or tail elements of the collection can be added and deleted through related operations. The List can be used as both a stack and a queue, which can meet most needs. If the key does not exist, create a new linked list.
If the key already exists, add new content. If all values are removed, the corresponding key will disappear.
The linked list operation is extremely efficient at both the head and tail, but the operation efficiency of the middle elements is very low.
- Application scenarios
- Delete data from collections with large amounts of data
List data display, focus list , fan list, message comments, etc... pagination, hot news (Top10), etc. The paging function can be easily implemented using lrange. In the blog system, the comments of each blog post can also be stored in a separate list.Task Queue
When processing command requests sent by the web client, the execution time of some operations may be longer than we expected. By placing the relevant information of the tasks to be executed, By placing tasks into a queue and then processing the queue, users can defer operations that take a while to complete. This practice of handing over work to a task processor is called a task queue. List can usually be used to implement a message queue and ensure order.Assignment syntax
lpush key value1 value2 ... valueNInsert one or more values into the head of the list Head (add from the left)rpush key value1 value2 ... valueNInsert one or more values into the head of the list (add from the right)lpushx key valueInsert a value into the head (leftmost) of an existing list. If the list does not exist, the operation is invalid.rpushx key valueInsert a value into the end (rightmost) of the existing list. If the list does not exist, the operation is invalid.Value syntax
##llen key
Get the length of the list
lindex key indexGet the elements of the list by index
lrange key start stopGet the elements within the specified range of the listDelete syntax
lpop key
Remove And get the first element of the list (removed from the left)
lpop keyRemove and get the last element of the list (removed from the right)
lrem key count value[[//]/ [Delete count] key[
blpop key1 key2 [timeout] ] Remove and get the first element of the list. If there are no elements in the list, the list will be blocked until the wait times out or is found. Until the element can be popped
brpop key1 key2 timeoutRemove and get the last element of the list. If there is no element in the list, the list will be blocked until the wait times out or a popable element is found
ltrim key start stopwill only in the elements within the specified range, and will delete the elements that are not within the specified range.Modify the syntax
lset key index value
Set the value of the list element by index
linsert key before|after world valueInsert the element value before or after an element world in the list.Advanced commands
rpoplpush source destination
Remove the last element from the source list, add the element to the destination list, and return. (You can operate on yourself, similar to a queue)
brpoplpush source destination timeoutRemove the last element of the source list, add the element to the destination list, and return; if there is no element in the source list, it will The blocking list waits until it times out or until a removable element is found.4. Unordered Set Set
Set is an unordered set of String type. Set members are unique, and duplicate data cannot appear in the set.Collections in Redis are implemented through hash tables, so the complexity of adding, deleting, and searching is O(1).
The maximum number of members in a collection is 232 - 1 (4294967295, each collection can store more than 4 billion members).
Similar to the Hashtable collection in JAVAThe underlying storage structure of Redis's set is particularly magical. The underlying storage structure uses two data structures, intset and hashtable. Intset can be understood as an array and hashtable. It is an ordinary hash table (key is the value of set, value is null).
- Intset is actually an array inside (int8_t coentents[] array), and the data is stored in order, because when searching for data, it is implemented through binary search.
Application scenarios
Perform intersection, union, and difference operations on data [calculation] between two sets
- It is very convenient to implement functions such as joint attention, common preferences, and second-degree friends. For all the collection operations above, you can also use different commands to choose whether to return the results to the client or store them in a new collection.
- Using uniqueness, you can count all independent IPs accessing the website
Assignment syntax
sadd key member1 member2 .. . memberN
Add one or more members to the collectionValue syntax
scard keyGet the number of members of the setsmembers keyReturn all members in the setsismember key memberDetermine whether the member element is Member of the set key (under development: verify whether it exists)srandmember key countReturn one or more random numbers in the setDelete syntax
srem key member1 member2...memberNRemove one or more members from the collectionspop kye countRemove and return one or more members from the collection Random element
smove source destination memberMove the member element from the source collection to the destination collectionDifference set syntax
sdiff key1 key2Returns the difference set of all given sets (left side)sdiffstore destination key1 key2Returns the difference set of all given sets and stores it in destination (the original value in destination Data clearing)Intersection syntax
sinter key1 key2Returns the intersection of all given sets (shared data)sinterstore destination key1 key2Returns the intersection of all given sets and stores them in destinationUnion syntax
sunion key1 key2Returns all given sets The union of setssunionstore destination key1 key2The union of all given sets is stored in the destination set5. Ordered set Zset
Redis zset, like set, is also a collection of string type elements and does not allow duplicate members. The difference is that each element is associated with a double type score. Redis uses scores to sort the members of the collection from small to large. The members of zset are unique, but the scores can be repeated.
