Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Variable function declaration priority in Javascript
Variable function declaration priority in Javascript
- 黄舟Original
- 2017-03-01 14:32:301677browse
Case One
console.log(a); //输出function a(){}
function a() {};
var a=3;Case Two
function a() {};
var a=3;
console.log(a);//输出3Why are the outputs of the two different?
Analysis:
For case one
The execution process can be refined as
#1. First, it will apply for a space, start to declare function a, and then declare variable a during execution , it is found that there is already a declaration of a, so no declaration is made
2. Then, console.log(a) is executed; that is, the output function a
#3. The final execution is to perform the assignment operation, and set a=3. At this time, the function a is converted to a variable type and assigned a value of 3. For verification, you can change the program to the following
#
a();
function a() {
console.log(5);
};
var a=3;
a();You can find that the program execution results are as follows:
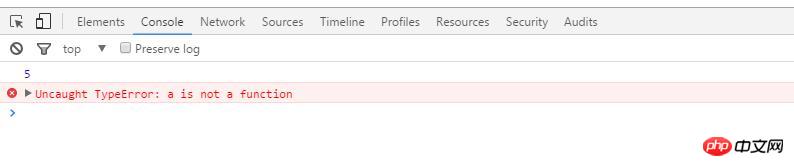
##Because before the assignment, a is still a function. After the assignment statement is executed, a It becomes 3, and an error will be reported when executing a().
For Case 2
# #Similarly, it can be seen that function a is first declared, then declares variable a, and finds that there is already a declaration of a, so it does not declare it. Next, the assignment statement is executed to convert function a into a variable. Finally output the value of variable a
Summary:
1)函数被申明的优先级高于变量 2)被声明过的变量名或是函数名不会被重复申明 3)变量和赋值语句一起书写,在js引擎解析时,会将其拆成声明和赋值2部分,声明置顶,赋值保留在原来位置 补充 1.下面代码执行结果为 以上就是Javascript中变量函数申明优先级的内容,更多相关内容请关注PHP中文网(www.php.cn)!var x=0;
f();
console.log(x);
var f=function(){
x=1;
}
f();
console.log(x);
function f(){
x=2;
}
f();
console.log(x);
答案:2 1 1
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

