Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Interpretation of vue source code architecture (detailed)
Interpretation of vue source code architecture (detailed)
- 不言forward
- 2019-01-24 10:03:053356browse
The content of this article is about the interpretation of vue source code architecture (detailed). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Download
Go to github to downloadVue
npm install npm run dev
Run it
rollup flow
#Vue uses rollup packaging, flow standard data type
rollup can be applied with webpack first, it reads almost the same, time is limited, after all, only 5 minutes, you don’t need to read the rollup document for this
Entry
Open package.json
Let’s look at the scripts configuration
"dev": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --environment TARGET:web-full-dev", "dev:cjs": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --environment TARGET:web-runtime-cjs-dev",
Find scripts /config.js
Open
Different configs will be selected depending on the configuration of TARGET
At the same time, process.env.NODE_ENV is configured here. Environment
TARGET has CommonJS , ES Modules, UMD about js introduced types
There are also weex, ssr
'web-runtime-cjs-dev': {
entry: resolve('web/entry-runtime.js'),
dest: resolve('dist/vue.runtime.common.dev.js'),
format: 'cjs',
env: 'development',
banner
}
Set the alias path under alias.js
Let’s introduce src/platforms
first There are separate web and weex entrances for web and weex
Under the web file are CommonJS, ES Modules, UMD regarding the js introduction type, and the server packaging entrance
Open web/entry-runtime.js
Introduction
import Vue from './runtime/index' export default Vue
Open ./runtime/index
import Vue from 'core/index'
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
export default Vue
Added the mount method on the vue prototype
Processed devtools, there is no installation reminder to install devtools
Given this prompt, dev environment prompt
You are running Vue in development mode. Make sure to turn on production mode when deploying for production. See more tips at https://vuejs.org/guide/deployment.html
platforms directory folder is explained
core directory
Open core/instance/index
What comes into view is
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
The first thing to execute is initMixin(Vue)
Open init
export function initMixin (Vue) {
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm = this
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++
let startTag, endTag
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`
mark(startTag)
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// 处理传入的options
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
// 传入的options,默认的options一起合并挂载到vm.$options上
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 代理
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// 生命周期
initLifecycle(vm)
// emit on 事件
initEvents(vm)
// 处理render vdom
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
// 处理Injections
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
// 双向数据绑定,监听订阅
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag)
}
// 渲染到dom
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}
lifecycle
Open lifecycle
export function callHook (vm: Component, hook: string) {
// disable dep collection when invoking lifecycle hooks
pushTarget()
//执行对象的周期函数,周期函数最后被处理成数组
const handlers = vm.$options[hook]
const info = `${hook} hook`
if (handlers) {
for (let i = 0, j = handlers.length; i <p>When callingHook, it is executed Corresponding cycle, the </p><h3>Events</h3><p>initEvents written by the developer in the cycle function implements emit on and other methods. Please refer to the listener subscriber model, which will not be explained in detail here</p><h3> render</h3><h4>renderMixin function</h4><p>Added $nextTick _render prototype object</p><p>$nextTick will be called immediately after the dom is updated</p><p>nextTick(fn, this) It is a self-executing function </p><p>_render returns the js data of the node. It is not the dom</p><p> that made the Vdom</p><h4>initRender function</h4><p> added to the vm. The methods _c and $createElement are used to render </p><h3>state</h3><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">if (!(key in vm)) {
proxy(vm, `_props`, key)
}act as a proxy for the vue attribute. You can get the value of this.data.a by accessing this.a
export function initState (vm: Component) {
vm._watchers = []
const opts = vm.$options
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props)
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods)
if (opts.data) {
initData(vm)
} else {
observe(vm._data = {}, true /* asRootData */)
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed)
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch)
}
}Monitor data
stateMixin function
Add prototype object
Vue.prototype.$set = set Vue.prototype.$delete = del
Others
src/compiler does compilation processing
core/ componetd does keep-alive
core/util encapsulates the common method
core/vdom vdom algorithm
The above overall architecture analysis is completed
Attached picture 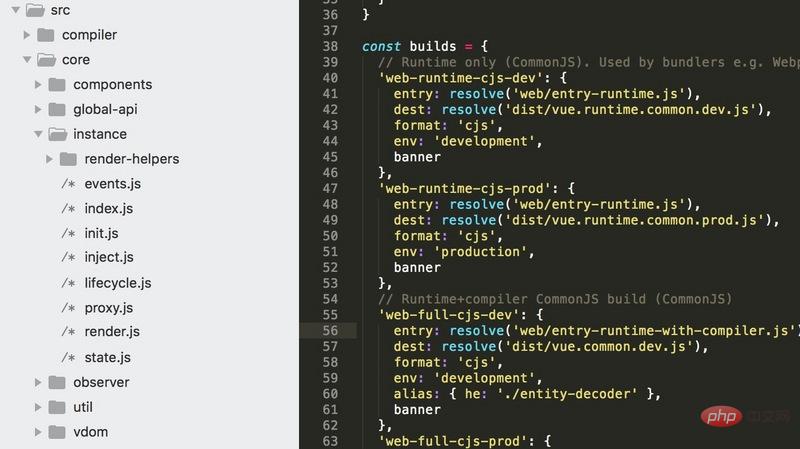
The above is the detailed content of Interpretation of vue source code architecture (detailed). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Learn and understand vue source code together
- Vue source code entry file example analysis
- How to use vue source code to parse event mechanism
- Dependency collection principle of Vue source code
- File structure and operating mechanism of Vue source code
- Learning analysis of hook functions in Vue source code
- What is AST? Parsing of AST syntax tree in Vue source code

