If you’re stepping into the world of Big Data, you have likely heard of Apache Spark, a powerful distributed computing system. PySpark, the Python library for Apache Spark, is a favorite among data enthusiasts for its combination of speed, scalability, and ease of use. But setting it up on your local machine can feel a bit intimidating at first.
Fear not — this article walks you through the entire process, addressing common questions and making the journey as straightforward as possible.
What is PySpark, and Why Should You Care?
Before going into installation, let’s understand what PySpark is. PySpark allows you to leverage the massive computational power of Apache Spark using Python. Whether you’re analyzing terabytes of data, building machine learning models, or running ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines, PySpark allows you to work with data more efficiently than ever.
Now that you understand PySpark, let’s go through the installation process.
Step 1: Ensure Your System Meets the Requirements
PySpark runs on various machines, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. Here’s what you need to install it successfully:
- Java Development Kit (JDK): PySpark requires Java (version 8 or 11 is recommended).
- Python: Ensure you have Python 3.6 or later.
- Apache Spark Binary: You’ll download this during the installation process.
To check your system readiness:
- Open your terminal or command prompt.
- Type java -version and python —version to confirm Java and Python installations.
If you don’t have Java or Python installed, follow these steps:
- For Java: Download it from Oracle’s official website.
- For Python: Visit Python’s download page.
Step 2: Install Java
Java is the backbone of Apache Spark. To install it:
1.Download Java: Visit the Java SE Development Kit download page. Choose the appropriate version for your operating system.
2.Install Java: Run the installer and follow the prompts. On Windows, you’ll need to set the JAVA_HOME environment variable. To do this:
- Copy the path variable, go to the local disk on your machine, select program files, look for the java folder open it you will see jdk-17 (your own version may not be 17). Open it, and you will be able to see your path and copy like below
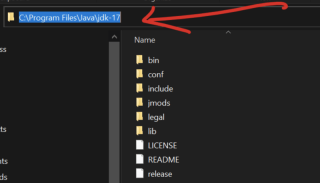
Search for Environment Variables in the Windows search bar.
Under System Variables, click New and set the variable name as JAVA_HOME and the value as your Java installation path you copied above (e.g., C:Program FilesJavajdk-17).
3.Verify Installation: Open a terminal or command prompt and type java-version.
Step 3: Install Apache Spark
1.Download Spark: Visit Apache Spark’s website and select the version compatible with your needs. Use the pre-built package for Hadoop (a common pairing with Spark).
2.Extract the Files:
- On Windows, use a tool like WinRAR or 7-Zip to extract the file.
- On macOS/Linux, use the command tar -xvf spark-.tgz
3.Set Environment Variables:
- For Windows: Add Spark’s bin directory to your system’s PATH variable.
- For macOS/Linux: Add the following lines to your .bashrc or .zshrc file:
export SPARK_HOME=/path/to/spark export PATH=$SPARK_HOME/bin:$PATH
4.Verify Installation: Open a terminal and type spark-shell. You should see Spark’s interactive shell start.
Step 4: Install Hadoop (Optional but Recommended)
While Spark doesn’t strictly require Hadoop, many users install it for its HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) support. To install Hadoop:
- Download Hadoop binaries from Apache Hadoop’s website.
- Extract the files and set up the HADOOP_HOME environment variable.
Step 5: Install PySpark via pip
Installing PySpark is a breeze with Python’s pip tool. Simply run:
pip install pyspark
To verify, open a Python shell and type:
pip install pysparkark.__version__)
If you see a version number, congratulations! PySpark is installed ?
Step 6: Test Your PySpark Installation
Here’s where the fun begins. Let’s ensure everything is working smoothly:
Create a Simple Script:
Open a text editor and paste the following code:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("PySparkTest").getOrCreate()
data = [("Alice", 25), ("Bob", 30), ("Cathy", 29)]
columns = ["Name", "Age"]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, columns)
df.show()
Save it as test_pyspark.py
Run the Script:
In your terminal, navigate to the script’s directory and type:
export SPARK_HOME=/path/to/spark export PATH=$SPARK_HOME/bin:$PATH
You should see a neatly formatted table displaying the names and ages.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with the best instructions, hiccups happen. Here are some common problems and solutions:
Issue: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError
Solution: Double-check your JAVA_HOME and PATH variables.Issue: PySpark installation succeeded, but the test script failed.
Solution: Ensure you’re using the correct Python version. Sometimes, virtual environments can cause conflicts.Issue: The spark-shell command doesn’t work.
Solution: Verify that the Spark directory is correctly added to your PATH.
Why Use PySpark Locally?
Many users wonder why they should bother installing PySpark on their local machine when it’s primarily used in distributed systems. Here’s why:
- Learning: Experiment and learn Spark concepts without requiring a cluster.
- Prototyping: Test small data jobs locally before deploying them to a larger environment.
- Convenience: Debug issues and develop applications with ease.
Boost Your PySpark Productivity
To get the most out of PySpark, consider these tips:
Set Up a Virtual Environment: Use tools like venv or conda to isolate your PySpark installation.
Integrate with IDEs: Tools like PyCharm and Jupyter Notebook make PySpark development more interactive.
Leverage PySpark Documentation: Visit Apache Spark’s documentation for in-depth guidance.
Engage with the PySpark Community
Getting stuck is normal, especially with a powerful tool like PySpark. Engage with the vibrant PySpark community for help:
Join Forums: Websites like Stack Overflow have dedicated Spark tags.
Attend Meetups: Spark and Python communities often host events where you can learn and network.
Follow Blogs: Many data professionals share their experiences and tutorials online.
Conclusion
Installing PySpark on your local machine may seem daunting at first, but following these steps makes it manageable and rewarding. Whether you’re just starting your data journey or sharpening your skills, PySpark equips you with the tools to tackle real-world data problems.
PySpark, the Python API for Apache Spark, is a game-changer for data analysis and processing. While its potential is immense, setting it up on your local machine can feel challenging. This article breaks down the process step-by-step, covering everything from installing Java and downloading Spark to testing your setup with a simple script.
With PySpark installed locally, you can prototype data workflows, learn Spark’s features, and test small-scale projects without needing a full cluster.
The above is the detailed content of How to Install PySpark on Your Local Machine. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How do you slice a Python array?May 01, 2025 am 12:18 AM
How do you slice a Python array?May 01, 2025 am 12:18 AMThe basic syntax for Python list slicing is list[start:stop:step]. 1.start is the first element index included, 2.stop is the first element index excluded, and 3.step determines the step size between elements. Slices are not only used to extract data, but also to modify and invert lists.
 Under what circumstances might lists perform better than arrays?May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Under what circumstances might lists perform better than arrays?May 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMListsoutperformarraysin:1)dynamicsizingandfrequentinsertions/deletions,2)storingheterogeneousdata,and3)memoryefficiencyforsparsedata,butmayhaveslightperformancecostsincertainoperations.
 How can you convert a Python array to a Python list?May 01, 2025 am 12:05 AM
How can you convert a Python array to a Python list?May 01, 2025 am 12:05 AMToconvertaPythonarraytoalist,usethelist()constructororageneratorexpression.1)Importthearraymoduleandcreateanarray.2)Uselist(arr)or[xforxinarr]toconvertittoalist,consideringperformanceandmemoryefficiencyforlargedatasets.
 What is the purpose of using arrays when lists exist in Python?May 01, 2025 am 12:04 AM
What is the purpose of using arrays when lists exist in Python?May 01, 2025 am 12:04 AMChoosearraysoverlistsinPythonforbetterperformanceandmemoryefficiencyinspecificscenarios.1)Largenumericaldatasets:Arraysreducememoryusage.2)Performance-criticaloperations:Arraysofferspeedboostsfortaskslikeappendingorsearching.3)Typesafety:Arraysenforc
 Explain how to iterate through the elements of a list and an array.May 01, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Explain how to iterate through the elements of a list and an array.May 01, 2025 am 12:01 AMIn Python, you can use for loops, enumerate and list comprehensions to traverse lists; in Java, you can use traditional for loops and enhanced for loops to traverse arrays. 1. Python list traversal methods include: for loop, enumerate and list comprehension. 2. Java array traversal methods include: traditional for loop and enhanced for loop.
 What is Python Switch Statement?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:08 PM
What is Python Switch Statement?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:08 PMThe article discusses Python's new "match" statement introduced in version 3.10, which serves as an equivalent to switch statements in other languages. It enhances code readability and offers performance benefits over traditional if-elif-el
 What are Exception Groups in Python?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:07 PM
What are Exception Groups in Python?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:07 PMException Groups in Python 3.11 allow handling multiple exceptions simultaneously, improving error management in concurrent scenarios and complex operations.
 What are Function Annotations in Python?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
What are Function Annotations in Python?Apr 30, 2025 pm 02:06 PMFunction annotations in Python add metadata to functions for type checking, documentation, and IDE support. They enhance code readability, maintenance, and are crucial in API development, data science, and library creation.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.






