Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Detailed explanation of the replication principle and configuration of high-performance Mysql master-slave architecture
Detailed explanation of the replication principle and configuration of high-performance Mysql master-slave architecture
- coldplay.xixiforward
- 2021-02-11 09:59:243839browse
##Free learning recommendation: mysql video tutorial
1 Replication Overview
Mysql’s built-in replication function is the foundation for building large-scale, high-performance applications. Distribute MySQL data to multiple systems. This distribution mechanism is achieved by copying the data of a certain MySQL host to other hosts (slaves) and executing it again. During replication one server acts as the master server and one or more other servers act as slave servers. The master server writes updates to binary log files and maintains an index of the files to track log rotation. These logs record updates sent to slave servers. When a slave connects to the master, it notifies the master of the location of the last successful update the slave read in the log. The slave receives any updates that have occurred since then, then blocks and waits for the master to be notified of new updates. Please note that when you replicate, all updates to the tables being replicated must be done on the primary server. Otherwise, you must be careful to avoid conflicts between user updates to tables on the master server and updates to tables on the slave server.
1.1 Replication types supported by mysql:
(1): Statement-based replication: SQL statements executed on the master server are executed on the slave server. statement. MySQL uses statement-based replication by default, which is relatively efficient. Once it is found that exact copying cannot be performed, row-based copying will be automatically selected.
(2): Row-based replication: Copy the changed content instead of executing the command on the slave server. Supported from mysql5.0
(3): Mixed type replication: Used by default Statement-based replication, once it is found that statement-based replication cannot be accurate, row-based replication will be used.
1.2. Problems solved by replication
MySQL replication technology has the following characteristics: (1) Data distribution
(2) Load balancing
.
Overall, there are three steps to replication:
(2) The slave copies the master’s binary log events to its relay log; (3) The slave redoes the events in the relay log, and the changes reflect its own data.
The following figure describes the copying process:
The first part of the process is for the master to record the binary log. Before each transaction completes updating data, the master records these changes in the secondary log. MySQL writes transactions serially to the binary log, even if the statements in the transaction are interleaved. After the event is written to the binary log, the master notifies the storage engine to commit the transaction.
The next step is for the slave to copy the master’s binary log to its own relay log. First, the slave starts a worker thread-the I/O thread. The I/O thread opens a normal connection on the master and then starts the binlog dump process. The Binlog dump process reads events from the master's binary log. If it has caught up with the master, it sleeps and waits for the master to generate new events. The I/O thread writes these events to the relay log.
The SQL slave thread (SQL slave thread) handles the last step of the process. The SQL thread reads events from the relay log and replays the events to update the slave's data to make it consistent with the data in the master. As long as the thread is consistent with the I/O thread, the relay log will usually be in the OS's cache, so the overhead of the relay log is very small.
In addition, there is also a working thread in the master: Like other MySQL connections, opening a connection in the master by slave will also cause the master to start a thread. The replication process has an important limitation - replication is serialized on the slave, which means that parallel update operations on the master cannot be performed in parallel on the slave.
2. Master-slave replication configuration
There are two MySQL database servers Master and slave. Master is the master server and slave is the slave server. In the initial state , the data information in the Master and the slave are the same. When the data in the Master changes, the slave also changes accordingly, so that the data information of the master and the slave are synchronized to achieve the purpose of backup.
Key points:
The medium responsible for transmitting various modification actions between the master and slave servers is the binary change log of the master server. This log records various modification actions that need to be transmitted to the slave server. Therefore, the master server must activate the binary logging function. The slave server must have sufficient permissions for it to connect to the master server and request the master server to transfer the binary change log to it.
Environment:
The MySQL database versions of Master and slave are both 5.0.18
IP address: 10.100.0.100
2.1. Create Copy account
1. Create a backup account in the Master's database: Each slave uses a standard MySQL username and password to connect to the master. The user performing the replication operation will be granted REPLICATION SLAVE permission. The username and password will be stored in the text file master.info
The command is as follows:
mysql > GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE,RELOAD,SUPER ON *.* TO backup@’10.100.0.200’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘1234’;
Create an account backup, and only allow access from the 10.100.0.200 address Come up and log in, the password is 1234.
