 Web Front-end
Web Front-end H5 Tutorial
H5 Tutorial Use Html5 to implement simple selection sorting algorithm and demonstration, with code attached
Use Html5 to implement simple selection sorting algorithm and demonstration, with code attachedUse Html5 to implement simple selection sorting algorithm and demonstration, with code attached
Simple selection sort is a type of selection sort algorithm. Basic idea: In each pass, the record with the smallest keyword is selected from the records to be sorted, and the order is placed at the end of the sorted record sequence until all sorting is completed. Since in each loop, the positions of elements with equal values will change, it is an unstable sort.
-------------------------------------------------- -------------------------
As shown below:
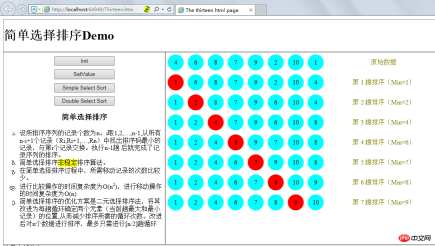
The optimization solution for simple selection sorting is to use binary selection sorting, which is to improve it to determine the positions of two elements (the largest and smallest records in the current cycle) in each cycle, thereby reducing the number of cycles required for sorting. After the improvement, to sort n data, only [n/2] loops are needed at most.
As shown in the figure below:

Algorithm principle will not be described in detail. Use Html5 to implement a simple selection sorting algorithm and demonstration code as follows :


nbsp;html>
<title>The thirteen html page</title>
<style>
ul li
{
list-style-type:georgian;
text-align:left;
}
.mark
{
width:280px;
height:40px;
color:Olive;
text-align:center;
line-height:40px;
margin:5px;
float:left;
}
.redball
{
width:40px;
height:40px;
border-radius:20px;
background-color:Red;
text-align:center;
line-height:40px;
margin:5px;
float:left;
}
.ball
{
width:40px;
height:40px;
border-radius:20px;
background-color:Aqua;
text-align:center;
line-height:40px;
margin:5px;
float:left;
}
.line
{
clear:left;
}
header
{
height:80px;
border:1px solid gray;
}
.left
{
border:1px solid gray;
float:left;
width:30%;
height:480px;
margin-left:0px;
margin-right:0px;
}
aside
{
text-align:center;
}
section
{
width:69.5%;
float:left;
height:480px;
border:1px solid gray;
margin-left:0px;
margin-right:0px;
}
footer
{
clear:left;
height:60px;
border:1px solid gray;
}
input[type="button"]
{
width:150px;
text-align:center;
margin-top:10px;
}
</style>
<script>
function initDiv() {
var mainArea = document.getElementById("mainArea");
var childs = mainArea.childNodes;
//添加节点之前先删除,应该从后往前删除,否则节点移动,只能删除一半
for (var i = childs.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
mainArea.removeChild(childs[i]);
}
for (var i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
var newDivLine = document.createElement("div");
newDivLine.setAttribute("class", "line");
newDivLine.setAttribute("id", i);
mainArea.appendChild(newDivLine);
for (var j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
var newDiv = document.createElement("div");
var id = i.toString() + j.toString();
newDiv.setAttribute("id", id);
if (j < 8) {
newDiv.setAttribute("class", "ball");
} else {
newDiv.setAttribute("class", "mark");
}
newDivLine.appendChild(newDiv);
}
}
}
//初始元素赋值
function setElementsValue() {
var arrTmp = [4, 6, 8, 7, 9, 2, 10, 1];
for (var i = 0; i < arrTmp.length; i++) {
