Accept blocking model is a relatively old model, but it contains a lot of interesting knowledge, such as blocking/non-blocking, locks, timeout retransmission...
Service End program acceptSever.php
<?php set_time_limit(0); # 设置脚本执行时间无限制
class SocketServer
{
private static $socket;
function SocketServer($port)
{
global $errno, $errstr;
if ($port < 1024) {
die("Port must be a number which bigger than 1024/n");
}
$socket = stream_socket_server("tcp://0.0.0.0:{$port}", $errno, $errstr);
if (!$socket) die("$errstr ($errno)");
while ($conn = stream_socket_accept($socket, -1)) { // 这样设置不超时才有用
static $id = 0; # 进程 id
static $ct = 0; # 接收数据的长度
$ct_last = $ct;
$ct_data = ''; # 接受的数据
$buffer = ''; # 分段读取数据
$id++;
echo "Client $id come" . PHP_EOL;
# 持续监听
while (!preg_match('{/r/n}', $buffer)) { // 没有读到结束符,继续读
// if (feof($conn)) break; // 防止 popen 和 fread 的 bug 导致的死循环
$buffer = fread($conn, 1024);
echo 'R' . PHP_EOL; # 打印读的次数
$ct += strlen($buffer);
$ct_data .= preg_replace('{/r/n}', '', $buffer);
}
$ct_size = ($ct - $ct_last) * 8;
echo "[$id] " . __METHOD__ . " > " . $ct_data . PHP_EOL;
fwrite($conn, "Received $ct_size byte data./r/n");
fclose($conn);
}
fclose($socket);
}
}
new SocketServer(2000);
Client program acceptClient.php
<?php # 日志记录
function debug ($msg)
{
error_log($msg, 3, './socket.log');
}
if ($argv[1]) {
$socket_client = stream_socket_client('tcp://0.0.0.0:2000', $errno, $errstr, 30);
/* 设置脚本为非阻塞 */
# stream_set_blocking($socket_client, 0);
/* 设置脚本超时时间 */
# stream_set_timeout($socket_client, 0, 100000);
if (!$socket_client) {
die("$errstr ($errno)");
} else {
# 填充容器
$msg = trim($argv[1]);
for ($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++) {
$res = fwrite($socket_client, "$msg($i)");
usleep(100000);
echo 'W'; // 打印写的次数
# debug(fread($socket_client, 1024)); // 将产生死锁,因为 fread 在阻塞模式下未读到数据时将等待
}
fwrite($socket_client, "/r/n"); // 传输结束符
# 记录日志
debug(fread($socket_client, 1024));
fclose($socket_client);
}
}
else {
// $phArr = array();
// for ($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++) {
// $phArr[$i] = popen("php ".__FILE__." '{$i}:test'", 'r');
// }
// foreach ($phArr as $ph) {
// pclose($ph);
// }
for ($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++) {
system("php ".__FILE__." '{$i}:test'"); # 这里等于 php "当前文件" "脚本参数"
}
}Code analysis
First, explain the above code logic: client acceptClient.php sends data in a loop , and finally send the terminator; the server accept Server.php uses the accept blocking method to receive the socket connection, and then receives data in a loop until the terminator is received, and returns the result data (number of bytes received). The client receives the data returned by the server. , write to the log. Although the logic is very simple, there are several situations worth analyzing:
A> By default, when running php socket_client.php test, the client will print 10 W, and the server will print several R, followed by For the received data, socket.log records the reception result data returned by the server. The effect is as follows: 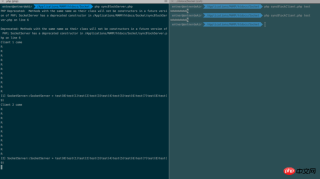
This situation is easy to understand and will not be repeated. Then, use the telnet command to open multiple clients at the same time. You will find that the server only processes one client at a time, as shown in the figure: 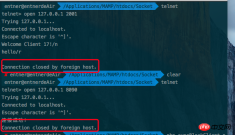
Others need to be queued later. "; This is the characteristic of blocking IO. The weaknesses of this mode are obvious and the efficiency is extremely low.
B> Only open the comment code on line 29 of socket_client.php and run php socket_client.php test again. The client prints a W and the server also prints an R. After that, both programs are stuck. Why is this? After analyzing the logic, you will find that this is because the client wants to return data to the server before sending the terminator; and the server, because it has not received the terminator, is also asking the client for the terminator. Cause deadlock. The reason why only one W and R is typed is because fread is blocking by default. To solve this deadlock, you must open the comment code on line 17 of socket_client.php and set a timeout of 0.1 seconds for the socket. If you run it again, you will find that a W and R appear every 0.1 seconds and then end normally. The reception result data returned by the server is also recorded normally. It can be seen that fread is blocking by default. We must pay special attention when programming. If the timeout is not set, deadlock will easily occur.