(If the new and old password algorithms of mysql version are different, you can set: set password for 'backup'@'10.100.0.200'=old_password('1234'))
2.2, Copy data
(If you completely newly install the mysql master-slave server, this step is not needed. Because the newly installed master and slave have the same data)
Shut down the Master Server, copy the data in the Master to the B server to synchronize the data in the Master and slave, and ensure that writing operations are prohibited in the Master and slave servers before all setting operations are completed, so that the data in the two databases must be same!
2.3. Configure master
Next, configure the master, including opening the binary log and specifying the unique servr ID. For example, add the following value to the configuration file:
server-id=1log-bin=mysql-binserver-id:为主服务器A的ID值log-bin:二进制变更日值
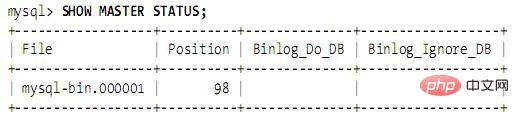
Restart the master and run SHOW MASTER STATUS. The output is as follows:
2.4. Configure slave
The configuration of slave is similar to that of master. You also need to restart the MySQL of slave. As follows:
log_bin = mysql-binserver_id = 2relay_log = mysql-relay-binlog_slave_updates = 1read_only = 1
server_id: is required and unique.
log_bin: It is not necessary for the slave to enable the binary log bin_log, but in some cases, it must be set. For example, if the slave is the master of another slave, bin_log must be set. Here, we enable binary logging and display the name (the default name is hostname, but problems will occur if hostname is changed).
relay_log: Configure the relay log. log_slave_updates means that the slave writes replication events into its own binary log (you will see its use later).
Some people enable the slave binary log but do not set log_slave_updates, and then check whether the slave data has changed. This is a wrong configuration.
read_only: Try to use read_only, which prevents data from being changed (except for special threads). However, read_only is not very practical, especially for applications that need to create tables on the slave.
2.5. Start slave
接下来就是让slave连接master,并开始重做master二进制日志中的事件。你不应该用配置文件进行该操作,而应该使用CHANGE MASTER TO语句,该语句可以完全取代对配置文件的修改,而且它可以为slave指定不同的master,而不需要停止服务器。如下:
mysql> CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='server1', -> MASTER_USER='repl', -> MASTER_PASSWORD='p4ssword', -> MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000001', -> MASTER_LOG_POS=0;
MASTER_LOG_POS的值为0,因为它是日志的开始位置。
你可以用SHOW SLAVE STATUS语句查看slave的设置是否正确:
mysql> SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G*************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Master_Host: server1 Master_User: repl Master_Port: 3306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000001 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 4 Relay_Log_File: mysql-relay-bin.000001 Relay_Log_Pos: 4 Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000001 Slave_IO_Running: No Slave_SQL_Running: No ...omitted... Seconds_Behind_Master: NULLSlave_IO_State, Slave_IO_Running, 和Slave_SQL_Running是No
