Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Teach you how to log in and log out of mysql on linux
Teach you how to log in and log out of mysql on linux
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-08-11 14:29:103393browse
For those who are new to mysql, the editor here presents a chapter on connecting and exiting mysql.
1. Because the windows environment involves environment variables, the editor will talk about it in separate chapters.
Under Linux, mysql is installed and the service is started.
You can start connecting to the database.
mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p
-hdatabase host
-uuser
-ppassword
-Pport (capital P)
For example, in the password part of
mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p12345 -P3306
-p, you can directly specify the password. If not specified, you will be prompted to enter the password.
Let’s first mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p to see if
prompts you to enter the password
?
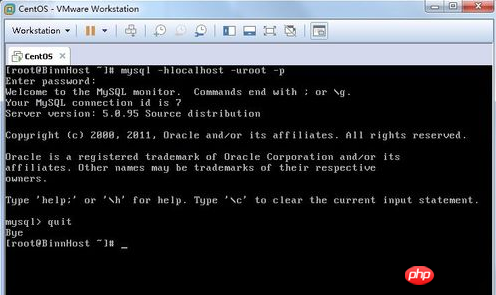
#2. After logging in, this is the command line interface of mysql.
We quit or exit to exit mysql.

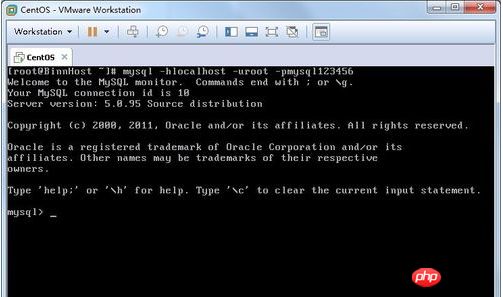
##3. The root password here It's mysql123456.
mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -pmysql123456Are you not prompted for a password?
#4. So what is the use of -P port number?
We all know that network software has a port number. Mysql defaults to 3306. If you modify the default port number, you need to specify the modified port number in -P. In fact, there is a simpler login method.mysql -uroot -pIn this way, only the user is specified, not the host, so the default login is localhost.
5. Of course, there is also a longer way of writing. (Generally used for shell programming, the parameters are more intuitive)
mysql --host=localhost --user=root --password --port=3306
For details, see man mysql
The above is the detailed content of Teach you how to log in and log out of mysql on linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!



