 Backend Development
Backend Development Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial Janus B: A Unified Model for Multimodal Understanding and Generation Tasks
Janus B: A Unified Model for Multimodal Understanding and Generation TasksJanus 1.3B
Janus is a new autoregressive framework that integrates multimodal understanding and generation. Unlike previous models, which used a single visual encoder for both understanding and generation tasks, Janus introduces two separate visual encoding pathways for these functions.
Differences in Encoding for Understanding and Generation
- In multimodal understanding tasks, the visual encoder extracts high-level semantic information such as object categories and visual attributes. This encoder focuses on inferring complex meanings, emphasizing higher-dimensional semantic elements.
- On the other hand, in visual generation tasks, emphasis is placed on generating fine details and maintaining overall consistency. As a result, lower-dimensional encoding that can capture spatial structures and textures is required.
Setting Up the Environment
Here are the steps to run Janus in Google Colab:
git clone https://github.com/deepseek-ai/Janus cd Janus pip install -e . # If needed, install the following as well # pip install wheel # pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
Vision Tasks
Loading the Model
Use the following code to load the necessary model for vision tasks:
import torch from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM from janus.models import MultiModalityCausalLM, VLChatProcessor from janus.utils.io import load_pil_images # Specify the model path model_path = "deepseek-ai/Janus-1.3B" vl_chat_processor = VLChatProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer vl_gpt = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) vl_gpt = vl_gpt.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda().eval()
Loading and Preparing Images for Encoding
Next, load the image and convert it into a format that the model can understand:
conversation = [
{
"role": "User",
"content": "<image_placeholder>\nDescribe this chart.",
"images": ["images/pie_chart.png"],
},
{"role": "Assistant", "content": ""},
]
# Load the image and prepare input
pil_images = load_pil_images(conversation)
prepare_inputs = vl_chat_processor(
conversations=conversation, images=pil_images, force_batchify=True
).to(vl_gpt.device)
# Run the image encoder and obtain image embeddings
inputs_embeds = vl_gpt.prepare_inputs_embeds(**prepare_inputs)
</image_placeholder>
Generating a Response
Finally, run the model to generate a response:
# Run the model and generate a response
outputs = vl_gpt.language_model.generate(
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
attention_mask=prepare_inputs.attention_mask,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
bos_token_id=tokenizer.bos_token_id,
eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id,
max_new_tokens=512,
do_sample=False,
use_cache=True,
)
answer = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0].cpu().tolist(), skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"{prepare_inputs['sft_format'][0]}", answer)
Example Output
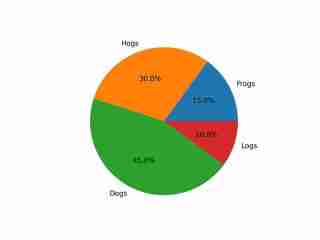
The image depicts a pie chart that illustrates the distribution of four different categories among four distinct groups. The chart is divided into four segments, each representing a category with a specific percentage. The categories and their corresponding percentages are as follows: 1. **Hogs**: This segment is colored in orange and represents 30.0% of the total. 2. **Frog**: This segment is colored in blue and represents 15.0% of the total. 3. **Logs**: This segment is colored in red and represents 10.0% of the total. 4. **Dogs**: This segment is colored in green and represents 45.0% of the total. The pie chart is visually divided into four segments, each with a different color and corresponding percentage. The segments are arranged in a clockwise manner starting from the top-left, moving clockwise. The percentages are clearly labeled next to each segment. The chart is a simple visual representation of data, where the size of each segment corresponds to the percentage of the total category it represents. This type of chart is commonly used to compare the proportions of different categories in a dataset. To summarize, the pie chart shows the following: - Hogs: 30.0% - Frog: 15.0% - Logs: 10.0% - Dogs: 45.0% This chart can be used to understand the relative proportions of each category in the given dataset.
The output demonstrates an appropriate understanding of the image, including its colors and text.