表明slave还没有开始复制过程。日志的位置为4而不是0,这是因为0只是日志文件的开始位置,并不是日志位置。实际上,MySQL知道的第一个事件的位置是4。
为了开始复制,你可以运行:
mysql> START SLAVE;运行SHOW SLAVE STATUS查看输出结果:mysql> SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G*************************** 1. row *************************** Slave_IO_State: Waiting for master to send event Master_Host: server1 Master_User: repl Master_Port: 3306 Connect_Retry: 60 Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000001 Read_Master_Log_Pos: 164 Relay_Log_File: mysql-relay-bin.000001 Relay_Log_Pos: 164 Relay_Master_Log_File: mysql-bin.000001 Slave_IO_Running: Yes Slave_SQL_Running: Yes ...omitted... Seconds_Behind_Master: 0
在这里主要是看:
Slave_IO_Running=Yes Slave_SQL_Running=Yes
slave的I/O和SQL线程都已经开始运行,而且Seconds_Behind_Master不再是NULL。日志的位置增加了,意味着一些事件被获取并执行了。如果你在master上进行修改,你可以在slave上看到各种日志文件的位置的变化,同样,你也可以看到数据库中数据的变化。
你可查看master和slave上线程的状态。在master上,你可以看到slave的I/O线程创建的连接:
在master上输入show processlist\G;
|
mysql> show processlist \G *************************** 1. row *************************** Id: 1 User: root Host: localhost:2096 db: test Command: Query Time: 0 State: NULL Info: show processlist *************************** 2. row *************************** Id: 2 User: repl Host: localhost:2144 db: NULL Command: Binlog Dump Time: 1838 State: Has sent all binlog to slave; waiting for binlog to be updated Info: NULL 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
行2为处理slave的I/O线程的连接。
在slave服务器上运行该语句:
|
mysql> show processlist \G *************************** 1. row *************************** Id: 1 User: system user Host: db: NULL Command: Connect Time: 2291 State: Waiting for master to send event Info: NULL *************************** 2. row *************************** Id: 2 User: system user Host: db: NULL Command: Connect Time: 1852 State: Has read all relay log; waiting for the slave I/O thread to update it Info: NULL *************************** 3. row *************************** Id: 5 User: root Host: localhost:2152 db: test Command: Query Time: 0 State: NULL Info: show processlist 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
行1为I/O线程状态,行2为SQL线程状态。
2.5、添加新slave服务器
假如master已经运行很久了,想对新安装的slave进行数据同步,甚至它没有master的数据。
此时,有几种方法可以使slave从另一个服务开始,例如,从master拷贝数据,从另一个slave克隆,从最近的备份开始一个slave。Slave与master同步时,需要三样东西:
(1)master的某个时刻的数据快照;
(2)master当前的日志文件、以及生成快照时的字节偏移。这两个值可以叫做日志文件坐标(log file coordinate),因为它们确定了一个二进制日志的位置,你可以用SHOW MASTER STATUS命令找到日志文件的坐标;
(3)master的二进制日志文件。
可以通过以下几中方法来克隆一个slave:
(1) 冷拷贝(cold copy)
停止master,将master的文件拷贝到slave;然后重启master。缺点很明显。
(2) 热拷贝(warm copy)
如果你仅使用MyISAM表,你可以使用mysqlhotcopy拷贝,即使服务器正在运行。
(3) 使用mysqldump
使用mysqldump来得到一个数据快照可分为以下几步:
锁表:如果你还没有锁表,你应该对表加锁,防止其它连接修改数据库,否则,你得到的数据可以是不一致的。如下:
mysql> FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK;
在另一个连接用mysqldump创建一个你想进行复制的数据库的转储:
shell> mysqldump --all-databases --lock-all-tables >dbdump.db
对表释放锁。
mysql> UNLOCK TABLES;
3、深入了解复制
已经讨论了关于复制的一些基本东西,下面深入讨论一下复制。
3.1、基于语句的复制(Statement-Based Replication)
