Home >Web Front-end >CSS Tutorial >A new beginning for div+css web page layout design (3)
A new beginning for div+css web page layout design (3)
- 黄舟Original
- 2016-12-29 14:17:131253browse
The following introduces the combination selector
The combination selector means that the same attributes are put together
For example
<h1>标题</h1> <h2>标题</h1> <h3>标题</h1> <h4>标题</h1> <h5>标题</h1>
I want the text of these five types of titles to change into red, obviously defining each one is too troublesome
We can do this
<h1>标题</h1> <h2>标题</h1> <h3>标题</h1> <h4>标题</h1> <h5>标题</h1>
Of course, we can also combine the id selector, class selector, and label selector together
,a,#b,div{
color:red
} Be careful to separate them with commas
If they are not separated by commas, it is the parent-child selector we will talk about below
<div id="a"> <h1>标题</h1> <h1>标题</h1> <h1>标题</h1> <h1>标题</h1> <h1>标题</h1> <div>
If you want hi in the div There are many ways to make the tags red
. One is to use the tag selector, but it will make all the H1 tags on the page red. If not
you can also use class tags, but each h1 tag must be Class trouble
We can do this
<div id="a"> <h1>标题</h1> <h1>标题</h1> <h1>标题</h1> <h1>标题</h1> <h1>标题</h1> <div>
This will be ok
If so
<div id="a"> <a><h1>标题</h1></a> <a><h1>标题</h1></a> <div>
This will be ok
<div id="a"> <a><h1>标题</h1></a> <a><h1>标题</h1></a> <div>
It’s very simple. In fact, the parent selection can control any label or class or id selector under it, that is, a grandchild or a great-grandson
So this is also possible
<div id="a"> <a><h1>标题</h1></a> <a><h1>标题</h1></a> <div>
But it is recommended not to do this. Because it is easy to get confused if the level is not clear
Another attribute selector, not very commonly used
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
[title]{
color:red;
}
</style> <head>
<body>
<div id="a">
<a title="a"><h1>标题</h1></a>
<a title="b"><h1>标题</h1></a>
<div>
</body>
</html>Must be learned
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
Documentation description is only useful
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">标题
标题
Only valid for equal to a
Attribute selector is particularly useful when setting styles for forms without class or id:input[type="text"] { width:150px; display:block; margin-bottom:10px; background-color:yellow; font-family: Verdana, Arial; } input[type="button"] { width:120px; margin-left:35px; display:block; font-family: Verdana, Arial; }But in fact it is not commonly used. You can master the content without doing the necessary training
The following is an introduction to the adjacent selector
This may be difficult to understand<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <style type="text/css"> h1 + p {margin-top:50px;} </style> <head> <body> <h1>标题</h1> <p>我离上面标题50px</p> <p>不变</p> <p>不变</p> </body> </html>This is actually for the style of the first p. Margin-top:50px means the outer margin is 50px. I will learn later
There is also a sub-element selector, which is also more difficult to understand
Look below first<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <style type="text/css"> p a {color:red;} </style> <head> <body> <p>你<a>好</a>吗</p> <p>你<span><a>好</a></span>吗</p> </body> </html>This is very familiar, the parent-child selector. I said that the father can control any of the child elements below, so both of them will turn red
If I I only want a to be a child element of p, and the other a to be a child element of span, so<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <style type="text/css"> p>a {color:red;} </style> <head> <body> <p>你<a>好</a>吗</p> <p>你<span><a>好</a></span>吗</p> </body> </html>Both of these selectors must add (of course this is not the only one) ), otherwise it will be invalid
These two selectors are very flexible. As an expert, you can advance. For beginners, it is better to lay a solid foundation for other selectors
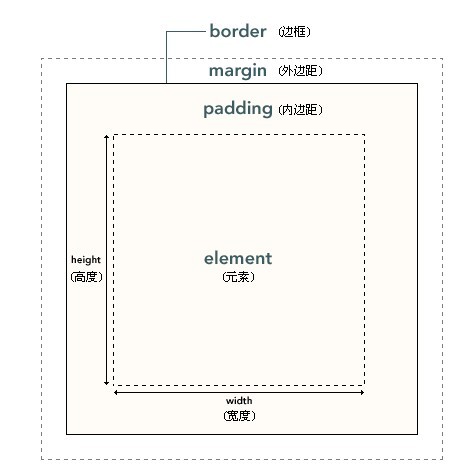
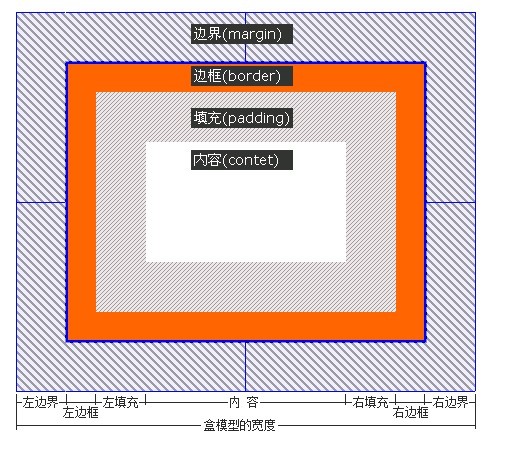
Now is the key content div Box model
This is a picture from W3C, I am looking at another picture
Actually take a look Just understand
The above is the content of the new beginning of div+css web layout design (3). For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn) !
Statement:The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cnPrevious article:A new beginning for div+css web page layout design (2)Next article:A new beginning for div+css web page layout design (2)