Image Generation Tasks
Loading the Model
Load the necessary model for image generation tasks with the following code:
import os import PIL.Image import torch import numpy as np from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM from janus.models import MultiModalityCausalLM, VLChatProcessor # Specify the model path model_path = "deepseek-ai/Janus-1.3B" vl_chat_processor = VLChatProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path) tokenizer = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer vl_gpt = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True) vl_gpt = vl_gpt.to(torch.bfloat16).cuda().eval()
Preparing the Prompt
Next, prepare the prompt based on the user’s request:
# Set up the prompt
conversation = [
{
"role": "User",
"content": "cute japanese girl, wearing a bikini, in a beach",
},
{"role": "Assistant", "content": ""},
]
# Convert the prompt into the appropriate format
sft_format = vl_chat_processor.apply_sft_template_for_multi_turn_prompts(
conversations=conversation,
sft_format=vl_chat_processor.sft_format,
system_prompt="",
)
prompt = sft_format + vl_chat_processor.image_start_tag
Generating the Image
The following function is used to generate images. By default, 16 images are generated:
@torch.inference_mode()
def generate(
mmgpt: MultiModalityCausalLM,
vl_chat_processor: VLChatProcessor,
prompt: str,
temperature: float = 1,
parallel_size: int = 16,
cfg_weight: float = 5,
image_token_num_per_image: int = 576,
img_size: int = 384,
patch_size: int = 16,
):
input_ids = vl_chat_processor.tokenizer.encode(prompt)
input_ids = torch.LongTensor(input_ids)
tokens = torch.zeros((parallel_size*2, len(input_ids)), dtype=torch.int).cuda()
for i in range(parallel_size*2):
tokens[i, :] = input_ids
if i % 2 != 0:
tokens[i, 1:-1] = vl_chat_processor.pad_id
inputs_embeds = mmgpt.language_model.get_input_embeddings()(tokens)
generated_tokens = torch.zeros((parallel_size, image_token_num_per_image), dtype=torch.int).cuda()
for i in range(image_token_num_per_image):
outputs = mmgpt.language_model.model(
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,
use_cache=True,
past_key_values=outputs.past_key_values if i != 0 else None,
)
hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
logits = mmgpt.gen_head(hidden_states[:, -1, :])
logit_cond = logits[0::2, :]
logit_uncond = logits[1::2, :]
logits = logit_uncond + cfg_weight * (logit_cond - logit_uncond)
probs = torch.softmax(logits / temperature, dim=-1)
next_token = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)
generated_tokens[:, i] = next_token.squeeze(dim=-1)
next_token = torch.cat([next_token.unsqueeze(dim=1), next_token.unsqueeze(dim=1)], dim=1).view(-1)
img_embeds = mmgpt.prepare_gen_img_embeds(next_token)
inputs_embeds = img_embeds.unsqueeze(dim=1)
dec = mmgpt.gen_vision_model.decode_code(
generated_tokens.to(dtype=torch.int),
shape=[parallel_size, 8, img_size // patch_size, img_size // patch_size],
)
dec = dec.to(torch.float32).cpu().numpy().transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
dec = np.clip((dec + 1) / 2 * 255, 0, 255)
visual_img = np.zeros((parallel_size, img_size, img_size, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
visual_img[:, :, :] = dec
os.makedirs('generated_samples', exist_ok=True)
for i in range(parallel_size):
save_path = os.path.join('generated_samples', f"img_{i}.jpg")
PIL.Image.fromarray(visual_img[i]).save(save_path)
# Run the image generation
generate(vl_gpt, vl_chat_processor, prompt)
The generated images will be saved in the generated_samples folder.
Sample of Generated Results
Below is an example of a generated image:

- Dogs are relatively well depicted.
- Buildings maintain overall shape, though some details, like windows, may appear unrealistic.
- Humans, however, are challenging to generate well, with notable distortions in both photo-realistic and anime-like styles.