MySQL 5.0及之前的版本仅支持基于语句的复制(也叫做逻辑复制,logical replication),这在数据库并不常见。master记录下改变数据的查询,然后,slave从中继日志中读取事件,并执行它,这些SQL语句与master执行的语句一样。
这种方式的优点就是实现简单。此外,基于语句的复制的二进制日志可以很好的进行压缩,而且日志的数据量也较小,占用带宽少——例如,一个更新GB的数据的查询仅需要几十个字节的二进制日志。而mysqlbinlog对于基于语句的日志处理十分方便。
但是,基于语句的复制并不是像它看起来那么简单,因为一些查询语句依赖于master的特定条件,例如,master与slave可能有不同的时间。所以,MySQL的二进制日志的格式不仅仅是查询语句,还包括一些元数据信息,例如,当前的时间戳。即使如此,还是有一些语句,比如,CURRENT USER函数,不能正确的进行复制。此外,存储过程和触发器也是一个问题。
另外一个问题就是基于语句的复制必须是串行化的。这要求大量特殊的代码,配置,例如InnoDB的next-key锁等。并不是所有的存储引擎都支持基于语句的复制。
3.2、基于记录的复制(Row-Based Replication)
MySQL增加基于记录的复制,在二进制日志中记录下实际数据的改变,这与其它一些DBMS的实现方式类似。这种方式有优点,也有缺点。优点就是可以对任何语句都能正确工作,一些语句的效率更高。主要的缺点就是二进制日志可能会很大,而且不直观,所以,你不能使用mysqlbinlog来查看二进制日志。
对于一些语句,基于记录的复制能够更有效的工作,如:
mysql> INSERT INTO summary_table(col1, col2, sum_col3) -> SELECT col1, col2, sum(col3) -> FROM enormous_table -> GROUP BY col1, col2;
假设,只有三种唯一的col1和col2的组合,但是,该查询会扫描原表的许多行,却仅返回三条记录。此时,基于记录的复制效率更高。
另一方面,下面的语句,基于语句的复制更有效:
mysql> UPDATE enormous_table SET col1 = 0;
此时使用基于记录的复制代价会非常高。由于两种方式不能对所有情况都能很好的处理,所以,MySQL 5.1支持在基于语句的复制和基于记录的复制之前动态交换。你可以通过设置session变量binlog_format来进行控制。
3.3、复制相关的文件
除了二进制日志和中继日志文件外,还有其它一些与复制相关的文件。如下:
(1)mysql-bin.index
Once the server turns on the binary log, it will generate a file with the same name as the second log file but ending with .index. It is used to track which binary log files are present on disk. MySQL uses it to locate binary log files. Its content is as follows (on my machine): 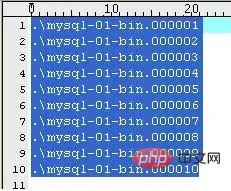
(2)mysql-relay-bin.index
The function of this file is similar to mysql-bin.index , but it's for relay logs, not binary logs. The content is as follows:
.\mysql-02-relay-bin.000017
.\mysql-02-relay-bin.000018
(3)master.info
Save Master related information. Do not delete it, otherwise, the slave will not be able to connect to the master after restarting. The content is as follows (on my machine): 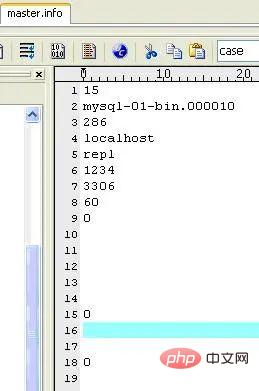
The I/O thread updates the master.info file, the content is as follows (on my machine):
|
.\mysql-02-relay-bin.000019 254 mysql-01-bin.000010 286 0 52813 |
(4)relay-log.info
Contains information about the current binary log and relay log in the slave.
3.4. Send replication events to other slaves
When setting log_slave_updates, you can let the slave act as the master of other slaves. At this time, the slave writes the events executed by the SQL thread into its own binary log. Then, its slave can obtain these events and execute them. As follows: 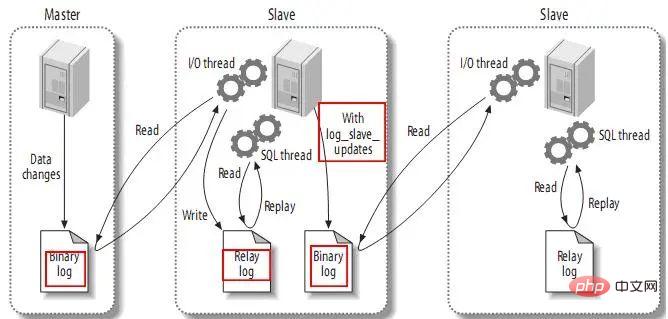
3.5. Replication Filters
Replication filtering allows you to copy only part of the data in the server. There are two types of replication filters: on the master Filter events in the binary log; filter events in the relay log on the slave. As follows:
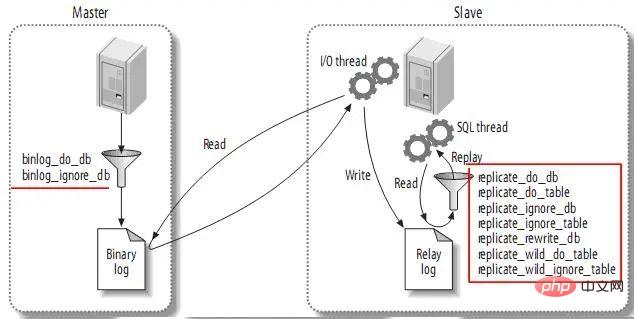
The replicated architectures are The following basic principles:
(1) Each slave can only have one master;
(2) Each slave can only have one unique server ID;
(3) Each master can have many slave;
(4) If you set log_slave_updates, the slave can be the master of other slaves, thereby spreading the master's updates.
