Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >MySQL Lecture 2: DML Data Operation Statements
MySQL Lecture 2: DML Data Operation Statements
- coldplay.xixiforward
- 2021-02-23 09:32:162129browse
Free learning recommendation: mysql video tutorial
##Article Directory
- 1. Insert
- 2. Modify update
- 3. Delete delete/truncate
- 4. DML statement exercises
1. Insert
Method 1:insert into table name (column name,...) values(value1,...); Method 2:
insert into table name set column name=value, column name=value...
| Whether it supports inserting multiple rows | Whether it supports subqueries | |
|---|---|---|
| √ | × | |
| √ | × |
2. Modify update
1. Modify the record syntax of a single table:update table name
set column=new value, column=new value,...
where filter condition;
update > where > ; set
update table 1 alias
[inner|left|right] join table 2 alias
on connection condition
set column=new value, column=new value,...
where filter condition;
【修改单表的记录】# 修改beautty表中姓周的女生电话为15888888888UPDATE beautySET phone='15888888888'WHERE NAME LIKE '%周%';【修改多表的记录】# 将张无忌的女朋友的电话号改为2333UPDATE boys b1JOIN beauty b2 ON b1.id=b2.boyfriend_idSET b2.phone='2333'WHERE b1.boyName='张无忌';
3. Delete delete/truncate
delete
Single table deletion:delete from table name where filter conditions
delete table 1 alias, table 2 alias
from table 1 alias
inner|left|right join table 2 alias on connection condition
where filter condition;
truncate
Clear Single table:truncate table table name;
There is no return value for truncate deletion, and there is a return value for delete deletion.
| Whether it is possible to add a where condition | Whether it can be rolled back | Is there a return value? | Efficiency | When there are auto-increasing columns in the table | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | √ | √ | Generally | Use delete to delete and then insert data. The self-increasing value starts from the breakpoint | |
