This tutorial demonstrates how to streamline complex Excel spreadsheets by grouping rows, making data easier to analyze. Learn to quickly hide or show row groups and collapse the entire outline to a specific level.
Large, detailed spreadsheets can be overwhelming. Excel's grouping feature offers a solution, allowing you to collapse and expand rows with similar content for clearer, more concise views.
- Automatic Row Grouping (Outline)
- Manual Row Grouping (Nested Groups)
- Collapsing Rows
- Expanding Rows
- Removing Outlines and Ungrouping
- Advanced Grouping Tips
- Automatic Subtotal Calculation
- Applying Default Styles to Summary Rows
- Selecting and Copying Only Visible Rows
- Hiding/Showing Outline Symbols
- Troubleshooting Missing Outline Symbols
Grouping Rows in Excel
Effective Excel row grouping requires structured worksheets: column headers, no blank rows/columns, and summary rows (subtotals) for each data subset. Once organized, group your data using these methods:
Automatic Row Grouping (Creating an Outline)
For single-level datasets, Excel's automatic grouping is quickest:
- Select a cell within the rows to group.
- Navigate to the Data tab > Outline group, click the arrow below Group, and choose Auto Outline.
That's it!
Example of automatically groupable rows:

The resulting outline, shown below, adds outline bars to the left of column A, clearly separating data levels.

Note: If summary rows are above detail rows, before creating an outline, go to the Data tab > Outline group, click the Outline dialog box launcher, and uncheck Summary rows below detail.

Once the outline is created, hide/show details by clicking the minus  or plus
or plus  signs. Collapse/expand to specific levels using the level buttons
signs. Collapse/expand to specific levels using the level buttons  in the top-left corner. See "Collapsing Rows" for details.
in the top-left corner. See "Collapsing Rows" for details.
Manual Row Grouping
For multi-level datasets, manual grouping is necessary. Ensure no hidden rows exist before starting.
1. Creating Outer Groups (Level 1)
Select a large data subset, including intermediate summary and detail rows. In the example below, to group data for row 9 (East Total), select rows 2-8.

On the Data tab, in the Outline group, click Group, select Rows, and click OK.

A bar appears, spanning the selected rows:

Repeat for additional outer groups. The example requires another for the North region (rows 10-16).
2. Creating Nested Groups (Level 2)
Select detail rows above the summary row and click Group. For example, select rows 2-3 for the Apples group within East, and rows 5-7 for Oranges. Repeat for North regions.
Result:

Tip: Use Shift Alt Right Arrow to create groups faster.
3. Adding More Levels
Add levels as needed. Adding a Grand Total row requires selecting rows 2-17 and grouping them. This creates four levels: Grand total, Region totals, Item subtotals, and Detail rows.

Collapsing Rows in Excel
Excel grouping allows hiding/showing detail rows and collapsing/expanding the entire outline to a specific level.
Collapsing Rows Within a Group
Click the minus button  to collapse a group. Alternatively, select a cell within the group and click Hide Detail on the Data tab.
to collapse a group. Alternatively, select a cell within the group and click Hide Detail on the Data tab.

Collapsing/Expanding the Entire Outline
Click the outline number (top-left) to collapse/expand to a specific level. Level 1 shows minimal data, while higher numbers expand all rows.
Expanding Rows in Excel
To expand a collapsed group, click a cell in the visible summary row and click Show Detail on the Data tab, or click the plus sign  .
.

Removing Outlines in Excel
Remove all groups at once by clearing the outline, or ungroup specific rows.
Removing the Entire Outline
Go to the Data tab > Outline group, click the arrow under Ungroup, and select Clear Outline.

Notes: Removing outlines doesn't delete data. Hidden rows might remain hidden; unhide them using appropriate methods. Undo doesn't work after outline removal; recreate it manually.
Ungrouping Specific Rows
Select rows, go to the Data tab > Outline group, click Ungroup, choose Rows, and click OK. Ungrouping non-adjacent rows requires repeating the process for each group.
Excel Grouping Tips
Automatic Subtotal Calculation
Use the Subtotal command with functions like SUM, COUNT, AVERAGE, etc., to automatically calculate subtotals and create outlines.
Applying Default Excel Styles
Excel predefines styles for summary rows (RowLevel_1, RowLevel_2). Apply these before or after grouping. Check Automatic styles in the Outline dialog box launcher to apply automatically.

Selecting and Copying Only Visible Rows
To select only visible rows, select them with the mouse, then go to Home tab > Editing group, click Find & Select > Go To Special, choose Visible cells only, and click OK.

Hiding and Showing Outline Symbols
Use Ctrl 8 to hide/show outline symbols.
Troubleshooting Missing Outline Symbols
Ensure "Show outline symbols if an outline is applied" is checked in File > Options > Advanced.

This tutorial covers row grouping in Excel. Column grouping follows a similar process.
The above is the detailed content of Excel: Group rows automatically or manually, collapse and expand rows. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PMThis tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
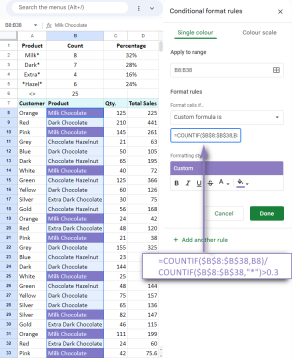 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PMMaster Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AMThis tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
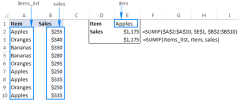 Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AMThis tutorial clarifies the function of Excel names and demonstrates how to define names for cells, ranges, constants, or formulas. It also covers editing, filtering, and deleting defined names. Excel names, while incredibly useful, are often overlo
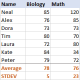 Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis tutorial clarifies the distinction between standard deviation and standard error of the mean, guiding you on the optimal Excel functions for standard deviation calculations. In descriptive statistics, the mean and standard deviation are intrinsi
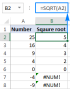 Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM
Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AMThis Excel tutorial demonstrates how to calculate square roots and nth roots. Finding the square root is a common mathematical operation, and Excel offers several methods. Methods for Calculating Square Roots in Excel: Using the SQRT Function: The
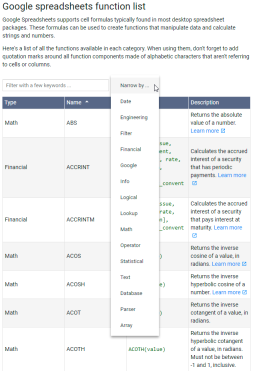 Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AMUnlock the Power of Google Sheets: A Beginner's Guide This tutorial introduces the fundamentals of Google Sheets, a powerful and versatile alternative to MS Excel. Learn how to effortlessly manage spreadsheets, leverage key features, and collaborate


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version