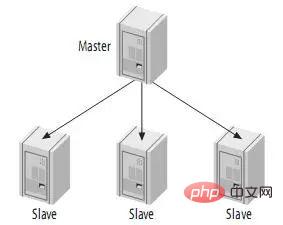 If there are few write operations and frequent read operations, this structure can be adopted. You can distribute read operations to other slaves to reduce the pressure on the master. However, when the number of slaves increases to a certain number, the load of the slaves on the master and the network bandwidth will become a serious problem.
If there are few write operations and frequent read operations, this structure can be adopted. You can distribute read operations to other slaves to reduce the pressure on the master. However, when the number of slaves increases to a certain number, the load of the slaves on the master and the network bandwidth will become a serious problem.
Although this structure is simple, it is very flexible and sufficient to meet most application needs. Some suggestions:
(1) Different slaves play different roles (such as using different indexes, or different storage engines);
(2) Use one slave as a backup master and only perform replication;
(3) Use a remote slave for disaster recovery;
可能有些读者朋友会有一个担心,这样搭建复制环境之后,难道不会造成两台MySQL之间的循环复制么?实际上MySQL自己早就想到了这一点,所以在MySQL的BinaryLog中记录了当前MySQL的server-id,而且这个参数也是我们搭建MySQLReplication的时候必须明确指定,而且Master和Slave的server-id参数值比需要不一致才能使MySQLReplication搭建成功。一旦有了server-id的值之后,MySQL就很容易判断某个变更是从哪一个MySQLServer最初产生的,所以就很容易避免出现循环复制的情况。而且,如果我们不打开记录Slave的BinaryLog的选项(--log-slave-update)的时候,MySQL根本就不会记录复制过程中的变更到BinaryLog中,就更不用担心可能会出现循环复制的情形了。
如图: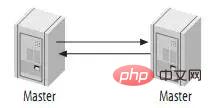
主动的Master-Master复制有一些特殊的用处。例如,地理上分布的两个部分都需要自己的可写的数据副本。这种结构最大的问题就是更新冲突。假设一个表只有一行(一列)的数据,其值为1,如果两个服务器分别同时执行如下语句:
在第一个服务器上执行:
mysql> UPDATE tbl SET col=col + 1;
在第二个服务器上执行:
mysql> UPDATE tbl SET col=col * 2;
那么结果是多少呢?一台服务器是4,另一个服务器是3,但是,这并不会产生错误。
实际上,MySQL并不支持其它一些DBMS支持的多主服务器复制(Multimaster Replication),这是MySQL的复制功能很大的一个限制(多主服务器的难点在于解决更新冲突),但是,如果你实在有这种需求,你可以采用MySQL Cluster,以及将Cluster和Replication结合起来,可以建立强大的高性能的数据库平台。但是,可以通过其它一些方式来模拟这种多主服务器的复制。
4.3、主动-被动模式的Master-Master(Master-Master in Active-Passive Mode)
这是master-master结构变化而来的,它避免了M-M的缺点,实际上,这是一种具有容错和高可用性的系统。它的不同点在于其中一个服务只能进行只读操作。如图: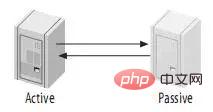
4.4 级联复制架构 Master –Slaves - Slaves
在有些应用场景中,可能读写压力差别比较大,读压力特别的大,一个Master可能需要上10台甚至更多的Slave才能够支撑注读的压力。这时候,Master就会比较吃力了,因为仅仅连上来的SlaveIO线程就比较多了,这样写的压力稍微大一点的时候,Master端因为复制就会消耗较多的资源,很容易造成复制的延时。