| × | × | × | is slightly higher than delete | Use truncate to delete and then insert data, which will grow automatically The value starts from 1 |
Learned the addition, deletion and modification of DML language statements, Try to complete the following exercises:
Answer:
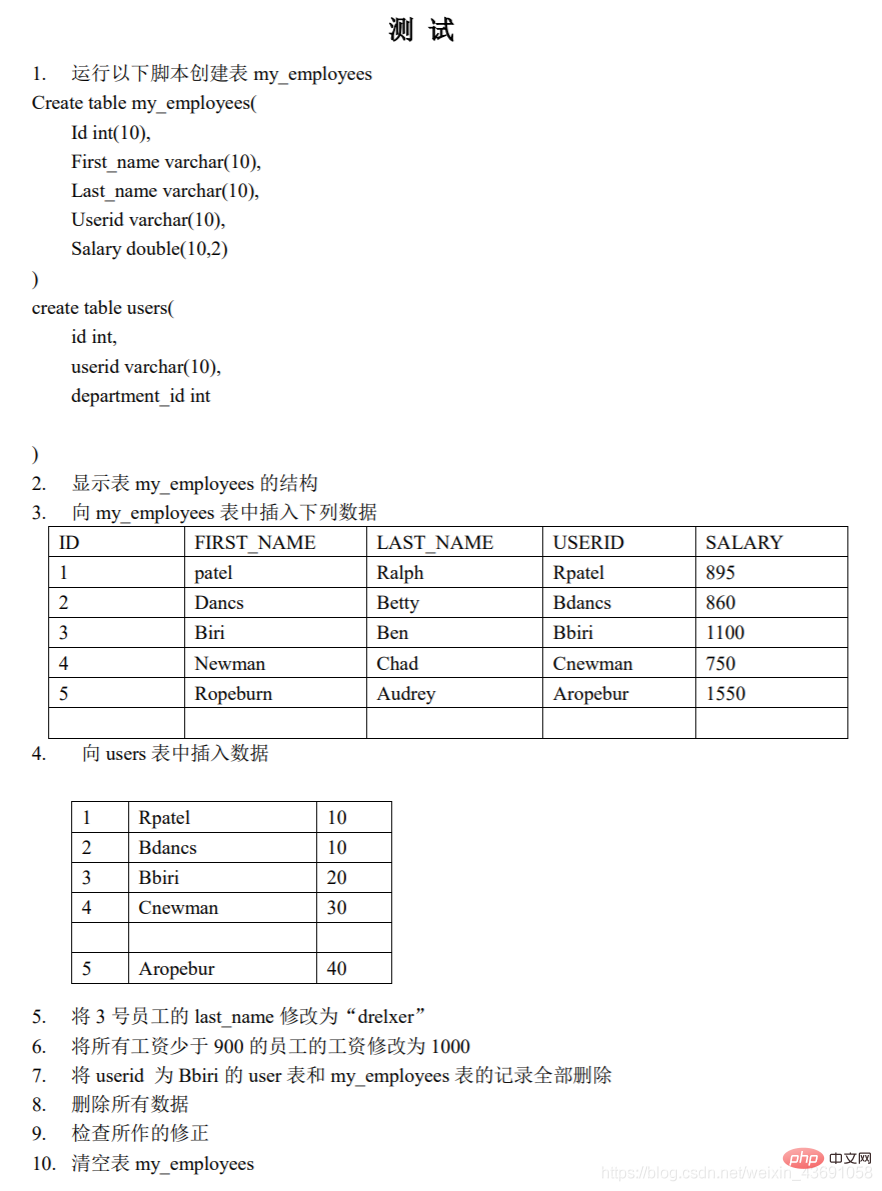
1. Execute the following sql statementCREATE TABLE my_employees(Id INT(10),
First_name VARCHAR(10),
Last_name VARCHAR(10),
Userid VARCHAR(10),
Salary DOUBLE(10,2)
);
CREATE TABLE users(
id INT ,
userid VARCHAR(10),
department_id INT
);
2.DESC my_employees
3.Method 1:INSERT INTO my_employees
VALUES(1,'patel','Ralph','Rpatel',895),
(2,'Dancs','Betty','Bdancs',860 ),
(3,'Biri','Ben','Bbiri',1100),
(4,'Newman','Chad','Cnewman',750),
(5, 'Ropeburn','Audrey','Aropebur',1550);
TRUNCATE TABLE my_employees;
Method 1:
INSERT INTO my_employees
SELECT 1,'patel','Ralph','Rpatel ',895 UNION
SELECT 2,'Dancs','Betty','Bdancs',860 UNION
SELECT 3,'Biri','Ben','Bbiri',1100 UNION
SELECT 4, 'Newman','Chad','Cnewman',750 UNION
SELECT 5,'Ropeburn','Audrey','Aropebur',1550;
4.INSERT INTO usersVALUE(1,'Rpatel',10),
(2,'Bdancs',10),
(3,'Bbiri',20),
(4,'Cnewman' ,30),
(5,'Aropebur',40);
5.UPDATE my_employeesSET Last_name='drelxer'
WHERE id=3;
6.UPDATE my_employeesSET salary=1000
WHERE salary
7.DELETE u,eFROM users u
JOIN my_employees e ON u.userid=e.userid
WHERE u.userid='Bbiri';
8.DELETE FROM my_employees;DELETE FROM users;
9.SELECT * FROM my_employees;SELECT * FROM users;
10.TRUNCATE TABLE my_employees;
More related free learning recommendations:mysql tutorial(Video)
The above is the detailed content of MySQL Lecture 2: DML Data Operation Statements. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Detailed explanation of the replication principle and configuration of high-performance Mysql master-slave architecture
- MySQL's little-known sorting method
- How to delete table fields in mysql
- Let's talk about commonly used date-related functions in MySQL
- What is the reason for the 1251 error when navicat connects to mysql8?