document.getElementById("0" + i.toString()).innerText = arrTmp[i];
}
document.getElementById("08").innerText = "原始数据";
}
//简单选择排序
function setSimpleSortValue() {
var arrTmp = [4, 6, 8, 7, 9, 2, 10, 1];
var m = 0;//表示要交换的最小坐标
for (var i = 0; i < arrTmp.length-1; i++) {
m = i;
for (var j = i + 1; j < arrTmp.length; j++) {
if (arrTmp[m] > arrTmp[j]) {
m = j;
}
}
if (arrTmp[i] > arrTmp[m]) {
var tmp = arrTmp[m];
arrTmp[m] = arrTmp[i];
arrTmp[i] = tmp;
}
//显示出来
for (var k = 0; k < arrTmp.length; k++) {
document.getElementById((i+1).toString() + k.toString()).innerText = arrTmp[k];
if (i == k) {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + (k).toString()).setAttribute("class", "redball");
} else {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + (k).toString()).attributes["class"].nodeValue="ball";;
}
}
document.getElementById((i+1).toString() + "8").innerText = "第 " + (i+1).toString() + " 趟排序(Min=" + arrTmp[i] + ")";
}
}
//二元选择排序
function setDoubleSelectSort() {
var arrTmp = [4, 6, 8, 7, 9, 2, 10, 1];
selectSortB(arrTmp);
var len=arrTmp.length;
for (var i = (len / 2)+1; i < len; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
document.getElementById((i).toString() + (j).toString()).innerText = "";
document.getElementById((i).toString() + (j).toString()).className="ball";
}
document.getElementById(i.toString() + "8").innerText = "";
}
}
//二元选择排序(升序)
function selectSortB(a) {
var len = a.length;
var temp, min, max;
for (var i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
min = i; max = i;
for (var j = i + 1; j <= len - 1 - i; j++) {
max = (a[j] > a[max]) ? j : max;//每一趟取出当前最大和最小的数组下标
min = (a[j] < a[min]) ? j : min;
};
temp = a[i];//先放小的
a[i] = a[min];
if (i == max) { //最大数在数组头部
if ((len - i - 1) !== min) {//最大数在头部,最小数在尾部
a[min] = a[len - i - 1];
}
a[len - i - 1] = temp;
}
else if ((len - i - 1) === min) {//最大数不在头部,最小数在尾部
a[len - i - 1] = a[max];
a[max] = temp
}
else {
//如果最大数在尾部,也是成立的,不用特殊讨论
a[min] = temp;
temp = a[len - i - 1];
a[len - i - 1] = a[max];
a[max] = temp;
}
//显示出来
for (var k = 0; k < a.length; k++) {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + k.toString()).innerText = a[k];
if (i == k || len - i - 1 == k) {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + (k).toString()).setAttribute("class", "redball");
} else {
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + (k).toString()).className = "ball";
}
}
document.getElementById((i + 1).toString() + "8").innerText = "第 " + (i + 1).toString() + " 趟排序(Min=" + a[i] + ",Max=" + a[len-i-1] + ")";
}
}
</script>
<header>
<h1 id="简单选择排序Demo">简单选择排序Demo</h1>
</header>
<aside>
<input>
<br>
<input>
<br>
<input>
<br>
<input>
<br>
<h3 id="简单选择排序">简单选择排序</h3>
<ul>
<li>设所排序序列的记录个数为n。i取1,2,…,n-1,从所有n-i+1个记录(Ri,Ri+1,…,Rn)中找出排序码最小的记录,与第i个记录交换。执行n-1趟 后就完成了记录序列的排序。</li>
<li>简单选择排序<mark>非稳定</mark>排序算法。</li>
<li>在简单选择排序过程中,所需移动记录的次数比较少。</li>
<li>进行比较操作的时间复杂度为O(n<sup>2</sup>),进行移动操作的时间复杂度为O(n)</li>
<li>简单选择排序的优化方案是二元选择排序法,将其改进为每趟循环确定两个元素(当前趟最大和最小记录)的位置,从而减少排序所需的循环次数。改进后对n个数据进行排序,最多只需进行[n/2]趟循环</li>
</ul>
</aside>
<section></section>
<footer>
这是底部信息
</footer>
View Code
About binary choice Special processing of sorting:
Under normal circumstances, a simple exchange is enough.
Special cases occur when four values are the same, such as a[i]=a[max], a[len-1-i]=a[min].