遇到这种情况如何解决呢?这时候我们就可以利用MySQL可以在Slave端记录复制所产生变更的BinaryLog信息的功能,也就是打开—log-slave-update选项。然后,通过二级(或者是更多级别)复制来减少Master端因为复制所带来的压力。也就是说,我们首先通过少数几台MySQL从Master来进行复制,这几台机器我们姑且称之为第一级Slave集群,然后其他的Slave再从第一级Slave集群来进行复制。从第一级Slave进行复制的Slave,我称之为第二级Slave集群。如果有需要,我们可以继续往下增加更多层次的复制。这样,我们很容易就控制了每一台MySQL上面所附属Slave的数量。这种架构我称之为Master-Slaves-Slaves架构
这种多层级联复制的架构,很容易就解决了Master端因为附属Slave太多而成为瓶颈的风险。下图展示了多层级联复制的Replication架构。
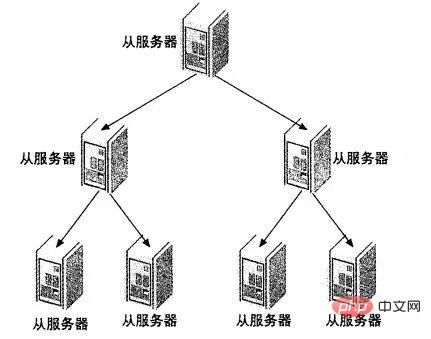
当然,如果条件允许,我更倾向于建议大家通过拆分成多个Replication集群来解决
上述瓶颈问题。毕竟Slave并没有减少写的量,所有Slave实际上仍然还是应用了所有的数据变更操作,没有减少任何写IO。相反,Slave越多,整个集群的写IO总量也就会越多,我们没有非常明显的感觉,仅仅只是因为分散到了多台机器上面,所以不是很容易表现出来。
此外,增加复制的级联层次,同一个变更传到最底层的Slave所需要经过的MySQL也会更多,同样可能造成延时较长的风险。
而如果我们通过分拆集群的方式来解决的话,可能就会要好很多了,当然,分拆集群也需要更复杂的技术和更复杂的应用系统架构。
4.5、带从服务器的Master-Master结构(Master-Master with Slaves)
这种结构的优点就是提供了冗余。在地理上分布的复制结构,它不存在单一节点故障问题,而且还可以将读密集型的请求放到slave上。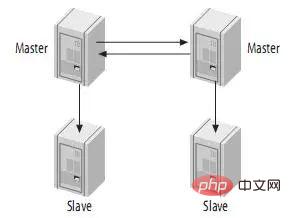
级联复制在一定程度上面确实解决了Master因为所附属的Slave过多而成为瓶颈的问题,但是他并不能解决人工维护和出现异常需要切换后可能存在重新搭建Replication的问题。这样就很自然的引申出了DualMaster与级联复制结合的Replication架构,我称之为Master-Master-Slaves架构
和Master-Slaves-Slaves架构相比,区别仅仅只是将第一级Slave集群换成了一台单独的Master,作为备用Master,然后再从这个备用的Master进行复制到一个Slave集群。
这种DualMaster与级联复制结合的架构,最大的好处就是既可以避免主Master的写入操作不会受到Slave集群的复制所带来的影响,同时主Master需要切换的时候也基本上不会出现重搭Replication的情况。但是,这个架构也有一个弊端,那就是备用的Master有可能成为瓶颈,因为如果后面的Slave集群比较大的话,备用Master可能会因为过多的SlaveIO线程请求而成为瓶颈。当然,该备用Master不提供任何的读服务的时候,瓶颈出现的可能性并不是特别高,如果出现瓶颈,也可以在备用Master后面再次进行级联复制,架设多层Slave集群。当然,级联复制的级别越多,Slave集群可能出现的数据延时也会更为明显,所以考虑使用多层级联复制之前,也需要评估数据延时对应用系统的影响。
5、复制的常见问题
错误一:change master导致的:
Last_IO_Error: error connecting to master 'repl1@IP:3306' - retry-time: 60 retries
错误二:在没有解锁的情况下停止slave进程:
mysql> stop slave;
ERROR 1192 (HY000): Can't execute the given command because you have active locked tables or an active transaction
错误三:在没有停止slave进程的情况下change master
mysql> change master to master_host=‘IP', master_user='USER', master_password='PASSWD', master_log_file='mysql-bin.000001',master_log_pos=106;
ERROR 1198 (HY000): This operation cannot be performed with a running slave; run STOP SLAVE first
错误四:A B的server-id相同:
Last_IO_Error: Fatal error: The slave I/O thread stops because master and slave have equal MySQL server ids;
these ids must be different for replication to work (or the --replicate-same-server-id option must be used on
slave but this does not always make sense; please check the manual before using it).