- The previous set was k1 v1 v2
- The current zset is k1 score1 v1 score2 v2
Application scenarios
- Ranking
①Twitter's public timeline can be stored with the publication time as the score, so that it will be automatically sorted by time when retrieved.
②A Sorted Set that stores the grades of the entire class. The set value can be the student ID number, and the score can be the test score. In this way, when the data is inserted into the set, natural sorting has already been performed.
③ Use Sorted Set to create a weighted queue. For example, the score of ordinary messages is 1, and the score of important messages is 2. Then the worker thread can choose to obtain the work tasks in the reverse order of the score. Prioritize important tasks.Assignment syntax
zadd key score1 member1 score2 member2Add one or more members to an ordered set, or update the score of an existing memberValue syntax
zcard keyGet the number of members of the ordered setzcount key min maxThe number of members in the set with the specified interval scorezrank key memberReturns the index of the specified member in the ordered set]zrange key start stop [with scores]Returns the number of members with the specified interval score through the index interval The ordered set is synthesized into the members in the specified range (low to high)zrevrange key start stop [with scores]Returns the ordered set through the index interval to synthesize the members in the specified range (high to low)
zlexcount key,min,maxCalculate the number of members in the specified dictionary range in an ordered setDelete syntax
del keyshift Remove setzrem key member [member ...]Remove one or more members from an ordered setzremrangebyrank key start stopRemove an ordered set All members of the given ranking interval (the first place is 0) (sorted from low to high)zremrangebyscore key min maxRemove all members of the given score interval from the ordered setScore auto-increment
zincrby key ncrement memberAdd increment to the score of the specified member in the ordered set6. HyperLoglog
Redis added the HyperLoglog structure in version 2.8.9. This structure is an algorithm used to do cardinality statistics.
Advantages: No matter how many input elements there are, the space required to calculate the cardinality is always fixed and very small.
Disadvantages: It will only calculate the base of the input element, but will not store the input element itself. The index cannot return each input element like a set.
What is a base number?
For example, if the data set is {1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5}, then the cardinality set of this data set is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, and the cardinality is 5. The so-called cardinality estimation is to quickly calculate the cardinality within the acceptable error range.
Why use HyperLogLog?
Traditionally, counting the base value of an object requires 12M of memory. If 10,000 objects are counted, nearly 120G of memory is required, which cannot be widely used in big data scenarios. However, HyperLogLog is used to count the base value of 100 million data. Value, it takes about 12M, and the memory usage is significantly reduced.
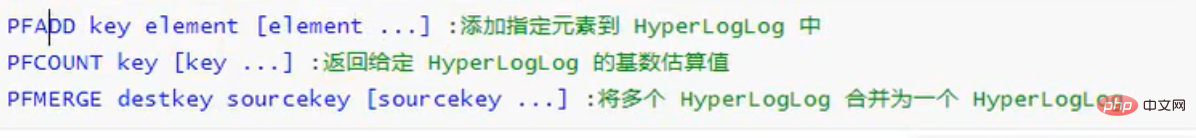
##pfadd key element1 element2 ... elementNAdd the specified element to the HyperLogLog
pfcount keyReturn the given HyperLogLog Estimated cardinality
pfmerge destkey sourcekey1 sourcekey2 ...sourcekeyNMerge multiple HyperLogLogs into one HyperLogLog
The above is the detailed content of Summary of Redis common data type operation instructions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- A guide to using Redis with Lumen
- What are the ways to start redis?
- Use redis database to store user information
- In-depth analysis of Redis
- Detailed explanation of PHP's list-type data structure based on redis to implement IP current limiting operation
- Introduction to several common basic objects in redis
- Analysis of redis event processing process