CSS相邻选择器与兄弟选择器
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
ul li {
list-style: none;
width: 30Px;
height: 30px;
border-radius: 50%;
text-align: center;
line-height: 30px;
display: inline-block;
border: 1px solid #555;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 1px #f60;
}
#bg-blue {
background: #333;
color: #fff;
}
/* 相邻选择器 */
#bg-blue+* {
background: red;
color: #fff;
}
/* 兄弟选择器 */
#bg-red~* {
background: lightseagreen;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li id="bg-blue">2</li>
<li id="bg-red">3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>7</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
<li>10</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
CSS相邻选择器与兄弟选择器的分析:它们都可以表示选中同级之后的兄弟元素。不同点是,相邻选择器用+*表示,同级只有下一个兄弟元素被选中,兄弟选择器用~*表示,同级后面的兄弟元素全部被选中。

CSS伪类选择器:nth-child() 和 nth-of-type()
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
ul {
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
}
ul li {
list-style: none;
}
ul li:nth-child(2) {
color: red;
}
ul li:nth-of-type(2) {
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<p>我是段落p标签</p>
<li>CSS伪类选择器</li>
<li>CSS伪类选择器</li>
<li>CSS伪类选择器</li>
<li>CSS伪类选择器</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
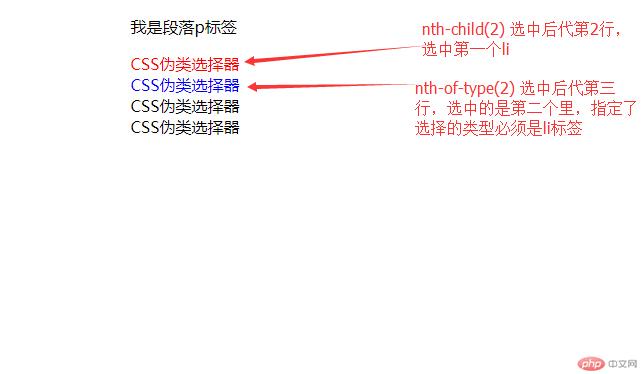
nth-child() 和 nth-of-type()都表示选取后代元素,它们的不同点是nth-child()表示后代第n个元素, nth-of-type()表示选取后代为指定类型的第n个元素,也就是是 nth-of-type()是指定类型的,选取的子元素类型更具体。
padding对盒子大小的影响和box-sizing的使用
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: lightseagreen;
}
.box2 {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
background: lightpink;
}
.box3 {
padding: 30px;
}
.box4 {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<p>box1,没有子元素,没有加padding值</p>
<hr>
<div class="box1 box3">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
<p>有子元素box2,.box3加padding值30px,box1被撑大</p>
<hr>
