 Web Front-end
Web Front-end HTML Tutorial
HTML Tutorial Learn how to write clean and standardized HTML tags_HTML/Xhtml_Webpage Production
Learn how to write clean and standardized HTML tags_HTML/Xhtml_Webpage ProductionLearn how to write clean and standardized HTML tags_HTML/Xhtml_Webpage Production
Good HTML code is the foundation of a beautiful website. When I teach people CSS, I always start by telling them: Good CSS only exists based on good HTML markup. It's like a house needs a solid foundation, right? Clean and semantic HTML markup has many advantages, but there are still many websites that use unfriendly markup writing methods.
Let’s take a look at some unfriendly HTML tags and discuss these issues to learn how to write neat and standardized HTML tags.
Script House Note: Chris Cyier used two documents here to explain the code of this article: bad code and good code. Please refer to these two documents when studying.
1. Strict DOCTYPE
To do this, we just need to follow the correct steps. There is no need to discuss whether to use HTML 4.01 or XHTML 1.0, both Strict requirements are placed on us writing correct code.
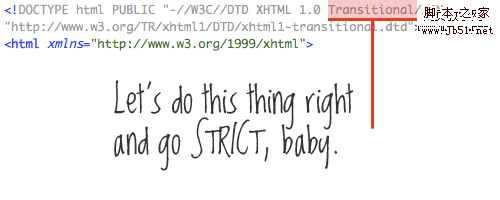
But anyway our code should not use any Tables tables for layout, so there is no need to use Transitional DOCTYPE.
Related Resources:
W3C recommended DTDs (Document Type Declarations)
Fix Your Site With the Right DOCTYPE! Note from Script Home
: The so-called DTD is a document type declaration. Simply put, it is some rules defined for a specific document. These rules include a series of element and entity declarations. - There are three XHTML document types: STRICT (strict type), TRANSITIONAL (transitional type) and FRAMESET (framework type)
. Currently, the one we use most is TRANSITIONAL. For example, this site currently uses XHTML 1.0 TRANSITIONAL. If your HTML code is well written, it is more convenient to convert the existing TRANSITIONAL to STRICT. On the contrary, there is no need to be too hasty to switch. Personally, I think STRICT is more rigorous, but using TRANSITIONAL does not have much impact.
2. Character set & encoding characters
In addition to the position of the character set declaration in our , Related resources:
Wikipedia: UTF-8
A tutorial on character code issues
The Extended ASCII table
3. Proper indentation When writing code, indentation will not affect the appearance of the web page, but using appropriate indentation can make the code more readable. The standard indentation method is to indent when you start a new element. One tab (or several spaces). Also, remember that the tag of the closing element is aligned with the opening tag.
Note from Script House: Some friends find it troublesome to indent when writing code. If you are the only one reading this code, it may not matter. As for the question, just feel free to it. But if it's a collaboration or if your work is published and shared publicly, then writing beautiful code that is more readable is necessary.
Related resources:
Clean up your Web pages with HTML TIDY

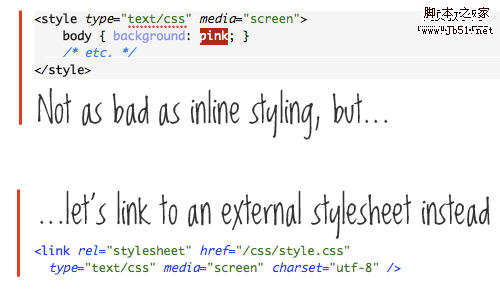
4. Using external CSS and JavaScriptWe have some CSS code that has been extended into our
Script Home Note: Of course, this problem may not be that serious. For example, as a WordPress theme, it is written in
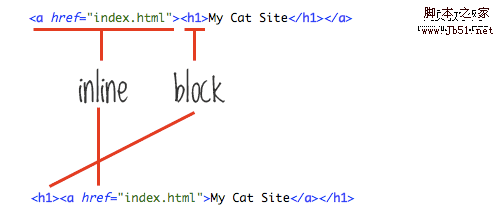
As a website title tag, this is perfect. And added a link to the homepage, but the mistake was that the link was placed outside , and the link surrounded . This simple nesting error is handled well by most browsers, but technically it's not possible.
The anchor link is an inline element, while
The title is a block element, and block elements should not be placed in inline elements.
6. Remove unnecessary DIVs
I don’t know who invented it first, but I like "pitis" this one word, which refers to the excessive use of ps in the HTML tag . At a certain stage of learning web design, everyone learns how to use a DIV to wrap many other elements to achieve convenient layout and styling. This has led to the abuse of the DIV element. We use it where it is needed, and we also use it where it is completely unnecessary.

In the example above, we use a p (”topNav”) to contain the UL list (”bigBarNavigation”). But both DIV and UL It is a block element, so there is no need to use DIV to wrap the UL element.
Related resources:
Divitis: what it is, and how to cure it.
7. Use better naming conventions
Now let’s talk about naming management. In the example mentioned in the previous article, our UL uses the ID name "bigBarNavigation." Among them, "Navigation" is a good description of the content of the block, but "big" and "Bar" describe the design rather than the content. It may be saying that this menu is a large toolbar. But if the design of this menu becomes vertical, then the name will appear confusing and irrelevant.
