HTML5 Audio(audio)
Audio on the Web
Until now, there was no standard for playing audio on web pages.
Today, most audio is played through plug-ins (such as Flash). However, not all browsers have the same plugins.
HTML5 specifies a standard way to include audio through the audio element.
The audio element can play sound files or audio streams.
Audio formats
Currently, the audio element supports three audio formats:
How it works
To play in HTML5 For audio, all you need is:
<audio src="song.ogg" controls="controls"> </audio>
control properties to add play, pause and volume controls.
The content inserted between <audio> and </audio> is for display by browsers that do not support the audio element:
Example
<audio src="song.ogg" controls="controls"> Your browser does not support the audio tag. </audio>
The above example uses an Ogg file and is suitable for Firefox, Opera and Chrome browsers.
To ensure that it works with Safari, the audio file must be of MP3 or Wav type.
The audio element allows multiple source elements. The source element can link different audio files. The browser will use the first recognized format:
Instance
<audio controls="controls"> <source src="song.ogg" type="audio/ogg"> <source src="song.mp3" type="audio/mpeg"> Your browser does not support the audio tag. </audio>
Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer 8 does not support the audio element . In IE 9, support for the audio element will be provided.
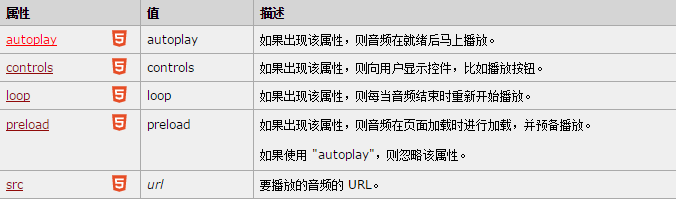
<audio> Attributes of tag