查看server-id
mysql> show variables like 'server_id';
手动修改server-id
mysql> set global server_id=2; #此处的数值和my.cnf里设置的一样就行
mysql> slave start;
错误五:change master之后,查看slave的状态,发现slave_IO_running 仍为NO
需要注意的是,上述几个错误做完操作之后要重启mysql进程,slave_IO_running 变为Yes
错误六:MySQL主从同步异常Client requested master to start replication from position > file size
字面理解:从库的读取binlog的位置大于主库当前binglog的值
这一般是主库重启导致的问题,主库从参数sync_binlog默认为1000,即主库的数据是先缓存到1000条后统一fsync到磁盘的binlog文件中。

当主库重启的时候,从库直接读取主库接着之前的位点重新拉binlog,但是主库由于没有fsync最后的binlog,所以会返回1236 的错误。
正常建议配置sync_binlog=1 也就是每个事务都立即写入到binlog文件中。
1、在从库检查slave状态:
偏移量为4063315
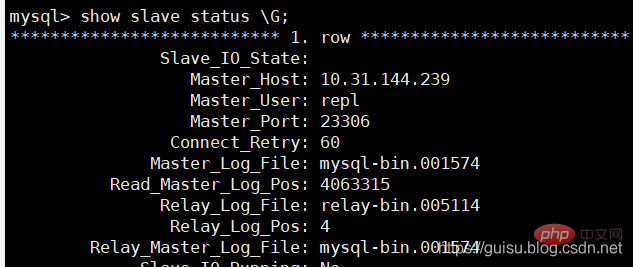
2、在主库检查mysql-bin.001574的偏移量位置
mysqlbinlog mysql-bin.001574 > ./mysql-bin.001574.bak
tail -10 ./mysql-bin.001574.bak
mysql-bin.001574文件最后几行 发现最后偏移量是4059237,从库偏移量的4063315远大主库的偏移量4059237,也就是参数sync_binlog=1000导致的。
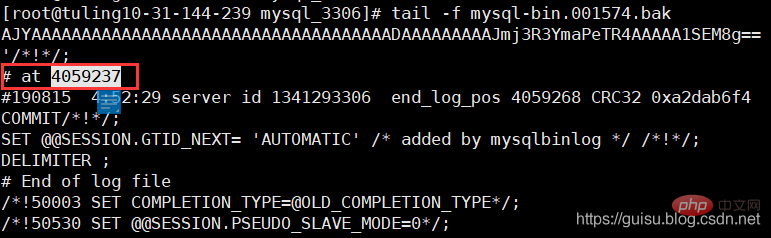
3、重新设置salve
mysql> stop slave;mysql> change master to master_log_file='mysql-bin.001574' ,master_log_pos=4059237;mysql> start slave;
错误8:数据同步异常情况
第一种:在master上删除一条记录,而slave上找不到。
Last_Error: Could not execute Delete_rows event on table market_edu.tl_player_task; Can't find record in 'tl_player_task', Error_code: 1032; handler error HA_ERR_KEY_NOT_FOUND; the event's master log mysql-bin.002094, end_log_pos 286434186
解决方法:由于master要删除一条记录,而slave上找不到故报错,这种情况主上都将其删除了,那么从机可以直接跳过。
可用命令:stop slave; set global sql_slave_skip_counter=1; start slave;
第二种:主键重复。在slave已经有该记录,又在master上插入了同一条记录。
Last_SQL_Error: Could not execute Write_rows event on table hcy.t1;
Duplicate entry '2' for key 'PRIMARY',
Error_code: 1062;
handler error HA_ERR_FOUND_DUPP_KEY; the event's master log mysql-bin.000006, end_log_pos 924
解决方法:在slave删除重复的主键
第三种:在master上更新一条记录,而slave上找不到,丢失了数据。
Last_SQL_Error: Could not execute Update_rows event on table hcy.t1;
Can't find record in 't1',
Error_code: 1032;
handler error HA_ERR_KEY_NOT_FOUND; the event's master log mysql-bin.000010, end_log_pos 263
解决方法:把丢失的数据在slave上填补,然后跳过报错即可。
insert into t1 values (2,'BTV');
stop slave ;set global sql_slave_skip_counter=1;start slave;
相关免费学习推荐:mysql数据库(视频)
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the replication principle and configuration of high-performance Mysql master-slave architecture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

