Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Detailed introduction to variables in mysql
Detailed introduction to variables in mysql
- 零下一度Original
- 2017-05-09 13:30:071482browse
Define variables
The syntax is as follows
declare var_name[,...] type [default value];
MYSQL Variable definition can only be done in stored procedure or Function is defined inside, unlike Oracle/SQL Server. The scope of this variable can only be within the begin...end block. Variable definitions must be written at the beginning of a compound statement, before any other statements. Multiple variables of the same type can be declared at one time. You can use default to assign a default value. declare can only be used in local variable definitions.
#举例 declare v_test int default 10;
Set variables
Method one
set var_name=expr,[,var_name2=expr ...]; #举例 set v_test=15;
Method two
select col_name[,...] into var_name[,...] table_expr; #举例 select sid into @a from test1;
If col_name (such as sid ) returns multiple rows of values, @a will only return the last row of values in the end.
Variable classification
Local variables (no need to add @)
Local variables are generally used in sql statement blocks. For example, the begin/end of a stored procedure. Its scope is limited to the statement block. After the statement block is executed, the local variable disappears. Local variables are generally declared with declare, and default can be used to indicate the default value.
create procedure add(in a int,in b int)
begin
declare c int default 0;#c定义的局部变量
set c = a + b;
select c as c;
end;User variables (one @)
User The scope of variables is wider than that of local variables. User variables can act on the entire current connection, but when the current connection is disconnected, the user variables defined by it will disappear.
User variables are defined in the following way: @Variable name
#举例 set @a = 1; set @b = 2; select @sum:=(@a + @b), @dif:=(@a - @b);
Result
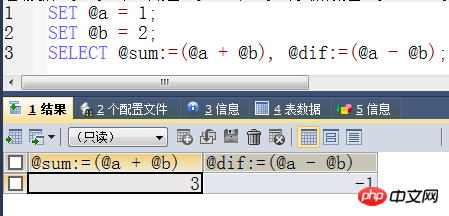
User Variables
Session variables (two @@)
The server maintains a series of session variables for each connected client. When the client connects, the client's session variables are initialized using the current values of the corresponding global variables. Setting session variables does not require special permissions, but the client can only change its own session variables, not those of other clients. The scope of session variables is the same as that of user variables, limited to the current connection. When the current connection is disconnected, all session variables set by it will become invalid.
#设置会话变量有如下三种方式: set session var_name = value; set @@session.var_name = value; set var_name = value; #查看一个会话变量也有如下三种方式: select @@var_name; select @@session.var_name; show session variables like "%var%";
Global variables (two @@)
Global variables affect the overall operation of the server. When the server starts, it initializes all global variables to their default values. These default values can be changed in an options file or by options specified on the command line. To change global variables, you must have SUPER permission. Global variables affect the entire life cycle of the server, but cannot span restarts. That is, all global variables set will become invalid after restarting. To make global variables continue to take effect after restarting, you need to change the corresponding configuration file.
#要设置一个全局变量,有如下两种方式: set global var_name = value; set @@global.var_name = value; //同上 #要想查看一个全局变量,有如下两种方式: select @@global.var_name; show global variables like "%var%";
Note: global here cannot be omitted. According to the manual, if you do not specify GLOBAL, SESSION or LOCAL when setting a variable with the set command, SESSION will be used by default.
【Related recommendations】
1. Free mysql online video tutorial
2. MySQL latest manual tutorial
3. Boolean Education Yan Shiba mysql introductory video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to variables in mysql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

