Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Examples of configuration and use of slow query logs in MySQL
Examples of configuration and use of slow query logs in MySQL
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-09-18 10:23:121504browse
MySQL slow query log provides query information that exceeds the specified time threshold, providing a main reference for performance optimization. It is a very practical function.
MySQL slow query log is turned on and The configuration is very simple. You can specify the recorded file (or table), and the exceeded time threshold can be recorded to slow sql.
To be honest, compared with sqlserver's trace or extended events (although the role of these two is not just So), MySQL configuration always gives people a very refreshing feeling.
1. Opening the slow query log
Under normal circumstances, you only need to add the slow_query_log = 1 configuration in the configuration file, that is, open the slow query log. If slow_query_log_file is not specified, it will automatically Generate a file with the host name + 'slow'.log.

2. By default, the time threshold for recording slow queries is 10s
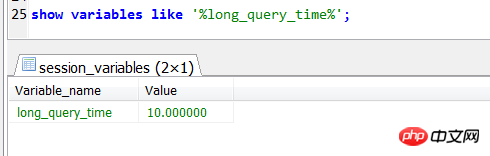
By default, slow_query_log = is specified In case 1, when you start MySQL, you can turn on slow queries and automatically generate a default file with the host name ++'slow'.log to record slow queries that exceed execution for more than 10 seconds.
You can also explicitly specify the slow query log file name (it will be automatically created if it does not exist) and the time threshold for recording slow queries (non-default 10s).
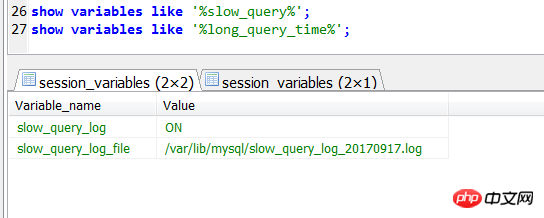
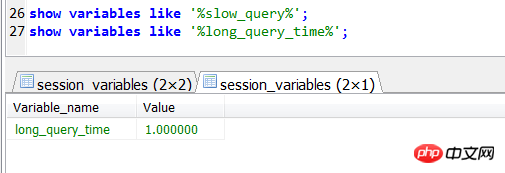
Note that when specifying long_query_time in the configuration file, no time unit is required, only a value is required, such as 1 represents 1s. If the time unit is specified, the service will not be able to start up.
The following is an example of slow sql recorded in the log file

3. Record the slow query log to Table
Configuration: You need to add a log_output configuration so that slow queries can be recorded in the table

There is a default slow_log table under the mysql library , you can directly set slow_query_log_file = slow_log to record the slow query log into the table.

The recorded slow sql is as follows. It can be found that sql_text is a binary information, not the original sql text

You can convert it through the CONVERT function.

About the difference between slow queries recorded in log files and tables:
1. Slow queries recorded in log files and tables , the record itself is not much different. If it is recorded in the table, the execution time information of the slow query cannot be accurate to the subtle.
2. If the slow query information is recorded in the table, it is convenient for query, but because it is Structured data may be a little slower than recording it in a slow query log file (flat text file) (personal guess). If it is recorded to a file, it needs the mysqldumpslow tool to parse it.
3. Slow queries do not record queries that fail to execute. For example, long_query_time is set to 10 (10 seconds). If a query exceeds 10 seconds, but fails to execute due to other reasons, MySQL's slow queries will not be recorded. This query information.
The above is the detailed content of Examples of configuration and use of slow query logs in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

