Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Introduction to the console.assert() function in JavaScript
Introduction to the console.assert() function in JavaScript
- 高洛峰Original
- 2017-02-03 14:31:471800browse
In the development and maintenance process of JavaScript programs, Assert (assertion) is a good feature used to ensure the correctness of the program. On browsers with debugging tools, this feature can be achieved by calling console.assert(). For example, in the following code, the console.assert() statement ensures that the score variable value length of the cat object is 3:
function cat(name, age, score){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
var c = new cat("miao", 2, [6,8,7]);
console.assert(c.score.length==3, "Assertion of score length failed");In the console.assert() statement, the first parameter is the result that needs to be asserted. Normally it should be true; the second parameter is the error message printed on the console when an error occurs. For example, when the array length of the score variable in the above example is not 3:
function cat(name, age, score){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
var c = new cat("miao", 2, [6,8]);
console.assert(c.score.length==3, "Assertion of score length failed");After the code is executed, the Firebug console will print the error message:
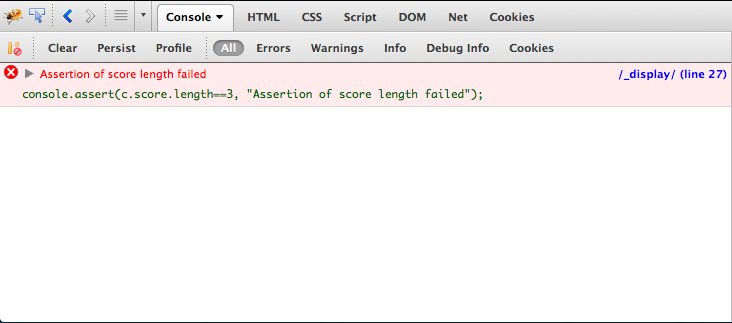
Browser support
console.assert() is better supported by browsers with debugging tools. All major browsers support this function. However, it is worth mentioning that Firefox itself does not support this function. The Firebug plug-in must be installed on Firefox to use console.assert().
For more articles related to the introduction of the console.assert() function in JavaScript, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- An in-depth analysis of the Bootstrap list group component
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript function currying
- Complete example of JS password generation and strength detection (with demo source code download)
- Angularjs integrates WeChat UI (weui)
- How to quickly switch between Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese with JavaScript and the trick for websites to support switching between Simplified and Traditional Chinese_javascript skills

