 Software Tutorial
Software Tutorial Office Software
Office Software Excel MONTH function - month name from date, last day of month, etc.
Excel MONTH function - month name from date, last day of month, etc.This tutorial delves into the intricacies of Excel's MONTH and EOMONTH functions. Through numerous formula examples, you'll learn to extract month information from dates, determine the first and last days of any month, convert between month names and numbers, and much more.
Previously, we explored weekday calculations. Now, we'll focus on the larger time unit of months and the Excel functions designed for this purpose.
This tutorial covers:
- Excel MONTH function: Syntax and applications.
- Extracting month numbers from dates.
- Extracting month names from dates.
- Converting between month numbers and names.
- Determining the last day of a month (using EOMONTH).
- Finding the first day of a month.
- Calculating the number of days in a month.
- Summing data by month.
- Conditional formatting of dates based on month.
Excel MONTH Function: Syntax and Usage
Excel's MONTH function efficiently extracts the month from a date, returning a number from 1 (January) to 12 (December). Compatible with Excel versions 2000 and later, its syntax is straightforward:
MONTH(serial_number)
where serial_number represents any valid date. While =MONTH(DATE(2015,3,1)) correctly returns 3 (March), using text input like =MONTH("1-Mar-2015") also works, though direct cell referencing is generally preferred for clarity and to avoid potential issues in complex formulas. For instance, =MONTH(A1) retrieves the month from cell A1, and =MONTH(TODAY()) provides the current month's number.
Extracting Month Numbers from Dates
Several methods exist for obtaining month numbers:
-
MONTH Function:
=MONTH(A2)(month from A2),=MONTH(DATE(2015,4,15))(returns 4 for April). -
TEXT Function:
=TEXT(A2, "m")(month number without leading zero),=TEXT(A2,"mm")(month number with leading zero). Remember, the TEXT function returns text strings, not numbers, which may affect subsequent calculations.
The image below illustrates the output of these formulas, highlighting the numerical (right-aligned) vs. text (left-aligned) results.

Extracting Month Names from Dates
To obtain month names instead of numbers, use the TEXT function with different codes:
-
=TEXT(A2, "mmm")(abbreviated name, e.g., Jan),=TEXT(A2,"mmmm")(full name, e.g., January).
Alternatively, for display purposes only (without affecting cell functionality as dates), format cells directly using "mmm" or "mmmm" in custom number formatting.


Converting Month Numbers to Names
To convert month numbers (1-12) to names, use these formulas (where A2 holds the month number):
For abbreviated names: =TEXT(A2*28, "mmm") or =TEXT(DATE(2015, A2, 1), "mmm")
For full names: =TEXT(A2*28, "mmmm") or =TEXT(DATE(2015, A2, 1), "mmmm")
These formulas leverage the fact that Excel treats 1 as January 1st, 1900. Multiplying by 28 provides a date within the correct month.

Converting Month Names to Numbers
Use =MONTH(DATEVALUE(A2 & "1")) (where A2 contains the month name) to convert month names to numbers. DATEVALUE converts the text to a date serial number, and MONTH extracts the month number.

Getting the Last Day of the Month (EOMONTH Function)
The EOMONTH(start_date, months) function returns the last day of a month. start_date is the starting date, and months is the offset (positive for future, negative for past). =EOMONTH(A2, 0) gives the last day of the month in A2. =EOMONTH(TODAY(),0) provides the last day of the current month.

Finding the First Day of the Month
Several methods exist to find the first day:
- Using the month number:
=DATE(year, month_number, 1) - From a date:
=DATE(YEAR(A2), MONTH(A2), 1) - Based on the current date:
=EOMONTH(TODAY(),-1) 1(current month),=EOMONTH(TODAY(),0) 1(next month).


Calculating the Number of Days in a Month
There's no dedicated function, but these formulas work:
- Using the month number:
=DAY(DATE(year, month_number 1, 1) - 1) - From a date:
=DAY(EOMONTH(A1, 0))

Summing Data by Month
Use SUMIF with a helper column containing month numbers (=MONTH(A2)), or use SUMPRODUCT((MONTH($A$2:$A$15)=$E2)*($B$2:$B$15)) (dates in A, values in B, month number in E2).

Conditional Formatting Based on Month
Use conditional formatting rules based on formulas like =MONTH($A2)=MONTH(TODAY()) (highlight current month) or =AND(OR(DAY($A2)=25, DAY($A2)=31), MONTH(A2)=12) (highlight Christmas/New Year's).


The MONTH function's versatility extends far beyond its initial appearance. This tutorial provides a comprehensive foundation for leveraging its capabilities within your Excel work.
The above is the detailed content of Excel MONTH function - month name from date, last day of month, etc.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Excel WEEKNUM function – convert week number to date and vice versaMay 09, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Excel WEEKNUM function – convert week number to date and vice versaMay 09, 2025 am 11:11 AMExcel's WEEKNUM function: Your guide to week number calculations While Excel offers numerous functions for dates, the WEEKNUM function stands alone for week number calculations. This tutorial explores its syntax, arguments, and practical applications
 Excel MONTH function - month name from date, last day of month, etc.May 09, 2025 am 10:59 AM
Excel MONTH function - month name from date, last day of month, etc.May 09, 2025 am 10:59 AMThis tutorial delves into the intricacies of Excel's MONTH and EOMONTH functions. Through numerous formula examples, you'll learn to extract month information from dates, determine the first and last days of any month, convert between month names an
 WEEKDAY formula in Excel to get day of week, weekends and workdaysMay 09, 2025 am 10:25 AM
WEEKDAY formula in Excel to get day of week, weekends and workdaysMay 09, 2025 am 10:25 AMIf you are looking for an Excel function to get day of week from date, you've landed on the right page. This tutorial will teach you how to use the WEEKDAY formula in Excel to convert a date to a weekday name, filter, highlight and count
 Convert date to text in Excel - TEXT function and no-formula waysMay 09, 2025 am 10:11 AM
Convert date to text in Excel - TEXT function and no-formula waysMay 09, 2025 am 10:11 AMThis article explores several methods for converting Excel dates into text strings, offering both formula-based and non-formula solutions. Traditionally, we start with a formula solution and then explore a couple of non-formula alternatives. Using
 Excel: convert text to date and number to dateMay 09, 2025 am 09:36 AM
Excel: convert text to date and number to dateMay 09, 2025 am 09:36 AMThis tutorial demonstrates various Excel techniques for converting text and numbers into dates, including both formula-based and non-formula methods. You'll learn to efficiently transform text strings into usable date formats. Often, dates imported
 How to add and subtract dates in ExcelMay 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
How to add and subtract dates in ExcelMay 08, 2025 am 11:36 AMIn this tutorial, you will find a variety of useful formulas to add and subtract dates in Excel, such as subtracting two dates, adding days, weeks, months and years to a date, and more. If you have been following our tutorials to working
 Excel WORKDAY and NETWORKDAYS functions to calculate working daysMay 08, 2025 am 10:49 AM
Excel WORKDAY and NETWORKDAYS functions to calculate working daysMay 08, 2025 am 10:49 AMThis tutorial demonstrates how to use Excel's WORKDAY, WORKDAY.INTL, NETWORKDAYS, and NETWORKDAYS.INTL functions to efficiently calculate weekdays, considering custom weekend settings and holidays. Microsoft Excel offers specialized functions for wor
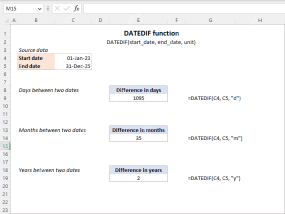 Excel DATEDIF function to get difference between two datesMay 08, 2025 am 10:45 AM
Excel DATEDIF function to get difference between two datesMay 08, 2025 am 10:45 AMThis tutorial provides a concise explanation of Excel's DATEDIF function and offers formula examples for calculating date differences in days, weeks, months, or years. We've previously covered date and time manipulation in Excel, including formattin


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software





