Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >mysql data control language example sharing
mysql data control language example sharing
- 小云云Original
- 2018-03-15 10:42:221291browse
Data control language is a statement used to manage mysql users and their permissions; this article mainly shares examples of mysql data control language with you, hoping to help everyone.
User Management
Location of user data: All users in mysql are stored in the user table in the system database (mysql) - no matter which database user, Stored here.
The initial content of the table is as follows: 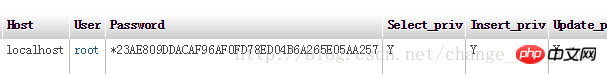
Create user:
Form:
create user ‘用户名’@’允许登录的地址/服务器’ identified by ‘密码’;
Description:
The address/server that allows login is the location that allows you to log in with the user name and password that you set, but not other locations;
MySQL's secure authentication requires 3 pieces of information.
Example: 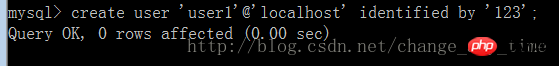
View the user table in mysql: 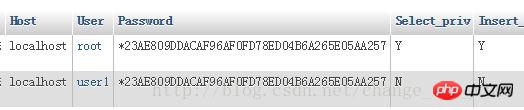
Delete user:
drop user '用户名'@'允许登录的地址或服务器名';
Modify user password
Modify your own password:
set password = password('密码');
Modify other people’s passwords (provided you have permission):
set password for '用户名'@'允许登录的地址' = password('密码');
Permission management
Permissions: MySQL database divides everything that can be done into about 30 permissions, each of which is represented by a "word"!
For example:
-
select: means that the data can be queried; update: means that the data can be modified; delete: means that the data can be deleted;…….
There is a permission named "all": indicating all permissions;
has the following permissions: 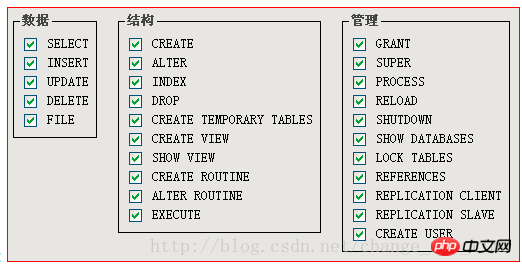
Another performance Format (with Chinese instructions): 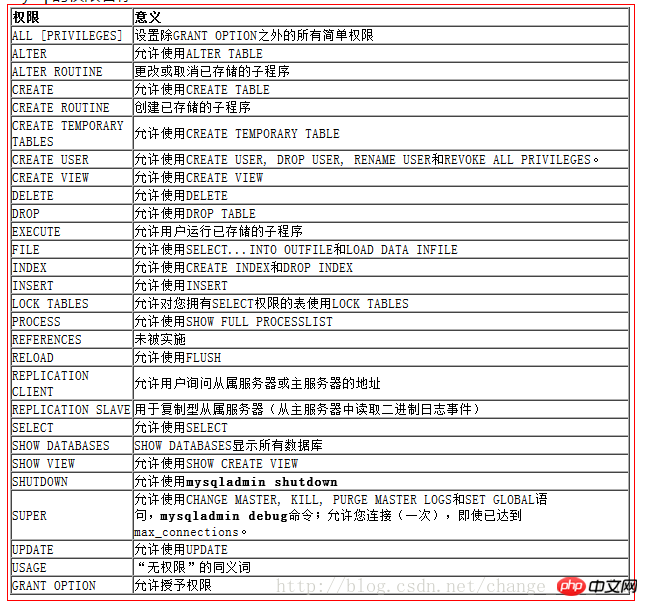
Grant permission:
Form:
grant 权限列表 on 某库.某个对象 to ‘用户名’@’允许登录的位置’ 【identified by ‘密码’】;
Instructions:
Permission list, that is, nouns for multiple permissions, separated by commas, such as: select, insert, update. You can also write: all
- ##a certain library. An object represents the empowerment of a "subordinate unit" in a specified database; the subordinate units include: table name, view name, stored procedure name; stored function name;
There are 2 special syntaxes:1.
*.*: Represents all subordinate units in all databases;2.
A certain library. *: represents all subordinate units in the specified library;
- [identified by 'password'] is an omitted part. If not omitted, it means assigned At the same time, change its password;
- If the user is not stored, a new user is actually created at this time; and its password must be set at this time
revoke 权限列表 on 某库.某个对象 from '用户名'@'允许登录的位置'
The meaning is exactly the same as in grant;
Data control language is a statement used to manage mysql users and their permissions;User management
The location of user data: all users in mysql , are stored in the user table in the system database (mysql) - no matter which database users are stored here.The initial content of the table is as follows:

create user ‘用户名’@’允许登录的地址/服务器’ identified by ‘密码’;Description:
- The address/server that allows login is the location that allows you to log in with the user name and password that you set, but not other locations;
- MySQL's secure authentication requires 3 pieces of information.
 View the user table in mysql:
View the user table in mysql: 
drop user '用户名'@'允许登录的地址或服务器名';
Modify user passwordModify your own password:set password = password('密码');Modify other people’s passwords (provided you have permission):
set password for '用户名'@'允许登录的地址' = password('密码');Permission management
Permissions: MySQL database divides everything that can be done into about 30 permissions, each of which is represented by a "word"!for example:
select:代表可以查询数据; update:代表可以修改数据; delete:代表可以删除数据;…….
有一个权限名叫做“all”:表示所有权限;
有如下权限: 
另一个表现形式(带中文说明): 
授予权限:
形式:
grant 权限列表 on 某库.某个对象 to ‘用户名’@’允许登录的位置’ 【identified by ‘密码’】;
说明:
权限列表,就是,多个权限的名词,相互之间用逗号分开,比如: select, insert, update 也可以写:all
某库.某个对象,表示,给指定的某个数据库中的某个“下级单位”赋权; 下级单位有:表名,视图名,存储过程名; 存储函数名;
有2个特殊的语法:
1、*.*: 代表所有数据库中的所有下级单位;
2、某库.*:代表指定的该库中的所有下级单位;
【identified by ‘密码’】是可省略部分,如果不省略,就表示赋权的同时,也去修改它的密码;
如果该用户未存储,此时其实就是创建一个新用户;并此时就必须设置其密码了
剥夺权限:
形式:
revoke 权限列表 on 某库.某个对象 from '用户名'@'允许登录的位置'
其含义,跟grant中完全一样;
相关推荐:
The above is the detailed content of mysql data control language example sharing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