In the code, I chose to first assign the minimum value min to a[i], and at the same time take out the value of a[i], and then discussed three situations in the code
①: When max is When the head of the array is at the head of the array, the situation of whether min is at the tail of the array is discussed under the condition ①;
②: When min is at the tail of the array (and max is not at the head of the array)
③: In general, the same applies [min is at the head of the array, max is at the tail of the array]
For more related articles about using Html5 to implement simple selection sorting algorithms and demonstrations, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
 H5 Code Examples: Practical Applications and TutorialsApr 25, 2025 am 12:10 AM
H5 Code Examples: Practical Applications and TutorialsApr 25, 2025 am 12:10 AMH5 provides a variety of new features and functions, greatly enhancing the capabilities of front-end development. 1. Multimedia support: embed media through and elements, no plug-ins are required. 2. Canvas: Use elements to dynamically render 2D graphics and animations. 3. Local storage: implement persistent data storage through localStorage and sessionStorage to improve user experience.
 The Connection Between H5 and HTML5: Similarities and DifferencesApr 24, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Connection Between H5 and HTML5: Similarities and DifferencesApr 24, 2025 am 12:01 AMH5 and HTML5 are different concepts: HTML5 is a version of HTML, containing new elements and APIs; H5 is a mobile application development framework based on HTML5. HTML5 parses and renders code through the browser, while H5 applications need to run containers and interact with native code through JavaScript.
 The Building Blocks of H5 Code: Key Elements and Their PurposeApr 23, 2025 am 12:09 AM
The Building Blocks of H5 Code: Key Elements and Their PurposeApr 23, 2025 am 12:09 AMKey elements of HTML5 include,,,,,, etc., which are used to build modern web pages. 1. Define the head content, 2. Used to navigate the link, 3. Represent the content of independent articles, 4. Organize the page content, 5. Display the sidebar content, 6. Define the footer, these elements enhance the structure and functionality of the web page.
 HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
HTML5 and H5: Understanding the Common UsageApr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AMThere is no difference between HTML5 and H5, which is the abbreviation of HTML5. 1.HTML5 is the fifth version of HTML, which enhances the multimedia and interactive functions of web pages. 2.H5 is often used to refer to HTML5-based mobile web pages or applications, and is suitable for various mobile devices.
 HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AM
HTML5: The Building Blocks of the Modern Web (H5)Apr 21, 2025 am 12:05 AMHTML5 is the latest version of the Hypertext Markup Language, standardized by W3C. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, multimedia support and form enhancements, improving web structure, user experience and SEO effects. HTML5 introduces new semantic tags, such as, ,, etc., to make the web page structure clearer and the SEO effect better. HTML5 supports multimedia elements and no third-party plug-ins are required, improving user experience and loading speed. HTML5 enhances form functions and introduces new input types such as, etc., which improves user experience and form verification efficiency.
 H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AM
H5 Code: Writing Clean and Efficient HTML5Apr 20, 2025 am 12:06 AMHow to write clean and efficient HTML5 code? The answer is to avoid common mistakes by semanticizing tags, structured code, performance optimization and avoiding common mistakes. 1. Use semantic tags such as, etc. to improve code readability and SEO effect. 2. Keep the code structured and readable, using appropriate indentation and comments. 3. Optimize performance by reducing unnecessary tags, using CDN and compressing code. 4. Avoid common mistakes, such as the tag not closed, and ensure the validity of the code.
 H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AM
H5: How It Enhances User Experience on the WebApr 19, 2025 am 12:08 AMH5 improves web user experience with multimedia support, offline storage and performance optimization. 1) Multimedia support: H5 and elements simplify development and improve user experience. 2) Offline storage: WebStorage and IndexedDB allow offline use to improve the experience. 3) Performance optimization: WebWorkers and elements optimize performance to reduce bandwidth consumption.
 Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Deconstructing H5 Code: Tags, Elements, and AttributesApr 18, 2025 am 12:06 AMHTML5 code consists of tags, elements and attributes: 1. The tag defines the content type and is surrounded by angle brackets, such as. 2. Elements are composed of start tags, contents and end tags, such as contents. 3. Attributes define key-value pairs in the start tag, enhance functions, such as. These are the basic units for building web structure.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.






