Roboflow is a platform for annotating images for use in object detection AI.
I use this platform for C2SMR c2smr.fr, my computer vision association for maritime rescue.
In this article I show you how to use this platform and train your model with python.
You can find more sample code on my github : https://github.com/C2SMR/detector
I - Dataset
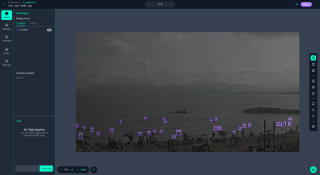
To create your dataset, go to https://app.roboflow.com/ and start annotating your image as shown in the following image.
In this example, I detour all the swimmers to predict their position in future images.
To get a good result, crop all the swimmers and place the bounding box just after the object to surround it correctly.
You can already use a public roboflow dataset, for this check https://universe.roboflow.com/
II - Training
For the training stage, you can use roboflow directly, but by the third time you'll have to pay, which is why I'm showing you how to do it with your laptop.
The first step is to import your dataset. To do this, you can import the Roboflow library.
pip install roboflow
To create a model, you need to use the YOLO algorithm, which you can import with the ultralytics library.
pip install ultralytics
In my script, I use the following command :
py train.py api-key project-workspace project-name project-version nb-epoch size_model
You must obtain :
- the access key
- workspace
- roboflow project name
- project dataset version
- number of epochs to train the model
- neural network size
Initially, the script downloads yolov8-obb.pt, the default yolo weight with pre-workout data, to facilitate training.
import sys
import os
import random
from roboflow import Roboflow
from ultralytics import YOLO
import yaml
import time
class Main:
rf: Roboflow
project: object
dataset: object
model: object
results: object
model_size: str
def __init__(self):
self.model_size = sys.argv[6]
self.import_dataset()
self.train()
def import_dataset(self):
self.rf = Roboflow(api_key=sys.argv[1])
self.project = self.rf.workspace(sys.argv[2]).project(sys.argv[3])
self.dataset = self.project.version(sys.argv[4]).download("yolov8-obb")
with open(f'{self.dataset.location}/data.yaml', 'r') as file:
data = yaml.safe_load(file)
data['path'] = self.dataset.location
with open(f'{self.dataset.location}/data.yaml', 'w') as file:
yaml.dump(data, file, sort_keys=False)
def train(self):
list_of_models = ["n", "s", "m", "l", "x"]
if self.model_size != "ALL" and self.model_size in list_of_models:
self.model = YOLO(f"yolov8{self.model_size}-obb.pt")
self.results = self.model.train(data=f"{self.dataset.location}/"
f"yolov8-obb.yaml",
epochs=int(sys.argv[5]), imgsz=640)
elif self.model_size == "ALL":
for model_size in list_of_models:
self.model = YOLO(f"yolov8{model_size}.pt")
self.results = self.model.train(data=f"{self.dataset.location}"
f"/yolov8-obb.yaml",
epochs=int(sys.argv[5]),
imgsz=640)
else:
print("Invalid model size")
if __name__ == '__main__':
Main()
III - Display
After training the model, you get the files best.py and last.py, which correspond to the weight.
With ultralytics library, you can also import YOLO and load your weight and then your test video.
In this example, I'm using the tracking function to get an ID for each swimmer.
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
import sys
def main():
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(sys.argv[1])
model = YOLO(sys.argv[2])
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
results = model.track(frame, persist=True)
res_plotted = results[0].plot()
cv2.imshow("frame", res_plotted)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == 27:
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
To analyze the prediction, you can obtain the model json as follows.
results = model.track(frame, persist=True) results_json = json.loads(results[0].tojson())
The above is the detailed content of ROBOFLOW - train & test with python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python: compiler or Interpreter?May 13, 2025 am 12:10 AMPython is an interpreted language, but it also includes the compilation process. 1) Python code is first compiled into bytecode. 2) Bytecode is interpreted and executed by Python virtual machine. 3) This hybrid mechanism makes Python both flexible and efficient, but not as fast as a fully compiled language.
 Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python For Loop vs While Loop: When to Use Which?May 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMUseaforloopwheniteratingoverasequenceorforaspecificnumberoftimes;useawhileloopwhencontinuinguntilaconditionismet.Forloopsareidealforknownsequences,whilewhileloopssuitsituationswithundeterminediterations.
 Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Python loops: The most common errorsMay 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMPythonloopscanleadtoerrorslikeinfiniteloops,modifyinglistsduringiteration,off-by-oneerrors,zero-indexingissues,andnestedloopinefficiencies.Toavoidthese:1)Use'i
 For loop and while loop in Python: What are the advantages of each?May 13, 2025 am 12:01 AM
For loop and while loop in Python: What are the advantages of each?May 13, 2025 am 12:01 AMForloopsareadvantageousforknowniterationsandsequences,offeringsimplicityandreadability;whileloopsareidealfordynamicconditionsandunknowniterations,providingcontrolovertermination.1)Forloopsareperfectforiteratingoverlists,tuples,orstrings,directlyacces
 Python: A Deep Dive into Compilation and InterpretationMay 12, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: A Deep Dive into Compilation and InterpretationMay 12, 2025 am 12:14 AMPythonusesahybridmodelofcompilationandinterpretation:1)ThePythoninterpretercompilessourcecodeintoplatform-independentbytecode.2)ThePythonVirtualMachine(PVM)thenexecutesthisbytecode,balancingeaseofusewithperformance.
 Is Python an interpreted or a compiled language, and why does it matter?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Is Python an interpreted or a compiled language, and why does it matter?May 12, 2025 am 12:09 AMPythonisbothinterpretedandcompiled.1)It'scompiledtobytecodeforportabilityacrossplatforms.2)Thebytecodeistheninterpreted,allowingfordynamictypingandrapiddevelopment,thoughitmaybeslowerthanfullycompiledlanguages.
 For Loop vs While Loop in Python: Key Differences ExplainedMay 12, 2025 am 12:08 AM
For Loop vs While Loop in Python: Key Differences ExplainedMay 12, 2025 am 12:08 AMForloopsareidealwhenyouknowthenumberofiterationsinadvance,whilewhileloopsarebetterforsituationswhereyouneedtoloopuntilaconditionismet.Forloopsaremoreefficientandreadable,suitableforiteratingoversequences,whereaswhileloopsoffermorecontrolandareusefulf
 For and While loops: a practical guideMay 12, 2025 am 12:07 AM
For and While loops: a practical guideMay 12, 2025 am 12:07 AMForloopsareusedwhenthenumberofiterationsisknowninadvance,whilewhileloopsareusedwhentheiterationsdependonacondition.1)Forloopsareidealforiteratingoversequenceslikelistsorarrays.2)Whileloopsaresuitableforscenarioswheretheloopcontinuesuntilaspecificcond


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool






