 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial jQuery 1.9.1 source code analysis series (fifteen) animation processing_jquery
jQuery 1.9.1 source code analysis series (fifteen) animation processing_jqueryFirst you need to have basic knowledge of queue. See previous chapter.
Related tutorial: Summary of animation processing under jQuery: http://www.jb51.net/article/42000.htm
jQuery 1.9.1 source code analysis series (15) Animation processing and easing animation core Tween: http://www.jb51.net/article/75821.htm
a. Detailed explanation of animation entry jQuery.fn.animate function execution process
-------------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
First call jQuery.speed according to the parameters to obtain the animation-related parameters, and get an object similar to the following; and generate the animation execution function doAnimation
optall = {
complete: fnction(){...},//动画执行完成的回调
duration: 400,//动画执行时长
easing: "swing",//动画效果
queue: "fx",//动画队列
old: false/fnction(){...},
}
var empty = jQuery.isEmptyObject( prop ),
optall = jQuery.speed( speed, easing, callback ),
doAnimation = function() {
//在特征的副本上操作,保证每个特征效果不会被丢失
var anim = Animation( this, jQuery.extend( {}, prop ), optall );
doAnimation.finish = function() {
anim.stop( true );
};
//空动画或完成需要立马解决
if ( empty || jQuery._data( this, "finish" ) ) {
anim.stop( true );
}
};
doAnimation.finish = doAnimation;
If there is no animation being executed, the animation will be executed immediately, otherwise the animation will be pushed into the animation queue to wait for execution
//没有动画在执行则马上执行动画,否则将动画压入动画队列等待执行 return empty || optall.queue === false ? this.each( doAnimation ) : this.queue( optall.queue, doAnimation );
It can be seen that the place where animation is actually executed is the Animation( this, jQuery.extend( {}, prop ), optall ) function
b. Detailed explanation of jQuery internal function Animation
-------------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------
Animation (elem, properties, options). properties are css features to be animated, options are animation-related options {complete: function () {…},duration: 400,easing: undefined,old: false,queue: "fx"}.
First, initialize a delay object, which is used to process the animation queue.
deferred = jQuery.Deferred().always( function() {
// don't match elem in the :animated selector
delete tick.elem;
}),
Then, generate a function tick that will be executed at every time point (the event interval between two adjacent time points is 13 milliseconds by default). This tick function will be saved in jQuery.timers, and then every time It will be taken out and executed when jQuery.fx.tick is executed.
tick = function() {
if ( stopped ) {
return false;
}
var currentTime = fxNow || createFxNow(),
remaining = Math.max( 0, animation.startTime + animation.duration - currentTime ),
// archaic crash bug won't allow us to use 1 - ( 0.5 || 0 ) (#12497)
temp = remaining / animation.duration || 0,
percent = 1 - temp,
index = 0,
length = animation.tweens.length;
//执行动画效果
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
animation.tweens[ index ].run( percent );
}
//生成进度报告
deferred.notifyWith( elem, [ animation, percent, remaining ]);
if ( percent < 1 && length ) {
return remaining;
} else {
//动画执行完毕,执行所有延时队列中的函数(包括清除动画相关的数据)
deferred.resolveWith( elem, [ animation ] );
return false;
}
}
We see jQuery’s handling of animation progress:
remaining = Math.max( 0, animation.startTime + animation.duration - currentTime )temp = remaining / animation.duration || 0,percent = 1 - temp,
Progress percentage = 1 - remaining time percentage.
Usually we handle it like this: Assume that the animation is executed once every 13 milliseconds, the current execution is the nth, and the total animation duration is T. Then
Progress percentage = (n*13)/T
In fact, the time n*13 obtained by this algorithm is inaccurate, because the CPU is not just executing your program, and the time slice allocated to you is often larger than n*13. Moreover, it is a very inaccurate value, causing the animation to feel fast and slow, and inconsistent. The jQuery method ensures the accuracy of the animation execution result at the current event point. After all, the event is the latest calculation result.
Third, generate the object animation composed of all the features used for animation (the structure of this object is as shown in the source code). What is saved in animation.props are the features passed in by the user (the final target of the animation).
animation = deferred.promise({
elem: elem,
props: jQuery.extend( {}, properties ),
opts: jQuery.extend( true, { specialEasing: {} }, options ),
originalProperties: properties,
originalOptions: options,
startTime: fxNow || createFxNow(),
duration: options.duration,
tweens: [],
createTween: function( prop, end ) {
var tween = jQuery.Tween( elem, animation.opts, prop, end,
animation.opts.specialEasing[ prop ] || animation.opts.easing );
animation.tweens.push( tween );
return tween;
},
stop: function( gotoEnd ) {
var index = 0,
// if we are going to the end, we want to run all the tweens
// otherwise we skip this part
length = gotoEnd ? animation.tweens.length : 0;
if ( stopped ) {
return this;
}
stopped = true;
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
animation.tweens[ index ].run( 1 );
}
// resolve when we played the last frame
// otherwise, reject
if ( gotoEnd ) {
deferred.resolveWith( elem, [ animation, gotoEnd ] );
} else {
deferred.rejectWith( elem, [ animation, gotoEnd ] );
}
return this;
}
})
Fourth, call propFilter to correct the css feature name so that it can be recognized by the browser. It should be noted that borderWidth/padding/margin does not refer to one css feature, but four (top, bottom, left, and right)
//经过propFilter,animation.opts.specialEasing添加了相应的特征 propFilter( props, animation.opts.specialEasing );
Give an example of the propFilter correction results.
Example 1, the modified result of css feature {height: 200} is:
props = { height: 200 }
animation.opts.specialEasing = {height: undefined}
Example 2: The correction result of css feature {margin:200} is:
props = { marginBottom: 200,marginLeft: 200,marginRight: 200,marginTop: 200 }
animation.opts.specialEasing = { marginBottom: undefined,marginLeft: undefined,marginRight: undefined,marginTop: undefined }
Fifth, call defaultPrefilter for adaptation processing: for example, the height/width animation requires display and overflow to be specific values to have an effect; for example, the show/hide animation requires a lot of CSS feature values. Animation, and call createTweens in the function to generate easing animation.
// animationPrefilters[0] = defaultPrefilter
for ( ; index < length ; index++ ) {
result = animationPrefilters[ index ].call( animation, elem, props, animation.opts );
if ( result ) {
return result;
}
}
The value function of animationPrefilters[index] is defaultPrefilter. There are several important aspects of defaultPrefilter function processing
DefaultPrefilter Key Point 1: Height/width related animations in inline elements need to set the display feature value to inline-block
// height/width overflow pass
if ( elem.nodeType === 1 && ( "height" in props || "width" in props ) ) {
//确保没有什么偷偷出来
//记录3个overflow相关特征,因为IE不能改变overflow特征值,
//当overflowX和overflowY设置了相同的值
opts.overflow = [ style.overflow, style.overflowX, style.overflowY ];
// 内联元素中height/width相关动画需要设置display特征值为inline-block
if ( jQuery.css( elem, "display" ) === "inline" &&
jQuery.css( elem, "float" ) === "none" ) {
// 内联元素接受inline-block;
// 块级元素必须内嵌在布局上
if ( !jQuery.support.inlineBlockNeedsLayout || css_defaultDisplay( elem.nodeName ) === "inline" ) {
style.display = "inline-block";
} else {
style.zoom = 1;
}
}
}
Key point 2 of defaultPrefilter: For height/width animation overflow, set it to "hidden" and restore it after the animation is completed. This helps improve rendering speed.
//对于height/width动画overflow都要设置为"hidden",动画完成后恢复
if ( opts.overflow ) {
style.overflow = "hidden";
//收缩包装块
if ( !jQuery.support.shrinkWrapBlocks ) {
anim.always(function() {
style.overflow = opts.overflow[ 0 ];
style.overflowX = opts.overflow[ 1 ];
style.overflowY = opts.overflow[ 2 ];
});
}
}
DefaultPrefilter focus 3: Special processing of show/hide animation: show/hide animation calls genFx to get the shape
props = {
height: "hide"
marginBottom: "hide"
marginLeft: "hide"
marginRight: "hide"
marginTop: "hide"
opacity: "hide"
paddingBottom: "hide"
paddingLeft: "hide"
paddingRight: "hide"
paddingTop: "hide"
width: "hide"
}
Push the features that need to be animated into the handle list, delete the corresponding features, and then generate the corresponding easing animation.
for ( index in props ) {
value = props[ index ];
//rfxtypes = /^(?:toggle|show|hide)$/。可以看到最终只有和show/hide的动画才会被饶茹handled中
if ( rfxtypes.exec( value ) ) {
delete props[ index ];
toggle = toggle || value === "toggle";
//如果当前节点的状态和指定的状态相同则不需要处理直接进行下一个状态判断
if ( value === ( hidden ? "hide" : "show" ) ) {
continue;
}
handled.push( index );
}
}
//有需要执行的动画处理则进入分支,里面会对各个特征动画生成缓动动画
length = handled.length;
if ( length ) {
dataShow = jQuery._data( elem, "fxshow" ) || jQuery._data( elem, "fxshow", {} );
if ( "hidden" in dataShow ) {
hidden = dataShow.hidden;
}
// toggle需要保存状态 - enables .stop().toggle() to "reverse"
if ( toggle ) {
dataShow.hidden = !hidden;
}
if ( hidden ) {
jQuery( elem ).show();
} else {
anim.done(function() {
jQuery( elem ).hide();
});
}
anim.done(function() {
var prop;
jQuery._removeData( elem, "fxshow" );
for ( prop in orig ) {
jQuery.style( elem, prop, orig[ prop ] );
}
});
for ( index = 0 ; index < length ; index++ ) {
prop = handled[ index ];
//生成缓动动画
tween = anim.createTween( prop, hidden ? dataShow[ prop ] : 0 );
orig[ prop ] = dataShow[ prop ] || jQuery.style( elem, prop );
if ( !( prop in dataShow ) ) {
dataShow[ prop ] = tween.start;
if ( hidden ) {
tween.end = tween.start;
tween.start = prop === "width" || prop === "height" ? 1 : 0;
}
}
}
}
Sixth, generate easing animation, show/hide has been processed in the defaultPrefilter function (source code above).
createTweens( animation, props );
我们来看一看createTweens中具体做了什么,先看一下createTweens之前的animation对象

然后看一下经过createTweens之后的animation对象的tweens数组变成了
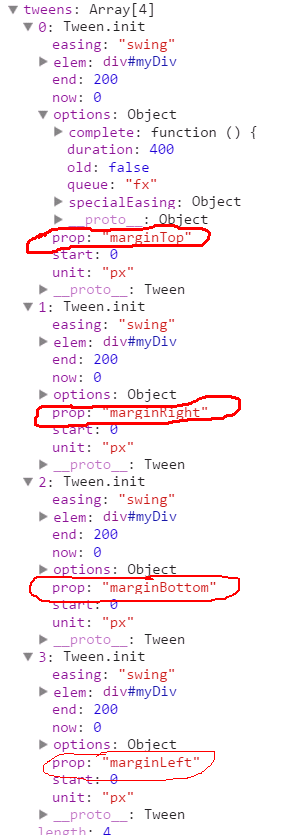
将margin分解成了四个属性(marginTop/Right/Bottom/Left)并且每个属性都有自己的动画特征。
第七,启动动画计时,定时执行tick
//启动动画计时
jQuery.fx.timer(
jQuery.extend( tick, {
elem: elem,
anim: animation,
queue: animation.opts.queue
})
);
最后,将传入的动画结束回调加入延时队列
//从options中获取回调函数添加到延时队列中 return animation.progress( animation.opts.progress ) .done( animation.opts.done, animation.opts.complete ) .fail( animation.opts.fail ) .always( animation.opts.always );
Animation函数流程到此为止
拓展:
前面提到的genFx函数是专门用在toggle、hide、show时获取相关的需要动画的特征的
最终生成的attrs = {
height: "show",
marginTop: "show",
marginRight: "show",//当includeWidth为false时没有
marginBottom: "show",
marginLeft: "show",//当includeWidth为false时没有
opacity: "show",
width: "show"
}
function genFx( type, includeWidth ) {
var which,
attrs = { height: type },
i = 0;
//如果包括宽度,步长值为1来完成所有cssExpand值,
//如果不包括宽度,步长值是2跳过左/右值
//cssExpand = [ "Top", "Right", "Bottom", "Left" ]
includeWidth = includeWidth? 1 : 0;
for( ; i < 4 ; i += 2 - includeWidth ) {
which = cssExpand[ i ];
attrs[ "margin" + which ] = attrs[ "padding" + which ] = type;
}
if ( includeWidth ) {
attrs.opacity = attrs.width = type;
}
return attrs;
}
Animation函数比较复杂,童鞋们可以随便使用例子去跟踪代码。这个是理解jQuery源码的一种比较好的方式。推荐两个例子:
第一个,有hide/show的例子:$("#id").hide(1000);
第二个,其他例子:$("#id").animate({"marginLeft":500},1000);
jQuery 1.9.1源码分析系列(十五)之动画处理 的全部内容就给大家介绍到这里,有问题随时给我留言,谢谢。!
 Replace String Characters in JavaScriptMar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Replace String Characters in JavaScriptMar 11, 2025 am 12:07 AMDetailed explanation of JavaScript string replacement method and FAQ This article will explore two ways to replace string characters in JavaScript: internal JavaScript code and internal HTML for web pages. Replace string inside JavaScript code The most direct way is to use the replace() method: str = str.replace("find","replace"); This method replaces only the first match. To replace all matches, use a regular expression and add the global flag g: str = str.replace(/fi
 8 Stunning jQuery Page Layout PluginsMar 06, 2025 am 12:48 AM
8 Stunning jQuery Page Layout PluginsMar 06, 2025 am 12:48 AMLeverage jQuery for Effortless Web Page Layouts: 8 Essential Plugins jQuery simplifies web page layout significantly. This article highlights eight powerful jQuery plugins that streamline the process, particularly useful for manual website creation
 Build Your Own AJAX Web ApplicationsMar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Build Your Own AJAX Web ApplicationsMar 09, 2025 am 12:11 AMSo here you are, ready to learn all about this thing called AJAX. But, what exactly is it? The term AJAX refers to a loose grouping of technologies that are used to create dynamic, interactive web content. The term AJAX, originally coined by Jesse J
 10 jQuery Fun and Games PluginsMar 08, 2025 am 12:42 AM
10 jQuery Fun and Games PluginsMar 08, 2025 am 12:42 AM10 fun jQuery game plugins to make your website more attractive and enhance user stickiness! While Flash is still the best software for developing casual web games, jQuery can also create surprising effects, and while not comparable to pure action Flash games, in some cases you can also have unexpected fun in your browser. jQuery tic toe game The "Hello world" of game programming now has a jQuery version. Source code jQuery Crazy Word Composition Game This is a fill-in-the-blank game, and it can produce some weird results due to not knowing the context of the word. Source code jQuery mine sweeping game
 How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How do I create and publish my own JavaScript libraries?Mar 18, 2025 pm 03:12 PMArticle discusses creating, publishing, and maintaining JavaScript libraries, focusing on planning, development, testing, documentation, and promotion strategies.
 Load Box Content Dynamically using AJAXMar 06, 2025 am 01:07 AM
Load Box Content Dynamically using AJAXMar 06, 2025 am 01:07 AMThis tutorial demonstrates creating dynamic page boxes loaded via AJAX, enabling instant refresh without full page reloads. It leverages jQuery and JavaScript. Think of it as a custom Facebook-style content box loader. Key Concepts: AJAX and jQuery
 How to Write a Cookie-less Session Library for JavaScriptMar 06, 2025 am 01:18 AM
How to Write a Cookie-less Session Library for JavaScriptMar 06, 2025 am 01:18 AMThis JavaScript library leverages the window.name property to manage session data without relying on cookies. It offers a robust solution for storing and retrieving session variables across browsers. The library provides three core methods: Session
 jQuery Parallax Tutorial - Animated Header BackgroundMar 08, 2025 am 12:39 AM
jQuery Parallax Tutorial - Animated Header BackgroundMar 08, 2025 am 12:39 AMThis tutorial demonstrates how to create a captivating parallax background effect using jQuery. We'll build a header banner with layered images that create a stunning visual depth. The updated plugin works with jQuery 1.6.4 and later. Download the


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools