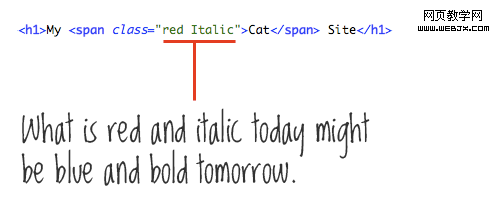
Friendly class and id names such as “mainNav,” “subNav,” “sidebar,” “footer,” “metaData, ”, they describe the content contained. Bad class and id names describe the design, such as “bigBoldHeader,” “leftSidebar,” and “roundedBox.”
Note from Script House: Chris emphasized whether to name based on content or design. A personal addition: Should ID and Class names be in uppercase or lowercase , or the first letter of the word is capitalized . First of all, completely capitalized words are not conducive to reading, so exclude them. Whether to use lowercase letters entirely or capitalize the first letter of words depends on personal preference. The important point is that no matter which rule you use, it should be consistent . Don't use all lowercase letters for one moment and capitalize the first letter for the next. It will be confusing.
In addition, I am personally confused about whether to add an underscore "_", a hyphen "-", or not for a longer name. Or maybe I think it’s too complicated. Whichever you use is fine, just keep it consistent.
 The Future of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Web Development TrendsApr 19, 2025 am 12:02 AM
The Future of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Web Development TrendsApr 19, 2025 am 12:02 AMThe future trends of HTML are semantics and web components, the future trends of CSS are CSS-in-JS and CSSHoudini, and the future trends of JavaScript are WebAssembly and Serverless. 1. HTML semantics improve accessibility and SEO effects, and Web components improve development efficiency, but attention should be paid to browser compatibility. 2. CSS-in-JS enhances style management flexibility but may increase file size. CSSHoudini allows direct operation of CSS rendering. 3.WebAssembly optimizes browser application performance but has a steep learning curve, and Serverless simplifies development but requires optimization of cold start problems.
 HTML: The Structure, CSS: The Style, JavaScript: The BehaviorApr 18, 2025 am 12:09 AM
HTML: The Structure, CSS: The Style, JavaScript: The BehaviorApr 18, 2025 am 12:09 AMThe roles of HTML, CSS and JavaScript in web development are: 1. HTML defines the web page structure, 2. CSS controls the web page style, and 3. JavaScript adds dynamic behavior. Together, they build the framework, aesthetics and interactivity of modern websites.
 The Future of HTML: Evolution and Trends in Web DesignApr 17, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Future of HTML: Evolution and Trends in Web DesignApr 17, 2025 am 12:12 AMThe future of HTML is full of infinite possibilities. 1) New features and standards will include more semantic tags and the popularity of WebComponents. 2) The web design trend will continue to develop towards responsive and accessible design. 3) Performance optimization will improve the user experience through responsive image loading and lazy loading technologies.
 HTML vs. CSS vs. JavaScript: A Comparative OverviewApr 16, 2025 am 12:04 AM
HTML vs. CSS vs. JavaScript: A Comparative OverviewApr 16, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe roles of HTML, CSS and JavaScript in web development are: HTML is responsible for content structure, CSS is responsible for style, and JavaScript is responsible for dynamic behavior. 1. HTML defines the web page structure and content through tags to ensure semantics. 2. CSS controls the web page style through selectors and attributes to make it beautiful and easy to read. 3. JavaScript controls web page behavior through scripts to achieve dynamic and interactive functions.
 HTML: Is It a Programming Language or Something Else?Apr 15, 2025 am 12:13 AM
HTML: Is It a Programming Language or Something Else?Apr 15, 2025 am 12:13 AMHTMLisnotaprogramminglanguage;itisamarkuplanguage.1)HTMLstructuresandformatswebcontentusingtags.2)ItworkswithCSSforstylingandJavaScriptforinteractivity,enhancingwebdevelopment.
 HTML: Building the Structure of Web PagesApr 14, 2025 am 12:14 AM
HTML: Building the Structure of Web PagesApr 14, 2025 am 12:14 AMHTML is the cornerstone of building web page structure. 1. HTML defines the content structure and semantics, and uses, etc. tags. 2. Provide semantic markers, such as, etc., to improve SEO effect. 3. To realize user interaction through tags, pay attention to form verification. 4. Use advanced elements such as, combined with JavaScript to achieve dynamic effects. 5. Common errors include unclosed labels and unquoted attribute values, and verification tools are required. 6. Optimization strategies include reducing HTTP requests, compressing HTML, using semantic tags, etc.
 From Text to Websites: The Power of HTMLApr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
From Text to Websites: The Power of HTMLApr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AMHTML is a language used to build web pages, defining web page structure and content through tags and attributes. 1) HTML organizes document structure through tags, such as,. 2) The browser parses HTML to build the DOM and renders the web page. 3) New features of HTML5, such as, enhance multimedia functions. 4) Common errors include unclosed labels and unquoted attribute values. 5) Optimization suggestions include using semantic tags and reducing file size.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's GuideApr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's GuideApr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AMWebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools





