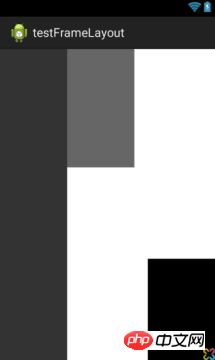Home >Web Front-end >CSS Tutorial >Complete explanation of Android Layout layout attributes
Complete explanation of Android Layout layout attributes
- 巴扎黑Original
- 2017-06-28 11:06:342948browse
Android Layout layout attributes full explanation
Android has basic Layout: FrameLayout, LinearLayout, TableLayout, RelativeLayout,AbsoluteLayout.
android developer Google documentation http://android.xsoftlab.net/reference/android/view/ViewGroup.html
FrameLayout
##
<FrameLayout android:layout_width="" //取值范围"match_parent"、"wrap_content"、"XXdp" 布局整体宽度 android:layout_height=""//取值范围"match_parent"、"wrap_content"、"XXdp" 布局整体高度 android:layout_weight=""//取值示例"1.0" 布局所占比重 android:layout_gravity="" //取值范围"center"、"top"、"bottom"、"left"、"right"、"right|bottom" 布局位置 android:layout_margin="" //取值示例"0dp" 距离父控件四个方向距离 android:layout_marginLeft="" //取值示例"0dp" 距离父控件左间距 android:layout_marginTop="" //取值示例"0dp" 距离父控件上间距 android:layout_marginRight="" //取值示例"0dp" 距离父控件右间距 android:layout_marginBottom="" //取值示例"0dp" 距离父控件下间距 android:layout_marginStart="" //取值示例"-50dp" "50dp" 控件离父控件开始的位置的距离(前者不显示前50dp) android:layout_marginEnd="" //取值示例"-50dp" "50dp" 控件离父控件结束的位置的距离(前者不显示后50dp) android:addStatesFromChildren="" //取值范围"true" 、"false" viewgroup的drawable属性是否把它的子类的drawable的state包含进来。测试中linearlayout如果不包含该属性(false),当子widget被点击时不会出现被选中的状态。也就是子类的state不会被传递给父类了 android:descendantFocusability="" //见下 android:splitMotionEvents="" //取值范围"true" "false" 定义布局是否传递touch事件到子布局 android:layoutMode="" //取值范围 "clipBounds" "opticalBounds" 见下 android:id="" android:tag="" //listView中区别Item非常有用的Tag标签(key-value) android:scrollX="" //The initial horizontal scroll offset, in pixels. [dimension]最初的水平滚动的偏移,以像素为单位。 android:scrollY="" //The initial virtual scroll offset, in pixels. [dimension]最初的竖直滚动的偏移,以像素为单位。 android:background="" android:padding="" //取值示例"0dp" 控件内容(文本图片子控件等)距离控件四个方向边界的距离 android:paddingLeft="" android:paddingTop="" android:paddingRight="" android:paddingBottom="" android:paddingStart="" //见下 文字对齐方式详解 android:paddingEnd="" //见下 文字对齐方式详解 android:foreground="" //设置布局的前景图,前景图不会被子元素覆盖 android:foregroundGravity="" //设置布局前景图的位置 android:foregroundInsidePadding="" // android:focusable="" //取值"true" "false" 能否获得焦点(按键) android:focusableInTouchMode="" //取值"true" "false" 是否可以通过touch获取到焦点(android:focusable 为先决条件) android:fitsSystemWindows="" //取值"true" "false" 设置布局调整时是否考虑系统窗口(如状态栏) android:fadeScrollbars="" //取值"true" "false" 滚动条自动隐藏 android:fadingEdge="" //设置拉滚动条时 ,边框渐变的方向。none(边框颜色不变),horizontal(水平方向颜色变淡),vertical(垂直方向颜色变淡)。 android:fadingEdgeLength="" //滚动条渐变长度 android:filterTouchesWhenObscured="" //取值范围 "true" "false"所在窗口被其它可见窗口遮住时,是否过滤触摸事件 android:visibility="" //取值范围 "gone" "visible" "invisible"(虽不可见,但占据布局位置) android:scrollbars=""//取值范围 "none" "horizontal" "vertical" 设置滚动条 android:scrollbar //outsideInset : 该ScrollBar显示在视图(view)的边缘,增加了view的padding. 如果可能的话,该ScrollBar仅仅覆盖这个view的背景. insideInset :该ScrollBar显示在padding区域里面,增加了控件的padding区域,该ScrollBar不会和视图的内容重叠. outsideOverlay : 该ScrollBar显示在视图(view)的边缘,不增加view的padding,该ScrollBar将被半透明覆盖 insideOverlay : 该ScrollBar显示在内容区域里面,不会增加了控件的padding区域,该ScrollBar以半透明的样式覆盖在视图(view)的内容 android:isScrollContainer="" //取值范围 "true""false" 设置当前View是否为滚动容器(是否可以为输入法腾出空间而隐藏) android:scrollbarFadeDuration="" //褪色时间 android:scrollbarDefaultDelayBeforeFade="" //设置滚动条N毫秒后开始淡化,以毫秒为单位。 android:scrollbarSize="" //设置滚动条大小 android:scrollbarThumbHorizontal="@drawable" //设置水平滚动条的drawable android:scrollbarThumbVertical="@drawable" //设置垂直滚动条的drawable. android:scrollbarTrackHorizontal="@drawable"//设置水平滚动条背景(轨迹)的色drawable android:scrollbarTrackVertical="@deawable" //设置垂直滚动条背景(轨迹)的drawable注意直接 android:scrollbarAlwaysDrawHorizontalTrack="true/false" //设置水平滚动条是否含有轨道 android:scrollbarAlwaysDrawVerticalTrack="true/false" // 设置垂直滚动条是否含有轨道 android:requiresFadingEdge="none/horizontal/vertical" //定义褪色时滚动边缘 android:nextFocusLeft="@+id/" //Up键按下之后,哪一个控件获得焦点(被选中) android:nextFocusRight="@+id/" android:nextFocusUp="@+id/" android:nextFocusDown="@+id/" android:nextFocusForward="@+id/" android:clickable="true/false" android:longClickable="true/false" android:saveEnabled="true/false" //设置是否在窗口冻结时(如旋转屏幕)保存View的数据 android:drawingCacheQuality="auto|low|hight" //设置绘图缓存质量 android:keepScreenOn="true/false" //View在可见的情况下是否保持唤醒状态 android:duplicateParentState="true/false" 如果设置此属性,将直接从父容器中获取绘图状态(光标,按下等)。 注意根据目前测试情况仅仅是获取绘图状态,而没有获取事件,也就是你点一下LinearLayout时Button有被点击的效果,但是不执行点击事件。 android:minHeight="" android:minWidth="" android:soundEffectsEnabled="true/false" // 设置点击或触摸时是否有声音效果 android:hapticFeedbackEnabled="true/false" // 实现单击某个视图,系统提供一个触力反馈(震动一下) android:contentDescription="@string/" //图片不可见时的文字描述(盲人) android:onClick="" android:overScrollMode="ifContentScrolls/always/never" //滚动到边界时的效果 android:alpha="0.1" //透明度 android:translationX="" //X轴的偏移距离 android:translationY="" android:transformPivotX="" //从某点的X轴偏移距离 android:transformPivotY="" android:rotation="" //旋转 android:rotationX="" android:rotationY="" android:scaleX="" //设置X轴缩放比例 android:scaleY="" android:verticalScrollbarPosition="defaultPosition/left/right" //设置垂直滚动条的位置 android:layerType="none/hardware/software" //绘图是否开启硬件加速 android:layoutDirection="" //定义布局图纸的方向 android:textDirection="" // android:textAlignment="inherit/....." //文字对齐方式 android:importantForAccessibility="noHideDescendants/...." //设置可达性的重要行 android:accessibilityLiveRegion="" android:labelFor="" //添加标签 android:measureAllChildren="" //见下 android:animateLayoutChanges="true" //添加默认布局动画 android:clipChildren="" //见下 android:clipToPadding="" //见下转载 android:layoutAnimation="" //设置layout动画 android:animationCache="" android:persistentDrawingCache="" android:alwaysDrawnWithCache="" />
android:descendantFocusability
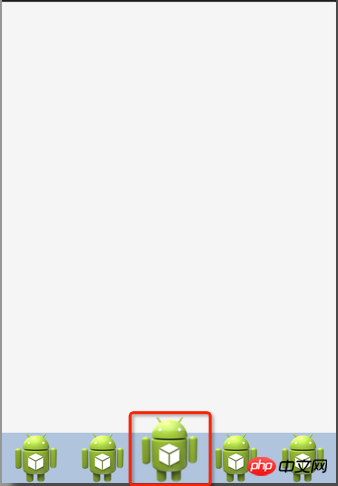
A very common problem in development. The listview in the project is not just a simple text. You often need to define the listview yourself. Your own Adapter inherits the BaseAdapter and writes it in the adapter according to the requirements. Problems arise. Maybe It will happen that when you click on each item, there will be no response and focus cannot be obtained. The reason is mostly because there are sub-controls such as ImageButton, Button, CheckBox and other sub-controls (which can also be said to be sub-class controls of Button or Checkable) in the Item you define. At this time, these sub-controls will get the focus, so they often click What changes when it comes to item is the sub-control, and there is no response when clicking on the item itself.
At this time, you can use descendantFocusability to solve the problem. The API description is as follows:
android:descendantFocusability
Defines the relationship between the ViewGroup and its descendants when looking for a View to take focus.Must be one of the following constant values.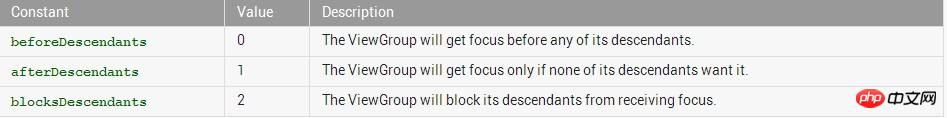
This attribute defines the relationship between the viewGroup and its child controls when a view gets focus.
There are three values for the attribute:
beforeDescendants: the viewgroup will give priority to its subclass controls and get the focus
## AfterDescendants: ViewGroup only gets the focus only when its subclasses do not need to get the focus
Atep.
## ###Usually we use the third method, which is to add the attribute android:descendantFocusability="blocksDescendants" to the root layout of the Item layout.
android:layoutMode
Defines the layout mode of this ViewGroup.
Must be one of the following constant values.
| Value | Description | |
|---|---|---|
clipBounds | 0Use the children's clip bounds when laying out this container. Child control clipping bounds. | |
opticalBounds | 1Use the children's optical bounds when laying out this container. Subcontrol fiber boundary. |
The above is the detailed content of Complete explanation of Android Layout layout attributes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!