Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >A brief introduction to mysql subquery
A brief introduction to mysql subquery
- 小云云Original
- 2018-03-15 10:41:452188browse
The basic meaning of a subquery is a "query statement" that appears in certain positions inside a query statement (select statement). This article mainly shares with you a brief introduction to mysql subqueries, hoping to help everyone.
Example: 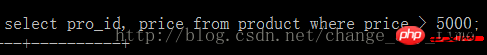
After modification: 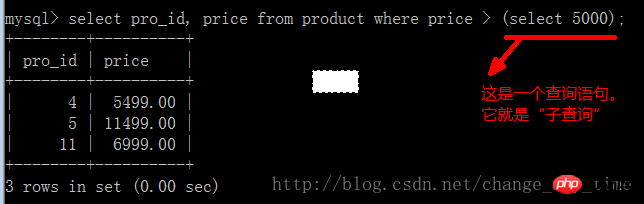
If the subtitle of "
select 5000" is The query statement, replaced by "the average price of all selected products", has practical meaning.
The subquery serves the main query
The main query is executed only after the subquery obtains certain result data. Query;
In form, it can be expressed as follows:
selelct field or expression or subquery [as alias] from table name Or link results or subqueries where fields or expressions or conditional judgments of subqueries
That is, subqueries can appear in these positions (having actually can also be used, because It has the same meaning as where);
Subquery, divided by position (occasion):
| Type | Form |
|---|---|
| #As the result data of the main query | select c1,(select f1 from tab2) as f11 from tab1; #The subquery here should only have A piece of data (one row, one column, scalar subquery) |
| As the conditional data of the main query | select c1 from tab1 where c1 in (select f1 from tab2); #here The subquery can be multiple data (multiple rows and one column, column subquery) |
| As the source data of the main query | select c1 from (select f1 as c1, f2 from tab2) as t2; #The subquery here can be any query result (table subquery) |
Common subqueries
Subqueries in comparison operators
Form:
Operand comparison operators (scalar subquery);
Explanation:
The operand is actually one of the two data of the comparison operator, usually A field name;
select .... from XXX where id > 5;
Example:
Find the highest priced product;
select * from product where price = (select max(price) from product );
Subquery using in
Previous usage of in:
XX in (值1,值2,值3,....);
Then the in subquery is:
XX in (列子查询)
Example:
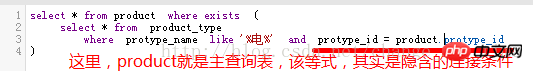
Find all products with the word "electricity" in all category names;
select * from product where protype_id in( select protype_id from product_type where protype_name like ‘%电%’ );
Subquery using any
Form:
操作数 比较运算符 any (列子查询);
Meaning:
When a certain operand (field) satisfies the comparison operator for any value of the column subquery, the condition is satisfied;
Example:
select * from tab1 where id > any (select f1 from tab2);
Subquery using all:
Form:
操作数 比较运算符 all (列子查询);
Meaning:
When a certain operand (field) For all data values of the column subquery, the comparison operator must be satisfied to satisfy the condition;
Example:
select * from tab2 where f1 > all ( select id from tab1 );
Use some subquery Query
One sentence: some is a synonym of any.
Query using exists
Form:
where exists( 子查询 )
Meaning:
If the subquery "has data", the results of exists is true, otherwise it is false
Explanation:
Because, the exists subquery Meaning, the main query often has a situation like this: either all of them are taken out, or none of them are taken out. If it is limited to this meaning (usage situation), it basically loses its practical significance.
So:
In actual applications, this subquery is often not an independent subquery, but needs to be followed by the data source (table of the "main query") ), establish some kind of relationship - usually a connection relationship. The way of establishment is "implicit", that is, the relationship is not reflected in the code, but there is the "substance" of its connection internally.
This implicit connection method is usually reflected in the where conditional statement in the subquery, using the data (fields) in the main query table;
Example:
Query all products with the word "electricity" in their category names in the product table;

The result is: 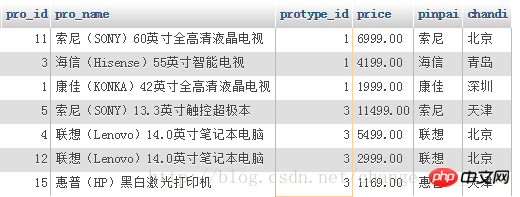
Note:
- This kind of subquery statement cannot "exist independently (run independently)", but must be used together with the main query;
- Other subqueries can be run independently and will get a running result.
- The conditions in this subquery should be set to have a certain correlation with a certain field of the main query. Usually this judgment is the "original connection condition" of the two tables
Finally A conclusion:
If a query requirement can be obtained using a join query or a subquery, it is usually recommended to use join interpolation, which is more efficient.
Related recommendations:
Detailed introduction to MySQL subquery
##What is a mysql subquery? How to filter using subqueries?
Optimization of MySQL subquery
The above is the detailed content of A brief introduction to mysql subquery. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!