<div class="box1 box3 box4">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
<p>有子元素,padding值30px,.box4加了box-sizing变为内部盒子,padding被内部消化</p>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例

margin外边距中的同级塌陷
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1,
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
color: #fff;
}
.box1 {
background: brown;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.box2 {
background: cornflowerblue;
margin-top: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">下边距50px</div>
<div class="box2">上边距30px</div>
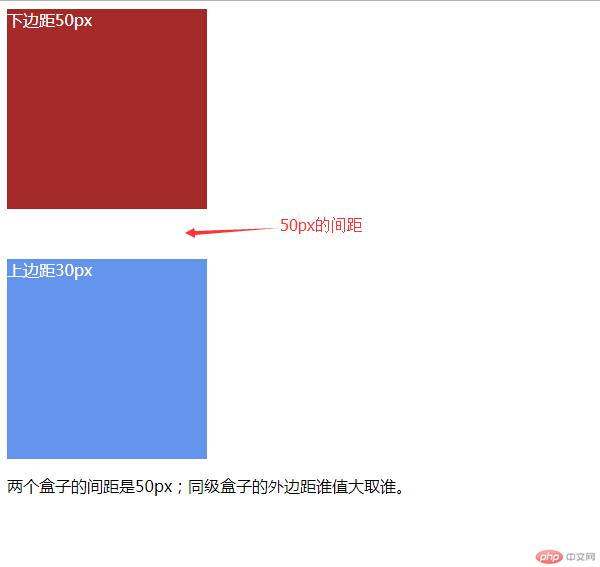
<p>两个盒子的间距是50px;同级盒子的外边距谁值大取谁,没有叠加。</p>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
margin外边距中的嵌套传递
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background: lightseagreen;
}
.box2 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: lightpink;
}
.box3 {
margin-top: 50px;
}
.box4 {
padding-top: 50px;
}
.box4 .box3 {
margin-top: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2 box3"></div>
</div>
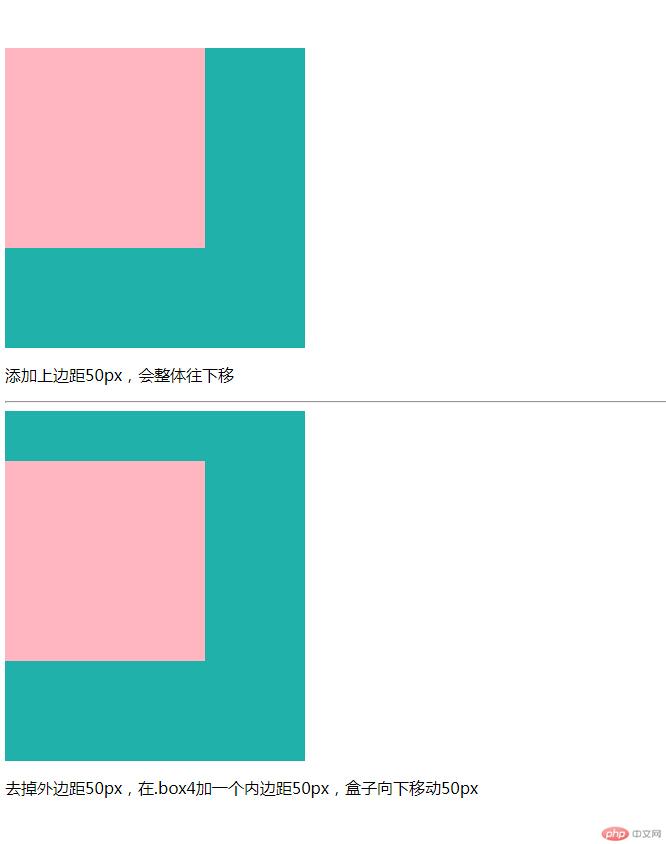
<p>添加上边距50px,会整体往下移</p>
<hr>
<div class="box1 box4">
<div class="box2 box3"></div>
</div>
<p>去掉外边距50px,在.box4加一个内边距50px,盒子向下移动50px</p>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
margin外边距中的自动挤压
实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box1 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background: lightseagreen;
margin-left: auto;
}
.box2 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background: pink;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
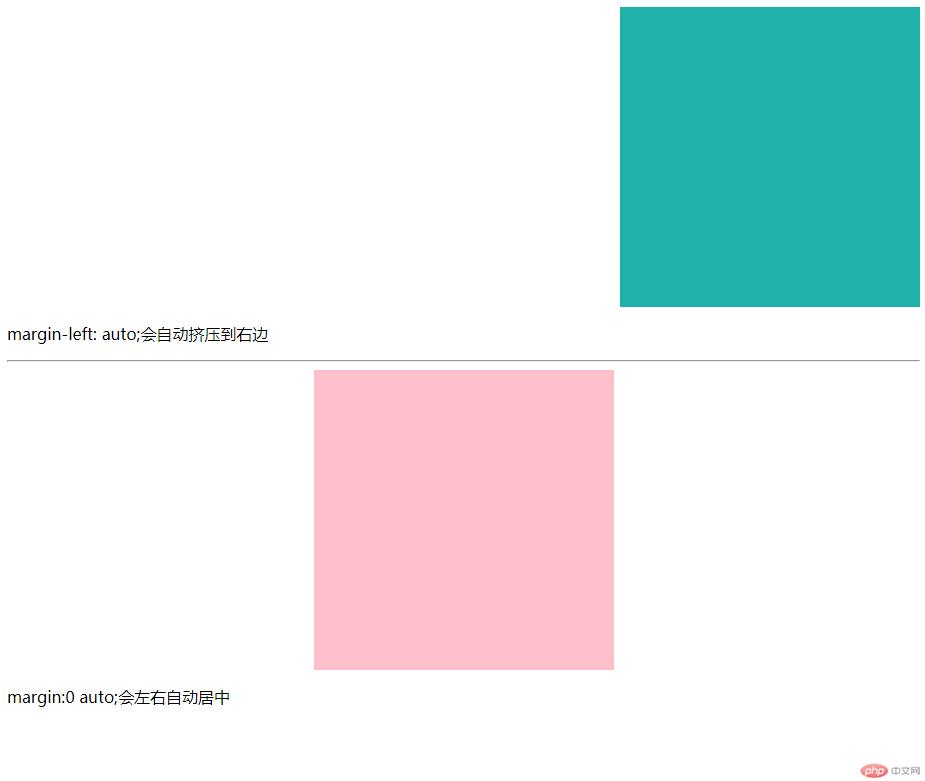
<p>margin-left: auto;会自动挤压到右边</p>
<hr>
<div class="box2"></div>
<p>margin:0 auto;会左右自动居中</p>
</body>
</html>运行实例 »
点击 "运行实例" 按钮查看在线实例
总结:熟悉CSS相邻选择器与兄弟选择器的用法,+*表示选中下一个,~*表示选中同级后的所有元素。
nth-of-type()是指定到类型的,适用于选取的子元素具体到类型。
margin通常用在外部同级的盒子上,调整间距,padding通常用在外部父盒子上,挤压内部盒子。
margin:0 auto用的最多,让盒子能够水平居中。