C> Open only 14 lines of comments, set the script to non-blocking, and run php socket_client.php test. The result is basically the same as case A. The only difference is that the socket.log does not record the return data. This is because when In our non-blocking mode, the client can continue execution without waiting for the response result from the server. When debug is executed, the read data is still empty, so socket.log is also empty. Here you can see the difference between the client running in blocking and non-blocking modes. Of course, when the client does not care about accepting the results, the non-blocking mode can be used to obtain maximum efficiency.
D> Running php socket_client.php is to run the above logic 10 times continuously. There is no problem with this; but what is very strange is that if you use 39-45 lines of code, use popen to open 10 processes at the same time. , will cause an infinite loop on the server side, which is very weird! Later, after investigation, it was found that as long as the connection created by the process opened with popen will cause fread or socket_read to error and directly return an empty string, resulting in an infinite loop, after checking the PHP source code, it was found that PHP's popen and fread functions are not native to C at all. , a large amount of php_stream_* implementation logic has been inserted into it. It is initially estimated that it is caused by the Socket connection interruption caused by a bug in it. The solution is to open the 33 lines of code in socket_server.php. If the connection is interrupted, jump out of the loop, but In this way, a lot of data will be lost, and this issue requires special attention!
Related recommendations:
Basic applications of PHP and Apache
What are PHP regular expressions? How to use PHP regular expressions (with code)
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to Accept blocking model in PHP network programming. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Explain the concept of a PHP session in simple terms.Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Explain the concept of a PHP session in simple terms.Apr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AMPHPsessionstrackuserdataacrossmultiplepagerequestsusingauniqueIDstoredinacookie.Here'showtomanagethemeffectively:1)Startasessionwithsession_start()andstoredatain$_SESSION.2)RegeneratethesessionIDafterloginwithsession_regenerate_id(true)topreventsessi
 How do you loop through all the values stored in a PHP session?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:06 AM
How do you loop through all the values stored in a PHP session?Apr 26, 2025 am 12:06 AMIn PHP, iterating through session data can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Start the session using session_start(). 2. Iterate through foreach loop through all key-value pairs in the $_SESSION array. 3. When processing complex data structures, use is_array() or is_object() functions and use print_r() to output detailed information. 4. When optimizing traversal, paging can be used to avoid processing large amounts of data at one time. This will help you manage and use PHP session data more efficiently in your actual project.
 Explain how to use sessions for user authentication.Apr 26, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain how to use sessions for user authentication.Apr 26, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe session realizes user authentication through the server-side state management mechanism. 1) Session creation and generation of unique IDs, 2) IDs are passed through cookies, 3) Server stores and accesses session data through IDs, 4) User authentication and status management are realized, improving application security and user experience.
 Give an example of how to store a user's name in a PHP session.Apr 26, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Give an example of how to store a user's name in a PHP session.Apr 26, 2025 am 12:03 AMTostoreauser'snameinaPHPsession,startthesessionwithsession_start(),thenassignthenameto$_SESSION['username'].1)Usesession_start()toinitializethesession.2)Assigntheuser'snameto$_SESSION['username'].Thisallowsyoutoaccessthenameacrossmultiplepages,enhanc
 What are some common problems that can cause PHP sessions to fail?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:16 AM
What are some common problems that can cause PHP sessions to fail?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:16 AMReasons for PHPSession failure include configuration errors, cookie issues, and session expiration. 1. Configuration error: Check and set the correct session.save_path. 2.Cookie problem: Make sure the cookie is set correctly. 3.Session expires: Adjust session.gc_maxlifetime value to extend session time.
 How do you debug session-related issues in PHP?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:12 AM
How do you debug session-related issues in PHP?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:12 AMMethods to debug session problems in PHP include: 1. Check whether the session is started correctly; 2. Verify the delivery of the session ID; 3. Check the storage and reading of session data; 4. Check the server configuration. By outputting session ID and data, viewing session file content, etc., you can effectively diagnose and solve session-related problems.
 What happens if session_start() is called multiple times?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:06 AM
What happens if session_start() is called multiple times?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:06 AMMultiple calls to session_start() will result in warning messages and possible data overwrites. 1) PHP will issue a warning, prompting that the session has been started. 2) It may cause unexpected overwriting of session data. 3) Use session_status() to check the session status to avoid repeated calls.
 How do you configure the session lifetime in PHP?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:05 AM
How do you configure the session lifetime in PHP?Apr 25, 2025 am 12:05 AMConfiguring the session lifecycle in PHP can be achieved by setting session.gc_maxlifetime and session.cookie_lifetime. 1) session.gc_maxlifetime controls the survival time of server-side session data, 2) session.cookie_lifetime controls the life cycle of client cookies. When set to 0, the cookie expires when the browser is closed.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.