The above is the detailed content of Janus B: A Unified Model for Multimodal Understanding and Generation Tasks. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Explain the performance differences in element-wise operations between lists and arrays.May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Explain the performance differences in element-wise operations between lists and arrays.May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMArraysarebetterforelement-wiseoperationsduetofasteraccessandoptimizedimplementations.1)Arrayshavecontiguousmemoryfordirectaccess,enhancingperformance.2)Listsareflexiblebutslowerduetopotentialdynamicresizing.3)Forlargedatasets,arrays,especiallywithlib
 How can you perform mathematical operations on entire NumPy arrays efficiently?May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
How can you perform mathematical operations on entire NumPy arrays efficiently?May 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMMathematical operations of the entire array in NumPy can be efficiently implemented through vectorized operations. 1) Use simple operators such as addition (arr 2) to perform operations on arrays. 2) NumPy uses the underlying C language library, which improves the computing speed. 3) You can perform complex operations such as multiplication, division, and exponents. 4) Pay attention to broadcast operations to ensure that the array shape is compatible. 5) Using NumPy functions such as np.sum() can significantly improve performance.
 How do you insert elements into a Python array?May 06, 2025 am 12:14 AM
How do you insert elements into a Python array?May 06, 2025 am 12:14 AMIn Python, there are two main methods for inserting elements into a list: 1) Using the insert(index, value) method, you can insert elements at the specified index, but inserting at the beginning of a large list is inefficient; 2) Using the append(value) method, add elements at the end of the list, which is highly efficient. For large lists, it is recommended to use append() or consider using deque or NumPy arrays to optimize performance.
 How can you make a Python script executable on both Unix and Windows?May 06, 2025 am 12:13 AM
How can you make a Python script executable on both Unix and Windows?May 06, 2025 am 12:13 AMTomakeaPythonscriptexecutableonbothUnixandWindows:1)Addashebangline(#!/usr/bin/envpython3)andusechmod xtomakeitexecutableonUnix.2)OnWindows,ensurePythonisinstalledandassociatedwith.pyfiles,oruseabatchfile(run.bat)torunthescript.
 What should you check if you get a 'command not found' error when trying to run a script?May 06, 2025 am 12:03 AM
What should you check if you get a 'command not found' error when trying to run a script?May 06, 2025 am 12:03 AMWhen encountering a "commandnotfound" error, the following points should be checked: 1. Confirm that the script exists and the path is correct; 2. Check file permissions and use chmod to add execution permissions if necessary; 3. Make sure the script interpreter is installed and in PATH; 4. Verify that the shebang line at the beginning of the script is correct. Doing so can effectively solve the script operation problem and ensure the coding process is smooth.
 Why are arrays generally more memory-efficient than lists for storing numerical data?May 05, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Why are arrays generally more memory-efficient than lists for storing numerical data?May 05, 2025 am 12:15 AMArraysaregenerallymorememory-efficientthanlistsforstoringnumericaldataduetotheirfixed-sizenatureanddirectmemoryaccess.1)Arraysstoreelementsinacontiguousblock,reducingoverheadfrompointersormetadata.2)Lists,oftenimplementedasdynamicarraysorlinkedstruct
 How can you convert a Python list to a Python array?May 05, 2025 am 12:10 AM
How can you convert a Python list to a Python array?May 05, 2025 am 12:10 AMToconvertaPythonlisttoanarray,usethearraymodule:1)Importthearraymodule,2)Createalist,3)Usearray(typecode,list)toconvertit,specifyingthetypecodelike'i'forintegers.Thisconversionoptimizesmemoryusageforhomogeneousdata,enhancingperformanceinnumericalcomp
 Can you store different data types in the same Python list? Give an example.May 05, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Can you store different data types in the same Python list? Give an example.May 05, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython lists can store different types of data. The example list contains integers, strings, floating point numbers, booleans, nested lists, and dictionaries. List flexibility is valuable in data processing and prototyping, but it needs to be used with caution to ensure the readability and maintainability of the code.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment





