Python for Data Science: A Beginner's Guide
This guide introduces Python's role in data science and provides a hands-on tutorial using pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib. We'll build a simple data science project to solidify your understanding.
Why Choose Python for Data Science?
Python's clear syntax, extensive libraries, and large, active community make it ideal for data science tasks. From data analysis and visualization to machine learning model building, Python offers efficient and accessible tools.
Introducing pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib
Three core Python libraries power data science workflows:
-
pandas: Master data manipulation and analysis. Easily read, write, and transform structured data (like CSV files and spreadsheets). Key data structures are DataFrames (tabular data) and Series (single columns).
-
NumPy: The foundation for numerical computation. Handles multi-dimensional arrays efficiently, providing mathematical functions for linear algebra and statistical analysis. Its
ndarrayobject and broadcasting capabilities are particularly powerful. -
Matplotlib: Create compelling data visualizations. Generate various charts and plots (line graphs, bar charts, scatter plots, etc.) to visually represent data insights. It integrates smoothly with pandas and NumPy.
Together, these libraries provide a comprehensive toolkit.
Getting Started
Prerequisites:
- Install Python.
- Choose a code editor (VS Code or Jupyter Notebook recommended).
Installation:
Use pip to install the libraries: pip install pandas numpy matplotlib
Verify installation by importing in Python:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Consult the official documentation for additional help: pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib.
A Simple Data Science Project: Movie Data Analysis
Objective: Analyze and visualize movie data from a CSV file.
Download the CSV file: [link to CSV file]
Environment Setup:
- Create a new Python project.
- Open Jupyter Notebook or your preferred editor.
1. Load and Inspect Data with pandas:
import pandas as pd
# Load movie data
movies = pd.read_csv('path/to/your/movies.csv') # Replace with your file path
# Inspect the data
movies # or movies.head() for a preview

2. Data Manipulation with pandas:
Filter movies released after 2000:
# Filter movies released after 2000 recent_movies = movies[movies['release_year'] > 2000] # Sort by release year recent_movies_sorted = recent_movies.sort_values(by='release_year') recent_movies_sorted

3. Data Analysis with NumPy:
Calculate the average movie rating:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt

4. Data Visualization with Matplotlib:
Create a bar chart showing average ratings per genre:
import pandas as pd
# Load movie data
movies = pd.read_csv('path/to/your/movies.csv') # Replace with your file path
# Inspect the data
movies # or movies.head() for a preview

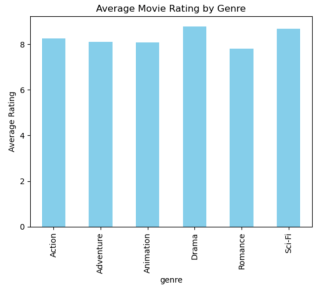
Learning Tips and Resources
- Start small: Practice with smaller datasets first.
- Experiment: Modify examples to explore different scenarios.
- Community resources: Use Stack Overflow and other forums.
- Practice projects: Build your own projects (e.g., weather data analysis).
-
Helpful resources:
- Automate the Boring Stuff with Python
- Python.org
- FreeCodeCamp Data Analysis with Python Course
- Kaggle Datasets
Conclusion
Mastering pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib provides a strong foundation for your data science journey. Practice consistently, explore resources, and enjoy the process!
The above is the detailed content of Python for Data Science: A Beginner&#s Introduction. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Are Python lists dynamic arrays or linked lists under the hood?May 07, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Are Python lists dynamic arrays or linked lists under the hood?May 07, 2025 am 12:16 AMPythonlistsareimplementedasdynamicarrays,notlinkedlists.1)Theyarestoredincontiguousmemoryblocks,whichmayrequirereallocationwhenappendingitems,impactingperformance.2)Linkedlistswouldofferefficientinsertions/deletionsbutslowerindexedaccess,leadingPytho
 How do you remove elements from a Python list?May 07, 2025 am 12:15 AM
How do you remove elements from a Python list?May 07, 2025 am 12:15 AMPythonoffersfourmainmethodstoremoveelementsfromalist:1)remove(value)removesthefirstoccurrenceofavalue,2)pop(index)removesandreturnsanelementataspecifiedindex,3)delstatementremoveselementsbyindexorslice,and4)clear()removesallitemsfromthelist.Eachmetho
 What should you check if you get a 'Permission denied' error when trying to run a script?May 07, 2025 am 12:12 AM
What should you check if you get a 'Permission denied' error when trying to run a script?May 07, 2025 am 12:12 AMToresolvea"Permissiondenied"errorwhenrunningascript,followthesesteps:1)Checkandadjustthescript'spermissionsusingchmod xmyscript.shtomakeitexecutable.2)Ensurethescriptislocatedinadirectorywhereyouhavewritepermissions,suchasyourhomedirectory.
 How are arrays used in image processing with Python?May 07, 2025 am 12:04 AM
How are arrays used in image processing with Python?May 07, 2025 am 12:04 AMArraysarecrucialinPythonimageprocessingastheyenableefficientmanipulationandanalysisofimagedata.1)ImagesareconvertedtoNumPyarrays,withgrayscaleimagesas2Darraysandcolorimagesas3Darrays.2)Arraysallowforvectorizedoperations,enablingfastadjustmentslikebri
 For what types of operations are arrays significantly faster than lists?May 07, 2025 am 12:01 AM
For what types of operations are arrays significantly faster than lists?May 07, 2025 am 12:01 AMArraysaresignificantlyfasterthanlistsforoperationsbenefitingfromdirectmemoryaccessandfixed-sizestructures.1)Accessingelements:Arraysprovideconstant-timeaccessduetocontiguousmemorystorage.2)Iteration:Arraysleveragecachelocalityforfasteriteration.3)Mem
 Explain the performance differences in element-wise operations between lists and arrays.May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Explain the performance differences in element-wise operations between lists and arrays.May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMArraysarebetterforelement-wiseoperationsduetofasteraccessandoptimizedimplementations.1)Arrayshavecontiguousmemoryfordirectaccess,enhancingperformance.2)Listsareflexiblebutslowerduetopotentialdynamicresizing.3)Forlargedatasets,arrays,especiallywithlib
 How can you perform mathematical operations on entire NumPy arrays efficiently?May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
How can you perform mathematical operations on entire NumPy arrays efficiently?May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMMathematical operations of the entire array in NumPy can be efficiently implemented through vectorized operations. 1) Use simple operators such as addition (arr 2) to perform operations on arrays. 2) NumPy uses the underlying C language library, which improves the computing speed. 3) You can perform complex operations such as multiplication, division, and exponents. 4) Pay attention to broadcast operations to ensure that the array shape is compatible. 5) Using NumPy functions such as np.sum() can significantly improve performance.
 How do you insert elements into a Python array?May 06, 2025 am 12:14 AM
How do you insert elements into a Python array?May 06, 2025 am 12:14 AMIn Python, there are two main methods for inserting elements into a list: 1) Using the insert(index, value) method, you can insert elements at the specified index, but inserting at the beginning of a large list is inefficient; 2) Using the append(value) method, add elements at the end of the list, which is highly efficient. For large lists, it is recommended to use append() or consider using deque or NumPy arrays to optimize performance.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)







